Abstract
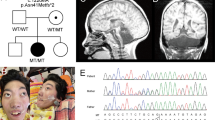
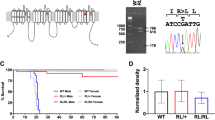
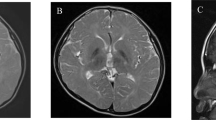
Cerebellar ataxia, mental retardation and dysequilibrium syndrome is a rare and heterogeneous condition. We investigated a consanguineous family from Turkey with four affected individuals exhibiting the condition. Homozygosity mapping revealed that several shared homozygous regions, including chromosome 13q12. Targeted next-generation sequencing of an affected individual followed by segregation analysis, population screening and prediction approaches revealed a novel missense variant, p.I376M, in ATP8A2. The mutation lies in a highly conserved C-terminal transmembrane region of E1 E2 ATPase domain. The ATP8A2 gene is mainly expressed in brain and development, in particular cerebellum. Interestingly, an unrelated individual has been identified, in whom mental retardation and severe hypotonia is associated with a de novo t(10;13) balanced translocation resulting with the disruption of ATP8A2. These findings suggest that ATP8A2 is involved in the development of the cerebro-cerebellar structures required for posture and gait in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Tan U : A new syndrome with quadrupedal gait, primitive speech, and severe mental retardation as a live model for human evolution. Int J Neurosci 2006; 116: 361–369.
Turkmen S, Demirhan O, Hoffmann K et al. Cerebellar hypoplasia and quadrupedal locomotion in humans as a recessive trait mapping to chromosome 17p. J Med Genet 2006; 43: 461–464.
Ozcelik T, Akarsu N, Uz E et al. Mutations in the very low-density lipoprotein receptor VLDLR cause cerebellar hypoplasia and quadrupedal locomotion in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 4232–4236.
Moheb LA, Tzschach A, Garshasbi M et al. Identification of a nonsense mutation in the very low-density lipoprotein receptor gene (VLDLR) in an Iranian family with dysequilibrium syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 2008; 16: 270–273.
Kolb LE, Arlier Z, Yalcinkaya C et al. Novel VLDLR microdeletion identified in two Turkish siblings with pachygyria and pontocerebellar atrophy. Neurogenetics 2010; 11: 319–325.
Turkmen S, Guo G, Garshasbi M et al. CA8 mutations cause a novel syndrome characterized by ataxia and mild mental retardation with predisposition to quadrupedal gait. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000487.
Gulsuner S, Tekinay AB, Doerschner K et al. Homozygosity mapping and targeted genomic sequencing reveal the gene responsible for cerebellar hypoplasia and quadrupedal locomotion in a consanguineous kindred. Genome Res 2011; 21: 1995–2003.
Boycott KM, Flavelle S, Bureau A et al. Homozygous deletion of the very low density lipoprotein receptor gene causes autosomal recessive cerebellar hypoplasia with cerebral gyral simplification. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 77: 477–483.
Tan U : Evidence for ‘Unertan Syndrome’ and the evolution of the human mind. Int J Neurosci 2006; 116: 763–774.
Cacciagli P, Haddad MR, Mignon-Ravix C et al. Disruption of the ATP8A2 gene in a patient with a t(10;13) de novo balanced translocation and a severe neurological phenotype. Eur J Hum Genet 2010; 18: 1360–1363.
Seelow D, Schuelke M, Hildebrandt F et al. HomozygosityMapper—an interactive approach to homozygosity mapping. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: W593–W599.
Li H, Ruan J, Durbin R : Mapping short DNA sequencing reads and calling variants using mapping quality scores. Genome Res 2008; 18: 1851–1858.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 2078–2079.
Li H, Durbin R : Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010; 26: 589–595.
Quinlan AR, Hall IM : BE DTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010; 26: 841–842.
Flicek P, Amode MR, Barrell D et al. Ensembl 2011. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: D800–D806.
Ng PC, Henikoff S : Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions. Genome Res 2001; 11: 863–874.
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 248–249.
Schwarz JM, Rödelsperger C, Schuelke M et al. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 575–576.
Davydov EV, Goode DL, Sirota M et al. Identifying a high fraction of the human genome to be under selective constraint using GERP++. PLoS Comput Biol 2010; 6: e1001025.
