Abstract
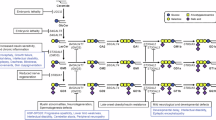
We report two children, born from consanguineous parents, who presented with early-onset refractory epilepsy associated with psychomotor delay, failure to thrive, blindness and deafness. Polarographic and spectrophotometric analyses in fibroblasts and liver revealed a respiratory chain (RC) dysfunction. Surprisingly, we identified a homozygous nonsense mutation in the GM3 synthase gene by using exome sequencing. GM3 synthase catalyzes the formation of GM3 ganglioside from lactosylceramide, which is the first step in the synthesis of complex ganglioside species. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed that the complete absence of GM3 ganglioside and its biosynthetic derivatives was associated with an upregulation of the alternative globoside pathway in fibroblasts. The accumulation of Gb3 and Gb4 globosides likely has a role in RC dysfunction and in the decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential leading to apoptosis, which we observed in fibroblasts. We show for the first time that GM3 synthase deficiency, responsible for early-onset epilepsy syndrome, leads to a secondary RC dysfunction. Our study highlights the role of secondary mitochondrial disorders that can interfere with the diagnosis and the evolution of other metabolic diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Debray F, Lambert M, Chevalier I et al: Long-term outcome and clinical spectrum of 73 pediatric patients with mitochondrial diseases. Pediatrics 2007; 119: 722–733.
Khurana D, Salganicoff L, Melvin J et al: Epilepsy and respiratory chain defects in children with mitochondrial encephalopathy. Neuropediatrics 2008; 39: 8–13.
Canafoglia L, Francheschetti S, Antozzi C et al: Epileptic phenotypes associated with mitochondrial disorders. Neurology 2001; 56: 1340–1346.
Lee Y, Kang H, Lee J et al: Mitochondrial respiratory chain defects: underlying etiology in various epileptic conditions. Epilepsia 2008; 44: 701–707.
El Sabbagh S, Lebre A, Bahi-Buisson N et al: Epileptic phenotypes in children with respiratory chain disorders. Epilepsia 2010; 51: 1225–1235.
Rustin P, Chretien D, Bourgeron T, Gerard B, Rotig A, Saudubray J : Biochemical and molecular investigations in respiratory chain deficiencies. Clin Chem Acta 1994; 228: 31–51.
Lerman-Sagie T, Rustin P, Lev D et al: Dramatic improvement in mitochondrial cardiomyopathy following treatment with idebenone. J Inherit Metab Dis 2001; 24: 28–34.
Leshinsky-Silver E, Levine A, Nissenkorn A et al: Neonatal liver failure and Leigh syndrome possibly due to the CoQ-responsive OXPHOS deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 2003; 79: 288–293.
Bradford M : A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of micrograms quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Annal Biochem 1976; 251: 69–72.
Rouzier C, Le Guedard-Méreuze S, Fragaki K et al: The severity of phenotype linked to SUCLG1 mutations could be correlated with residual amount of SUCLG1 protein. J Med Genet 2010; 47: 670–676.
Paul R, Santucci S, Saunières A, Desnuelle C, Paquis-Flucklinger V : Rapid mapping of mitochondrial DNA deletiond by large fragment PCR. Trends Genet 1996; 12: 131–132.
Bannwarth S, Procaccio V, Paquis-Flucklinger V : Surveyor nuclease: a new strategy for a rapid identification of heteroplasmic mitochondrial DNA mutations in patients with respiratory chain defects. Hum Mutat 2005; 25: 575–582.
Rotig A, Mollet J, Rio M, Munnich A : Infantile and prediatric quinone deficiency diseases. Mitochondrion 2007; 7S: S112–S121.
Lee H, Ann H, Lerno LJ, German J, Lebrilla C : Rapid profiling of bovine and human milk gangliosides by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom 2011; 305: 138–150.
Simpson M, Cross H, Proukakis C et al: Infantile-onset symptomatic epilepsy syndrome caused by a homozygous loss-of-function mutation of GM3 synthase. Nat Genet 2004; 11: 1225–1229.
James A, Wei Y-H, Pang C-Y, Murphy M : Altered mitochondrial function in fibroblasts containing MELAS or MERRF mitochondrial DNA mutations. Biochem J 1996; 318: 401–407.
Farukhi F, Dakkouri C, Wang H, Wiztnitzer M, Traboulsi E : Etiology of vision loss in ganglioside GM3 synthase deficiency. Ophtalmic Genet 2006; 27: 88–91.
Xu Y-H, Barnes S, Sun Y, Grabowski G : Multi-system disorders of glycosphingolipid and ganglioside metabolism. J Lipid Res 2010; 51: 1643–1675.
Fishman P, Max S, Tallman J, Brady R, Maclaren N, Cornblath M : Deficient ganglioside biosynthesis: a novel human sphingolipidosis. Science 1975; 187: 68–70.
Dawkins J, Hulme D, Brahmbliatt S, Auer-Grumbach M, Nicholson G : Mutations in SPTLC1, encoding serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit-1, cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 309–312.
Yamashita T, Hashiramoto A, Haluzik M et al: Enhanced insulin sensitivity in mice lacking ganglioside GM3. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2003; 100: 3445–3449.
Gudz T, Tserng K, Hoppel C : Direct inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III by cell-permeable ceramide. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 24154–24158.
Garcia-Ruiz C, Colell A, Mari M, Morales A, Fernadez-Checa J : Direct ineraction of GD3 ganglioside with mitochondria generates reactive oxygen species followed by mitochondrial permeability transition, cytochome c relaese, and caspase activation. FASEB 2000; 14: 847–858.
Higuchi Y, Miura T, Kajimoto T, Ohta Y : Effects of disialoganglioside GD3 on the mitochondrial membrane potential. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 3009–3013.
Cortan D, Cordero M, Garrido-Marraver J et al: Secondary coenzyme Q10 deficiency triggers mitochondria degradation by mitophagy in MELAS fibroblasts. FASEB 2011; 25: 2669–2687.
Fragaki K, Cano A, Benoist J et al: Fatal heart failure associated with CoQ10 and multiple OXPHOS deficiency in a child wiith propionic acidemia. Mitochondrion 2011; 11: 533–536.
Acknowledgements
We thank Charlotte Cochaud for technical help and Sylvie Bannwarth for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fragaki, K., Ait-El-Mkadem, S., Chaussenot, A. et al. Refractory epilepsy and mitochondrial dysfunction due to GM3 synthase deficiency. Eur J Hum Genet 21, 528–534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.202
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.202
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory role of GM1 and other gangliosides on microglia
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2022)
-
A patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell model for West syndrome caused by ST3GAL3 deficiency
European Journal of Human Genetics (2018)
-
Altered (neo-) lacto series glycolipid biosynthesis impairs α2-6 sialylation on N-glycoproteins in ovarian cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Lipid glycosylation: a primer for histochemists and cell biologists
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2017)