Abstract
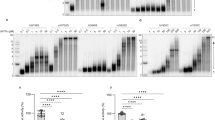
Polymerase gamma (POLG) is the gene most commonly involved in mitochondrial disorders with mitochondrial DNA instability and causes a wide range of diseases with recessive or dominant transmission. More than 170 mutations have been reported. Most of them are missense mutations, although nonsense mutations, splice-site mutations, small deletions and insertions have also been identified. However, to date, only one large-scale rearrangement has been described in a child with Alpers syndrome. Below, we report a large cohort of 160 patients with clinical, molecular and/or biochemical presentation suggestive of POLG deficiency. Using sequencing, we identified POLG variants in 22 patients (18 kindreds) including five novel pathogenic mutations. Two patients with novel mutations had unusual clinical presentation: the first exhibited an isolated ataxic neuropathy and the second was a child who presented with endocrine signs. We completed the sequencing step by quantitative multiplex PCR of short fluorescent fragments (QMPSF) analysis in 37 patients with either only one POLG heterozygous variant or a family history suggesting a dominant transmission. We identified a large intragenic deletion encompassing part of intron 21 and exon 22 of POLG in a child with refractory epilepsia partialis continua. In conclusion, we describe the first large French cohort of patients with POLG mutations, expanding the wide clinical and molecular spectrum observed in POLG disease. We confirm that large deletions in the POLG gene are rare events and we highlight the importance of QMPSF in patients with a single heterozygous POLG mutation, particularly in severe infantile phenotypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Graziewicz MA, Longley MJ, Copeland WC : DNA polymerase gamma in mitochondrial DNA replication and repair. Chem Rev 2006; 106: 383–405.
Van Goethem G, Dermaut B, Löfgren A : Mutation of POLG is associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia characterized by mtDNA deletions. Nat Genet 2001; 28: 211–212.
Lamantea E, Tiranti V, Bordoni A et al: Mutations of mitochondrial DNA polymerase gammaA are a frequent cause of autosomal dominant or recessive progressive external ophthalmoplegia. Ann Neurol 2002; 52: 211–219.
Winterthun S, Ferrari G, He L et al: Autosomal recessive mitochondrial ataxic syndrome due to mitochondrial polymerase gamma mutations. Neurology 2005; 64: 1204–1208.
Wong L-JC, Naviaux RK, Brunetti-Pierri N et al: Molecular and clinical genetics of mitochondrial diseases due to POLG mutations. Hum Mutat 2008; 29: E150–E172.
Compton AG, Troedson C, Wilson M et al: Application of oligonucleotide array CGH in the detection of a large intragenic deletion in POLG associated with Alpers syndrome. Mitochondrion 2011; 11: 104–107.
Tang S, Wang J, Lee N-C et al: Mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma mutations: an everexpanding molecular and clinical spectrum. J Med Genet 2011; 48: 669–681.
Paul R, Santucci S, Saunières A et al: Rapid mapping of mitochondrial dna deletions by large-fragment PCR. Trends Genet 1996; 12: 131–132.
Moraes CT, DiMauro S, Zeviani M et al: Mitochondrial DNA deletions in progressive external ophthalmoplegia and Kearns–Sayre syndrome. N Engl J Med 1989; 320: 1293–1299.
Rouzier C, Le Guédard-Méreuze S, Fragaki K et al: The severity of phenotype linked to SUCLG1 mutations could be correlated with residual amount of SUCLG1 protein. J Med Genet 2010; 47: 670–676.
Naïmi M, Bannwarth S, Procaccio V et al: Molecular analysis of ANT1, TWINKLE and POLG in patients with multiple deletions or depletion of mitochondrial DNA by a dHPLC-based assay. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 917–922.
Gouas L, Goumy C, Véronèse L et al: Gene dosage methods as diagnostic tools for the identification of chromosome abnormalities. Pathol Biol 2008; 56: 345–353.
Ceulemans S, van der Ven K, Del-Favero J : Targeted screening and validation of copy number variations. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 838: 311–328.
Saugier-Veber P, Goldenberg A, Drouin-Garraud V et al: Simple detection of genomic microdeletions and microduplications using QMPSF in patients with idiopathic mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 1009–1017.
Lee YS, Kennedy WD, Yin YW : Structural insight into processive human mitochondrial DNA synthesis and disease-related polymerase mutations. Cell 2009; 139: 312–324.
Kurt B, Jaeken J, Van Hove J et al: A novel POLG gene mutation in 4 children with Alpers-like hepatocerebral syndromes. Arch Neurol 2010; 67: 239–244.
