Abstract
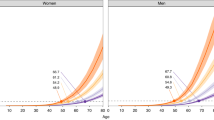
Recently our group completed a genome-wide linkage study investigating Australian and Spanish families with inherited risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). A minor linkage peak from that study located on chromosome 1 correlates with the location of a known CRC risk-modifying gene, prostaglandin synthase (PTGS2). PTGS2 encodes the inducible prostaglandin synthase enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Prostaglandins are implicated in the initiation of carcinogenesis and progression of tumours. Sequencing of PTGS2 in a small subset of affected individuals identified a high frequency of the minor C allele of single nucleotide polymorphism rs5275. We then genotyped the rs5275 polymorphism in 183 affected and 223 unaffected individuals from our CRC predisposed families. Tests for association in the presence of linkage were made using family-based association tests. The C allele was found to be significantly associated (P<0.01) with diagnosis of hereditary non-syndromic CRC (P=0.0094, dominant model) and an earlier age of diagnosis (P=0.0089, heterozygous-advantage model). Interestingly, by stratifying the age of diagnosis data, we observed a speculative gender-discordant effect. Relative to other groups, female CC carriers were diagnosed less when young, but by 60 years of age were the most at risk group. Conversely, CT carriers of both genders showed a consistently earlier diagnosis relative to TT carriers. Our results suggest potential differential age-and gender-dependent efficacies of chemopreventative COX-2 inhibitors in the context of non-syndromic colorectal cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Coussens LM, Werb Z : Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002; 420: 860–867.
Castellone MD, Teramoto H, Williams BO, Druey KM, Gutkind JS : Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer cell growth through a Gs-axin-beta-catenin signaling axis. Science 2005; 310: 1504–1510.
Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Kliewer E, Wajda A : Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Cancer 2001; 91: 854–862.
Cuzick J, Otto F, Baron JA et al: Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: an international consensus statement. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 501–507.
Eberhart CE, Coffey RJ, Radhika A, Giardiello FM, Ferrenbach S, DuBois RN : Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression in human colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology 1994; 107: 1183–1188.
Koki AT, Masferrer JL : Celecoxib: a specific COX-2 inhibitor with anticancer properties. Cancer Control 2002; 9: 28–35.
Sonoshita M, Takaku K, Oshima M, Sugihara K, Taketo MM : Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in fibroblasts and endothelial cells of intestinal polyps. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 6846–6849.
Oshima M, Dinchuk JE, Kargman SL et al: Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Apc delta716 knockout mice by inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). Cell 1996; 87: 803–809.
Bertagnolli MM, Eagle CJ, Zauber AG et al: Celecoxib for the prevention of sporadic colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 873–884.
Frattini M, Carnevali I, Signoroni S et al: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in FAP patients carrying germ line MYH mutations. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2005; 14: 2049–2052.
Papafili A, Hill MR, Brull DJ et al: Common promoter variant in cyclooxygenase-2 represses gene expression: evidence of role in acute-phase inflammatory response. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002; 22: 1631–1636.
Cok SJ, Morrison AR : The 3′-untranslated region of murine cyclooxygenase-2 contains multiple regulatory elements that alter message stability and translational efficiency. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 23179–23185.
Moore AE, Young LE, Dixon DA : A common single-nucleotide polymorphism in cyclooxygenase-2 disrupts microRNA-mediated regulation. Oncogene 2012; 31: 1592–1598.
Vogel U, Christensen J, Wallin H, Friis S, Nexo BA, Tjonneland A : Polymorphisms in COX-2, NSAID use and risk of basal cell carcinoma in a prospective study of Danes. Mutat Res 2007; 617: 138–146.
Yang H, Gu J, Lin X et al: Profiling of genetic variations in inflammation pathway genes in relation to bladder cancer predisposition. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 2236–2244.
Jung JH, Chae YS, Moon JH et al: TNF superfamily gene polymorphism as prognostic factor in early breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2010; 136: 685–694.
Cox DG, Buring J, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ : A polymorphism in the 3′ untranslated region of the gene encoding prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2 is not associated with an increase in breast cancer risk: a nested case-control study. Breast Cancer Res 2007; 9: R3.
Siezen CL, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Peeters PH, Kram NR, van Doeselaar M, van Kranen HJ : Polymorphisms in the genes involved in the arachidonic acid-pathway, fish consumption and the risk of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 2006; 119: 297–303.
Ali IU, Luke BT, Dean M, Greenwald P : Allellic variants in regulatory regions of cyclooxygenase-2: association with advanced colorectal adenoma. Br J Cancer 2005; 93: 953–959.
Kim JG, Chae YS, Sohn SK et al: Prostaglandin synthase 2/cyclooxygenase 2 (PTGS2/COX2) 8473T>C polymorphism associated with prognosis for patients with colorectal cancer treated with capecitabine and oxaliplatin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2009; 64: 953–960.
Siezen CL, van Leeuwen AI, Kram NR, Luken ME, van Kranen HJ, Kampman E : Colorectal adenoma risk is modified by the interplay between polymorphisms in arachidonic acid pathway genes and fish consumption. Carcinogenesis 2005; 26: 449–457.
