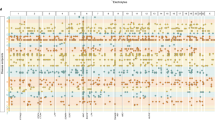
Abstract
The difficulties arising from association analysis with rare variants underline the importance of suitable reference population cohorts, which integrate detailed spatial information. We analyzed a sample of 1684 individuals from Western France, who were genotyped at genome-wide level, from two cohorts D.E.S.I.R and CavsGen. We found that fine-scale population structure occurs at the scale of Western France, with distinct admixture proportions for individuals originating from the Brittany Region and the Vendée Department. Genetic differentiation increases with distance at a high rate in these two parts of Northwestern France and linkage disequilibrium is higher in Brittany suggesting a lower effective population size. When looking for genomic regions informative about Breton origin, we found two prominent associated regions that include the lactase region and the HLA complex. For both the lactase and the HLA regions, there is a low differentiation between Bretons and Irish, and this is also found at the genome-wide level. At a more refined scale, and within the Pays de la Loire Region, we also found evidence of fine-scale population structure, although principal component analysis showed that individuals from different departments cannot be confidently discriminated. Because of the evidence for fine-scale genetic structure in Western France, we anticipate that rare and geographically localized variants will be identified in future full-sequence analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA et al: Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2009; 106: 9362–9367.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ et al: Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009; 461: 747–753.
Lupski JR, Belmont JW, Boerwinkle E, Gibbs RA : Clan genomics and the complex architecture of human disease. Cell 2011; 147: 32–43.
Cirulli ET, Goldstein DB : Uncovering the roles of rare variants in common disease through whole-genome sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 2010; 11: 415–425.
McClellan J, King M-C : Genetic heterogeneity in human disease. Cell 2010; 141: 210–217.
Kristiansson K, Naukkarinen J, Peltonen L : Isolated populations and complex disease gene identification. Genome Biol 2008; 9: 109.
Henn BM, Gravel S, Moreno-Estrada A, Acevedo-Acevedo S, Bustamante CD : Fine-scale population structure and the era of next-generation sequencing. Hum Mol Genet 2010; 19: R221–R226.
Mathieson I, McVean G : Differential confounding of rare and common variants in spatially structured populations. Nat Genet 2012; 44: 243–246.
Menozzi P, Piazza A, Cavalli-Sforza L : Synthetic maps of human gene frequencies in Europeans. Science 1978; 201: 786–792.
Heath SC, Gut IG, Brennan P et al: Investigation of the fine structure of European populations with applications to disease association studies. Eur J Hum Genet 2008; 16: 1413–1429.
Novembre J, Johnson T, Bryc K et al: Genes mirror geography within Europe. Nature 2008; 456: 98–101.
Jay F, Sjödin P, Jakobsson M, Blum MGB : Anisotropic isolation by distance: the main orientations of human genetic differentiation. Mol Biol Evol 2013; 30: 513–525.
Humphreys K, Grankvist A, Leu M et al: The genetic structure of the Swedish population. PLoS One 2011; 6: e22547.
O’Dushlaine CT, Morris D, Moskvina V et al: Population structure and genome-wide patterns of variation in Ireland and Britain. Eur J Hum Genet 2010; 18: 1248–1254.
Salmela E, Lappalainen T, Liu J et al: Swedish population substructure revealed by genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism data. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16747.
Di Gaetano C, Voglino F, Guarrera S et al: An overview of the genetic structure within the Italian population from genome-wide data. PLoS One 2012; 7: e43759.
Esko T, Mezzavilla M, Nelis M et al: Genetic characterization of northeastern Italian population isolates in the context of broader European genetic diversity. Eur J Hum Genet 2012; 21: 659–665.
Abdellaoui A, Hottenga J-J, Knijff de P et al: Population structure, migration, and diversifying selection in the Netherlands. Eur J Hum Genet 2013; 21: 1277–1285.
O’Dushlaine C, McQuillan R, Weale ME et al: Genes predict village of origin in rural Europe. Eur J Hum Genet 2010; 18: 1269–1270.
Colonna V, Nutile T, Ferrucci RR et al: Comparing population structure as inferred from genealogical versus genetic information. Eur J Hum Genet 2009; 17: 1635–1641.
Biswas S, Scheinfeldt LB, Akey JM : Genome-wide insights into the patterns and determinants of fine-scale population structure in humans. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 84: 641–650.
Pellen N Hasard, coïncidence, prédestination... et s’il fallait plutôt regarder du côté de nos aïeux? Analyse démographique et historique des réseaux généalogiques et des structures familiales des patients atteints de mucoviscidose en Bretagne. Thèse de doctorat en démographie historique. Versailles, France: Université de Versailles-Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines, 2012.
Blayo Y, Henry L : Données démographiques sur la Bretagne et l’Anjou de 1740 à 1829. Ann Démographie Hist 1967; 1967: 91–171.
Dupaquier J : La dynamique démographique de la France de l’Ouest au XIXe s. Norois 1988; 140: 409–414.
Nelson MR, Bryc K, King KS et al: The Population Reference Sample, POPRES: a resource for population, disease, and pharmacological genetics research. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 83: 347–358.
Balkau B : [An epidemiologic survey from a network of French Health Examination Centres, (D.E.S.I.R.): epidemiologic data on the insulin resistance syndrome]. Rev Dépidémiologie Santé Publique 1996; 44: 373–375.
Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J et al: A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 2007; 445: 881–885.
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K : Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res 2009; 19: 1655–1664.
Patterson N, Price AL, Reich D : Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet 2006; 2: e190.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al: PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Duforet-Frebourg N, Blum MGB : Non-stationary patterns of isolation-by-distance: inferring measures of local genetic differentiation with Bayesian kriging. Evolution 2013; 68: 1110–1123.
Stouffer SA, Suchman EA, Devinney LC, Star SA, Williams RM Jr : The American Soldier: Adjustment During Army Life. (Studies in Social Psychology in World War II, Volume 1). Princeton University Press, NJ, USA, 1949.
McVean G : A genealogical interpretation of principal components analysis. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000686.
Hohenberg P : Migrations et fluctuations démographiques dans la France rurale, 1836-1901. Ann Économies Sociétés Civilis 1974; 29: 461–497.
Leprohon R : Vie et mort des Bretons sous Louis XIV. Brasparts, France: Bibliophiles de Bretagne, 1984.
Pimenoff VN, Laval G, Comas D et al: Similarity in recombination rate and linkage disequilibrium at CYP2C and CYP2D cytochrome P450 gene regions among Europeans indicates signs of selection and no advantage of using tagSNPs in population isolates. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2012; 22: 846–857.
Evseeva I, Nicodemus KK, Bonilla C, Tonks S, Bodmer WF : Linkage disequilibrium and age of HLA region SNPs in relation to classic HLA gene alleles within Europe. Eur J Hum Genet 2010; 18: 924–932.
McEvoy B, Richards M, Forster P, Bradley DG : The Longue Durée of genetic ancestry: multiple genetic marker systems and Celtic origins on the Atlantic facade of Europe. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 693–702.
Dubut V, Chollet L, Murail P et al: mtDNA polymorphisms in five French groups: importance of regional sampling. Eur J Hum Genet 2004; 12: 293–300.
Busby GB, Brisighelli F, Sánchez-Diz P et al: The peopling of Europe and the cautionary tale of Y chromosome lineage R-M269. Proc Biol Sci 2012; 279: 884–892.
Itan Y, Jones BL, Ingram CJE, Swallow DM, Thomas MG : A worldwide correlation of lactase persistence phenotype and genotypes. BMC Evol Biol 2010; 10: 36.
Fix AG : Gene frequency clines in Europe: demic diffusion or natural selection? J R Anthropol Inst 1996; 2: 625–643.
Winney B, Boumertit A, Day T et al: People of the British Isles: preliminary analysis of genotypes and surnames in a UK-control population. Eur J Hum Genet 2012; 20: 203–210.
Chen W, Li B, Zeng Z et al: Genotype calling and haplotyping in parent-offspring trios. Genome Res 2013; 23: 142–151.
Acknowledgements
We thank Emmanuelle Bourcereau who was involved in patient recruitment of the CavsGen cohort. We also thank Professors Le Guerrier and Baufreton from University Hospitals of Rennes and Angers. We are grateful to the French Regional Council of Pays-de-la-Loire (Regional grant Biliv, grant VACARME - www.vacarme-project.org), the French Ministry of Health (PHRC/RNI-PROG/09/61: Génétique du rétrécissement aortique) and the French Ministry of Research (CavsGen project, ANR-13-BSV6-0011-01). We wish to thank the Fondation Genavie for its financial support. The POPRES data were obtained from dbGaP (accession no. phs000145.v3.p2). FS was funded by a Eurostars E!6490 Cardiomarks grant. MGBB is supported by the French National Research Agency (DATGEN project, ANR-2010-JCJC-1607-01). The D.E.S.I.R. study has been supported by INSERM contracts with CNAMTS, Lilly, Novartis Pharma and Sanofi-Aventis; by INSERM (Réseaux en Santé Publique, Interactions entre les déterminants de la santé), Cohortes Santé TGIR, the Association Diabète Risque Vasculaire, the Fédération Française de Cardiologie, La Fondation de France, ALFEDIAM, Société francophone du diabète, ONIVINS, Abbott, Ardix Medical, Bayer Diagnostics, Becton Dickinson, Cardionics, Merck Santé, Novo Nordisk, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Topcon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The D.E.S.I.R. Study Group INSERM U1018: B Balkau, P Ducimetière, E Eschwège; INSERM U367: F Alhenc-Gelas; CHU D’Angers: A Girault; Bichat Hospital: F Fumeron, M Marre, R Roussel; CHU de Rennes: F. Bonnet; CNRS UMR8090, Lille: S Cauchi, P Froguel; Centres d’Examens de Santé: Alençon, Angers, Blois, Caen, Chateauroux, Chartres, Cholet, Le Mans, Orléans, Tours; Institute de Recherche Médecine Générale: J Cogneau; General practitioners of the Region; Institute inter-Regional pour la Santé: C Born, E Caces, M Cailleau, O Lantieri, JG Moreau, F Rakotozafy, J Tichet, S Vol.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karakachoff, M., Duforet-Frebourg, N., Simonet, F. et al. Fine-scale human genetic structure in Western France. Eur J Hum Genet 23, 831–836 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.175
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.175
This article is cited by
-
The genetic structure of Norway
European Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
The genetic history of France
European Journal of Human Genetics (2020)
-
The Irish DNA Atlas: Revealing Fine-Scale Population Structure and History within Ireland
Scientific Reports (2017)