Abstract
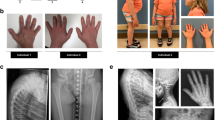
Borrone Dermato-Cardio-Skeletal (BDCS) syndrome is a severe progressive autosomal recessive disorder characterized by coarse facies, thick skin, acne conglobata, dysmorphic facies, vertebral abnormalities and mitral valve prolapse. We identified a consanguineous kindred with a child clinically diagnosed with BDCS. Linkage analysis of this family (BDCS1) identified five regions homozygous by descent with a maximum LOD score of 1.75. Linkage analysis of the family that originally defined BDCS (BDCS3) identified an overlapping linkage peak at chromosome 5q35.1. Sequence analysis identified two different homozygous mutations in BDCS1 and BDCS3, affecting the gene encoding the protein SH3 and PX domains 2B (SH3PXD2B), which localizes to 5q35.1. Western blot analysis of patient fibroblasts derived from affected individuals in both families demonstrated complete loss of SH3PXD2B. Homozygosity mapping and sequence analysis in a second published BDCS family (BDCS2) excluded SH3PXD2B. SH3PXD2B is required for the formation of functional podosomes, and loss-of-function mutations in SH3PXD2B have recently been shown to underlie 7 of 13 families with Frank-Ter Haar syndrome (FTHS). FTHS and BDCS share some overlapping clinical features; therefore, our results demonstrate that a proportion of BDCS and FTHS cases are allelic. Mutations in other gene(s) functioning in podosome formation and regulation are likely to underlie the SH3PXD2B-mutation-negative BDSC/FTHS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Borrone C, Di Rocco M, Crovato F, Camera G, Gambini C : New multisystemic disorder involving heart valves, skin, bones, and joints in two brothers. Am J Med Genet 1993; 46: 228–234.
van Steensel MA, Ceulen RP, Delhaas T, de Die-Smulders C : Two Dutch brothers with Borrone dermato-cardio-skeletal syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 2007; 143A: 1223–1226.
Bahlo M, Bromhead CJ : Generating linkage mapping files from Affymetrix SNP chip data. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 1961–1962.
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR : Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 2002; 30: 97–101.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al: The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 2078–2079.
Li H : Improving SNP discovery by base alignment quality. Bioinformatics 2011; 27: 1157–1158.
Leutenegger AL, Prum B, Genin E et al: Estimation of the inbreeding coefficient through use of genomic data. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 516–523.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al: PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Buschman MD, Bromann PA, Cejudo-Martin P, Wen F, Pass I, Courtneidge SA : The novel adaptor protein Tks4 (SH3PXD2B) is required for functional podosome formation. Mol Biol Cell 2009; 20: 1302–1311.
Gimona M, Buccione R, Courtneidge SA, Linder S : Assembly and biological role of podosomes and invadopodia. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2008; 20: 235–241.
Binks M, Jones GE, Brickell PM, Kinnon C, Katz DR, Thrasher AJ : Intrinsic dendritic cell abnormalities in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Eur J Immunol 1998; 28: 3259–3267.
Carman CV, Sage PT, Sciuto TE et al: Transcellular diapedesis is initiated by invasive podosomes. Immunity 2007; 26: 784–797.
Lehto VP, Hovi T, Vartio T, Badley RA, Virtanen I : Reorganization of cytoskeletal and contractile elements during transition of human monocytes into adherent macrophages. Lab Invest 1982; 47: 391–399.
Marchisio PC, Cirillo D, Naldini L, Primavera MV, Teti A, Zambonin-Zallone A : Cell-substratum interaction of cultured avian osteoclasts is mediated by specific adhesion structures. J Cell Biol 1984; 99: 1696–1705.
Moreau V, Tatin F, Varon C, Genot E : Actin can reorganize into podosomes in aortic endothelial cells, a process controlled by Cdc42 and RhoA. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 6809–6822.
Thompson O, Kleino I, Crimaldi L, Gimona M, Saksela K, Winder SJ : Dystroglycan, Tks5 and Src mediated assembly of podosomes in myoblasts. PLoS One 2008; 3: e3638.
Iqbal Z, Cejudo-Martin P, de Brouwer A et al: Disruption of the podosome adaptor protein TKS4 (SH3PXD2B) causes the skeletal dysplasia, eye, and cardiac abnormalities of Frank-Ter Haar Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 86: 254–261.
Mao M, Thedens DR, Chang B et al: The podosomal-adaptor protein SH3PXD2B is essential for normal postnatal development. Mamm Genome 2009; 20: 462–475.
Frank Y, Ziprkowski M, Romano A et al: Megalocornea associated with multiple skeletal anomalies: a new genetic syndrome? J Genet Hum 1973; 21: 67–72.
Hamel BC, Draaisma JM, Pinckers AJ et al: Autosomal recessive Melnick-Needles syndrome or ter Haar syndrome? Report of a patient and reappraisal of an earlier report. Am J Med Genet 1995; 56: 312–316.
Maas SM, Kayserili H, Lam J, Apak MY, Hennekam RC : Further delineation of Frank-ter Haar syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 2004; 131: 127–133.
Megarbane A, Tomey K, Wakim G : Congenital glaucoma, limb deformities, skeletal dysplasia, and facial anomalies: report of another family. Am J Med Genet 1997; 73: 67–71.
ter Haar B, Hamel B, Hendriks J, de Jager J : Melnick-Needles syndrome: indication for an autosomal recessive form. Am J Med Genet 1982; 13: 469–477.
Wallerstein R, Scott CI Jr., Nicholson L : Extended survival in a new case of ter Haar syndrome: further delineation of the syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1997; 70: 267–272.
Mao M, Hedberg-Buenz A, Koehn D, John SW, Anderson MG : Anterior segment dysgenesis and early-onset glaucoma in nee mice with mutation of Sh3pxd2b. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52: 2679–2688.
Acknowledgements
We thank the families involved in this research and are grateful to Hayley Mountford and Greta Gillies for assistance with patient samples. We thank John Bateman for collagen analysis in BDCS1. Skin fibroblasts from BDCS3 were obtained from the Cell Line and DNA Biobank from patients affected by genetic diseases (G.Gaslini Institute), Telethon Network of Genetic Biobank (Project GTB07001A). This work was funded in part by National Health and Medical Research Council Australia Program Grant 490037 to DJA and MB. KRS is supported by a PhD scholarship funded by the Pratt Foundation. MB is supported by an ARC Future Fellowship (FT100100764). MBD is supported by an NHMRC Practitioner Fellowship (546452) and PJL is supported by an NHMRC Career Development Fellowship (APP1032364). This work was made possible through Victorian State Government Operational Infrastructure Support and Australian Government NHMRC IRIISS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, G., Sunley, J., Smith, K. et al. Mutations in SH3PXD2B cause Borrone dermato-cardio-skeletal syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 22, 741–747 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.229
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.229
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome: a case presenting with gingival enlargement as the only clinical manifestation and a report of two new mutations in the ANTXR2 gene
BMC Oral Health (2021)
-
Enhanced endothelial motility and multicellular sprouting is mediated by the scaffold protein TKS4
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The scaffold protein Tks4 is required for the differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) into adipogenic and osteogenic lineages
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Accumulation of the PX domain mutant Frank-ter Haar syndrome protein Tks4 in aggresomes
Cell Communication and Signaling (2015)
-
Closing the Gap: Genetic and Genomic Continuum from Syndromic to Nonsyndromic Craniosynostoses
Current Genetic Medicine Reports (2014)