Canzian F, Franceschi S, Plummer M et al: Genetic polymorphisms in mediators of inflammation and gastric precancerous lesions. Eur J Cancer Prev 2008; 17: 178–183.
Campa D, Zienolddiny S, Maggini V, Skaug V, Haugen A, Canzian F : Association of a common polymorphism in the cyclooxygenase 2 gene with risk of non-small cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 2004; 25: 229–235.
Hu Z, Miao X, Ma H et al: A common polymorphism in the 3′UTR of cyclooxygenase 2/prostaglandin synthase 2 gene and risk of lung cancer in a Chinese population. Lung Cancer 2005; 48: 11–17.
Park JM, Choi JE, Chae MH et al: Relationship between cyclooxygenase 8473T>C polymorphism and the risk of lung cancer: a case-control study. BMC Cancer 2006; 6: 70.
Danforth KN, Hayes RB, Rodriguez C et al: Polymorphic variants in PTGS2 and prostate cancer risk: results from two large nested case-control studies. Carcinogenesis 2008; 29: 568–572.
Pu X, Lippman SM, Yang H, Lee JJ, Wu X : Cyclooxygenase-2 gene polymorphisms reduce the risk of oral premalignant lesions. Cancer 2009; 115: 1498–1506.
Lurie G, Terry KL, Wilkens LR et al: Pooled analysis of the association of PTGS2 rs5275 polymorphism and NSAID use with invasive ovarian carcinoma risk. Cancer Causes Control 2010; 21: 1731–1741.
Zhu W, Wei BB, Shan X, Liu P : -765G>C and 8473T>C polymorphisms of COX-2 and cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on 33 case-control studies. Mol Biol Rep 2010; 37: 277–288.
Vogel U, Christensen J, Wallin H et al: Polymorphisms in genes involved in the inflammatory response and interaction with NSAID use or smoking in relation to lung cancer risk in a prospective study. Mutat Res 2008; 639: 89–100.
Siezen CL, Tijhuis MJ, Kram NR et al: Protective effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on colorectal adenomas is modified by a polymorphism in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta. Pharmacogen Genomics 2006; 16: 43–50.
Saunders IW, Ross J, Macrae F et al: Evidence of linkage to chromosomes 10p15.3-p15.1, 14q24.3-q31.1 and 9q33.3-q34.3 in non-syndromic colorectal cancer families. Eur J Hum Genet 2012; 20: 91–96.
Lange C, Laird NM : On a general class of conditional tests for family-based association studies in genetics: the asymptotic distribution, the conditional power, and optimality considerations. Genet Epidemiol 2002; 23: 165–180.
Van Steen K, Lange C : PBAT: a comprehensive software package for genome-wide association analysis of complex family-based studies. Hum Genomics 2005; 2: 67–69.
Horvath S, Xu X, Laird NM : The family based association test method: strategies for studying general genotype--phenotype associations. Eur J Hum Genet 2001; 9: 301–306.
Chen WM, Manichaikul A, Rich SS : A generalized family-based association test for dichotomous traits. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 85: 364–376.
Mann JR, DuBois RN : Cyclooxygenase-2 and gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer J 2004; 10: 145–152.
Lange C, Blacker D, Laird NM : Family-based association tests for survival and times-to-onset analysis. Stat Med 2004; 23: 179–189.
Kato I, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, Koenig KL, Shore R, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A : Prospective study of factors influencing the onset of natural menopause. J Clin Epidemiol 1998; 51: 1271–1276.
Koo JH, Jalaludin B, Wong SKC, Kneebone A, Connor SJ, Leong RWL : Improved survival in young women with colorectal cancer. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103: 1488–1495.
Chlebowski RT, Wactawski-Wende J, Ritenbaugh C et al: Estrogen plus progestin and colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 991–1004.
Campbell-Thompson M, Lynch IJ, Bhardwaj B : Expression of estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes and ERβ isoforms in colon cancer. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 632–640.
Konstantinopoulos PA, Kominea A, Vandoros G et al: Oestrogen receptor beta (ERβ) is abundantly expressed in normal colonic mucosa, but declines in colon adenocarcinoma paralleling the tumour’s dedifferentiation. Eur J Cancer 2003; 39: 1251–1258.
Szczeklik W, Sanak M, Szczeklik A : Functional effects and gender association of COX-2 gene polymorphism G(-765)C in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 114: 248–253.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participating families in our linkage study. We also thank Dr Nicholas Archer and Dr Yalchin Oytam for critically reviewing this manuscript. This work is supported within CSIRO by the CSIRO Preventative Health National Research Flagship and at the ICO by contract/grant sponsor: Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and PI10/00748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ross, J., Lockett, L., Brookes, D. et al. An association between the PTGS2 rs5275 polymorphism and colorectal cancer risk in families with inherited non-syndromic predisposition. Eur J Hum Genet 21, 1389–1395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.53
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.53