Cooper GM, Stone EA, Asimenos G et al. Distribution and intensity of constraint in mammalian genomic sequence. Genome Res 2005; 15: 901–913.
Finn RD, Mistry J, Tate J et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38: D211–D222.
Bryson K, McGuffin LJ, Marsden RL et al. Protein structure prediction servers at University College London. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: W36–W38.
Hartl D, Irmler M, Romer I et al. Transcriptome and proteome analysis of early embryonic mouse brain development. Proteomics 2008; 8: 1257–1265.
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA : Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 44–57.
Rozen S, Skaletsky H : Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 2000; 132: 365–386.
Pfaffl MW : A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: e45.
Halleck MS, Lawler JFJR, Blackshaw S et al. Differential expression of putative transbilayer amphipath transporters. Physiol Genomics 1999; 1: 139–150.
Graham TR, Kozlow MM : Interplay of proteins and lipids in generating membrane curvature. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2010; 22: 430–436.
Puts CF, Holthuis JC : Mechanism and significance of P4 ATPase-catalyzed lipid transport: Lessons from a Na+/K+-pump. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1791: 603–611.
Meguro M, Kashiwagi A, Mitsuya K et al. A novel maternally expressed gene, ATP10C, encodes a putative aminophospholipid translocase associated with Angelman syndrome. Nat Genet 2001; 28: 19–20.
Stapelbroek JM, Peters TA, vanBeurden DH et al. ATP8B1 is essential for maintaining normal hearing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 9709–9714.
Klomp LWJ, Vargas JC, van Mil SWC et al. Characterization of mutations in ATP8B1 associated with hereditary cholestasis. Hepatology 2004; 40: 27–38.
Coleman JA, Kwok MC, Molday RS : Localization, purification, and functional reconstitution of the P4-ATPase Atp8a2, a phosphatidylserine flippase in photoreceptor disc membranes. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 32670–32679.
Wu C, Orozco C, Boyer J et al. BioGPS: an extensible and customizable portal for querying and organizing gene annotation resources. Genome Biol 2009; 10: R130.
Sarac O, Gulsuner S, Yildiz-Tasci Y et al. Neuro-opthalmologic findings in humans with quadrupedal locomotion. Ophthalmic Genet 2012, e-pub ahead of print 11 June 2012; PMID: 22686558.
Cohen D, Bar-Yosef U, Levy J et al. Homozygous CRYBB1 deletion mutation underlies autosomal recessive congenital cataract. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48: 2208–2213.
Harel T, Rabinowitz R, Hendler N et al. COL11A2 mutation associated with autosomal recessive Weissenbacher-Zweymuller syndrome: molecular and clinical overlap with otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED). Am J Med Genet A 2005; 132: 33–35.
Markus B, Narkis G, Landau D et al. Autosomal recessive lethal congenital contractural syndrome type 4 (LCCS4) caused by a mutation in MYBPC1. Hum Mutat 2012, e-pub ahead of print 18 May 2012 doi:10.1002/humu.22122PMID: 22610851.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Mary-Claire King for innumerable discussions and suggestions. We also thank the members of Family C for cooperation in this study. This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK-SBAG 108S036 and 108S355) and Turkish Academy of Sciences (TUBA research support) to TO; Yale Program on Neurogenetics, the Yale Center for Human Genetics and Genomics and National Institutes of Health grants RC02 NS070477 to MG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emre Onat, O., Gulsuner, S., Bilguvar, K. et al. Missense mutation in the ATPase, aminophospholipid transporter protein ATP8A2 is associated with cerebellar atrophy and quadrupedal locomotion. Eur J Hum Genet 21, 281–285 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.170
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.170
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of phosphatidylserine on the membrane in immunity and blood coagulation
Biomarker Research (2022)
-
Biallelic truncation variants in ATP9A are associated with a novel autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder
npj Genomic Medicine (2021)
-
Genome-wide association study for postweaning weight traits in Lori-Bakhtiari sheep
Tropical Animal Health and Production (2021)
-
Transcriptomic assessment of dietary fishmeal partial replacement by soybean meal and prebiotics inclusion in the liver of juvenile Pacific yellowtail (Seriola lalandi)
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)
-
ATP8A2-related disorders as recessive cerebellar ataxia
Journal of Neurology (2020)