Reichenbach J, Schubert R, Horvàth R et al: Fatal neonatal-onset mitochondrial respiratory chain disease with T cell immunodeficiency. Pediatr Res 2006; 60: 321–326.
Kollberg G, Moslemi A-R, Darin N et al: POLG mutations associated with progressive encephalopathy in childhood. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2006; 65: 758–768.
Harrower T, Stewart JD, Hudson G et al: POLG mutations manifesting as autosomal recessive axonal Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. Arch Neurol 2008; 65: 133–136.
Taanman J-W, Rahman S, Pagnamenta AT et al: Analysis of mutant DNA polymerase gamma in patients with mitochondrial DNA depletion. Hum Mutat 2009; 30: 248–254.
González-Vioque E, Blázquez A, Fernández-Moreira D et al: Association of novel POLG mutations and multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions with variable clinical phenotypes in a Spanish population. Arch Neurol 2006; 63: 107–111.
Blok MJ, van den Bosch BJ, Jongen E et al: The unfolding clinical spectrum of POLG mutations. J Med Genet 2009; 46: 776–785.
Nguyen KV, Østergaard E, Ravn SH et al: POLG mutations in Alpers syndrome. Neurology 2005; 65: 1493–1495.
Ferrari G, Lamantea E, Donati A et al: Infantile hepatocerebral syndromes associated with mutations in the mitochondrial DNA polymerase-gamma A. Brain 2005; 128: 723–731.
Hopkins SE, Somoza A, Gilbert DL : Rare autosomal dominant POLG mutation in a family with metabolic strokes, posterior column spinal degeneration, and multi-endocrine disease. J Child Neurol 2010; 25: 752–756.
Kasiviswanathan R, Copeland WC : Biochemical analysis of the Gly517Val POLG variant reveals wild-type like activity. Mitochondrion 2011; 11: 929–934.
Isohanni P, Hakonen AH, Euro L et al: POLG manifestations in childhood. Neurology 2011; 76: 811–815.
Horvath R, Hudson G, Ferrari G et al: Phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations of the mitochondrial polymerase gamma gene. Brain 2006; 129 (Part 7): 1674–1684.
Charbonnier F, Raux G, Wang Q et al: Detection of exon deletions and duplications of the mismatch repair genes in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer families using multiplex polymerase chain reaction of short fluorescent fragments. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 2760–2763.
Férec C, Casals T, Chuzhanova N et al: Gross genomic rearrangements involving deletions in the CFTR gene: characterization of six new events from a large cohort of hitherto unidentified cystic fibrosis chromosomes and meta-analysis of the underlying mechanisms. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 567–576.
Amara A, Adala L, Ben Charfeddine I et al: Correlation of SMN2, NAIP, p44, H4F5 and Occludin genes copy number with spinal muscular atrophy phenotype in Tunisian patients. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2012; 16: 167–174.
Chan SSL, Longley MJ, Copeland WC : The common Ala467Thr mutation in the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase (POLG) compromises catalytic efficiency and interaction with the accessory subunit. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 31341–31346.
Chan SSL, Longley MJ, Copeland WC : Modulation of the Trp748Ser mutation in DNA polymerase gamma by the E1143G polymorphism in mitochondrial disorders. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 3473–3483.
Van Goethem G, Löfgren A, Dermaut B, Ceuterick C, Martin J-J, Van Broeckhoven C : Digenic progressive external ophthalmoplegia in a sporadic patient: recessive mutations in POLG and C10orf2/Twinkle. Hum Mutat 2003; 22: 175–176.
Acknowledgements
We thank Christelle Camuso and Bernadette Chafino for technical help. This work was made possible by grants to VP-F from the Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM) and to CR from the CHU of Nice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rouzier, C., Chaussenot, A., Serre, V. et al. Quantitative multiplex PCR of short fluorescent fragments for the detection of large intragenic POLG rearrangements in a large French cohort. Eur J Hum Genet 22, 542–550 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.171
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.171
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clinical and Molecular Features of POLG-Related Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy with Dysarthria and Ophthalmoparesis
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2021)
-
Clinico-pathological and Molecular Spectrum of Mitochondrial Polymerase γ Mutations in a Cohort from India
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2021)
-
Novel biallelic mutations in POLG gene: large deletion and missense variant associated with PEO
Neurological Sciences (2021)
-
Contribution of nuclear and mitochondrial gene mutations in mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) syndrome
Journal of Neurology (2021)
-
Rod bipolar cell dysfunction in POLG retinopathy
Documenta Ophthalmologica (2021)