Abstract
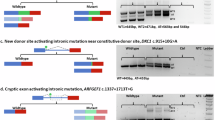
Recent development of next-generation DNA sequencing (NGS) techniques is changing the approach to search for mutations in human genetic diseases. We applied NGS to study an A-T patient in which one of the two expected mutations was not found after DHPLC, cDNA sequencing and MLPA screening. The 160-kb ATM genomic region was divided into 31 partially overlapping fragments of 4–6 kb and amplified by long-range PCR in the patient and mother, who carried the same mutation by segregation. We identified six intronic variants that were shared by the two genomes and not reported in the dbSNP(132) database. Among these, c.1236-405C>T located in IVS11 was predicted to be pathogenic because it affected splicing. This mutation creates a cryptic novel donor (5′) splice site (score 1.00) 405 bp upstream of the exon 12 acceptor (3′) splice site. cDNA analysis showed the inclusion of a 212-bp non-coding ‘pseudoexon’ with a premature stop codon. We validated the functional effect of the splicing mutation using a minigene assay. Using antisense morpholino oligonucleotides, designed to mask the cryptic donor splice-site created by the c.1236-405C>T mutation, we abrogated the aberrant splicing product to a wild-type ATM transcript, and in vitro reverted the functional ATM kinase impairment of the patients’ lymphoblasts. Resequencing is an effective strategy for identifying rare splicing mutations in patients for whom other mutation analyses have failed (DHPLC, MLPA, or cDNA sequencing). This is especially important because many of these patients will carry rare splicing variants that are amenable to antisense-based correction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Gatti RA : Ataxia-Telangiectasia; in: Scriver CRB AL, Sly WS, Valle D, (eds): The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001, pp 705–732.
Lavin MF, Spring K : Upregulation of Fas and apoptosis in thymic lymphomas in Atm knock-in mice. Toxicology 2002; 181-182: 483–489.
Shiloh Y : The ATM-mediated DNA-damage response: taking shape. Trends Biochem Sci 2006; 31: 402–410.
Cavalieri S, Funaro A, Porcedda P et al: ATM mutations in Italian families with ataxia telangiectasia include two distinct large genomic deletions. Hum Mutat 2006; 27: 1061.
Nakamura K, Du L, Tunuguntla R et al: Functional characterization and targeted correction of ATM mutations identified in Japanese patients with ataxia-telangiectasia. Hum Mutat 2012; 33: 198–208.
Cavalieri S, Funaro A, Pappi P, Migone N, Gatti RA, Brusco A : Large genomic mutations within the ATM gene detected by MLPA, including a duplication of 41kb from exon 4–20. Ann Hum Genet 2008; 72: 10–18.
Coutinho G, Xie J, Du L, Brusco A, Krainer AR, Gatti RA : Functional significance of a deep intronic mutation in the ATM gene and evidence for an alternative exon 28a. Hum Mutat 2005; 25: 118–124.
Reese MG, Eeckman FH, Kulp D, Haussler D : Improved splice site detection in Genie. J Comput Biol 1997; 4: 311–323.
Mancini C, Vaula G, Scalzitti L et al: Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts type 1 (MLC1) due to a homozygous deep intronic splicing mutation (c.895-226T>G) abrogated in vitro using an antisense morpholino oligonucleotide. Neurogenetics 2012; 13: 205–214.
Aartsma-Rus A, den Dunnen JT, van Ommen GJ : New insights in gene-derived therapy: the example of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2010; 1214: 199–212.
Lu QL, Yokota T, Takeda S, Garcia L, Muntoni F, Partridge T : The status of exon skipping as a therapeutic approach to duchenne muscular dystrophy. Mol Ther 2011; 19: 9–15.
Teraoka SN, Telatar M, Becker-Catania S et al: Splicing defects in the ataxia-telangiectasia gene, ATM: underlying mutations and consequences. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 64: 1617–1631.
Concannon P, Gatti RA : Diversity of ATM gene mutations detected in patients with ataxia-telangiectasia. Hum Mutat 1997; 10: 100–107.
Du L, Pollard JM, Gatti RA : Correction of prototypic ATM splicing mutations and aberrant ATM function with antisense morpholino oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 6007–6012.
Holbrook JA, Neu-Yilik G, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE : Nonsense-mediated decay approaches the clinic. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 801–808.
Gilad S, Chessa L, Khosravi R et al: Genotype-phenotype relationships in ataxia-telangiectasia and variants. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 62: 551–561.
Chun HH, Sun X, Nahas SA et al: Improved diagnostic testing for ataxia-telangiectasia by immunoblotting of nuclear lysates for ATM protein expression. Mol Genet Metab 2003; 80: 437–443.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Associations ‘Un vero sorriso’, ‘Gli Amici di Valentina’, and ‘Noi per Lorenzo’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavalieri, S., Pozzi, E., Gatti, R. et al. Deep-intronic ATM mutation detected by genomic resequencing and corrected in vitro by antisense morpholino oligonucleotide (AMO). Eur J Hum Genet 21, 774–778 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.266
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.266
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Deep Intronic Mutation in SERPING1 Caused Hereditary Angioedema Through Pseudoexon Activation
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2020)
-
Splicing profile by capture RNA-seq identifies pathogenic germline variants in tumor suppressor genes
npj Precision Oncology (2020)
-
Atm reactivation reverses ataxia telangiectasia phenotypes in vivo
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Oligonucleotide therapies for disorders of the nervous system
Nature Biotechnology (2017)
-
Updated genetic testing of Italian patients referred with a clinical diagnosis of primary hyperoxaluria
Journal of Nephrology (2017)