Abstract
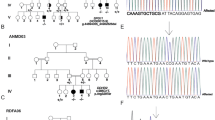
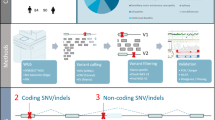
X-linked recessive dystonia-parkinsonism is a rare movement disorder that is highly prevalent in Panay Island in the Philippines. Earlier studies identified seven different genetic alterations within a 427-kb disease locus on the X chromosome; however, the exact disease-causing variant among these is still not unequivocally determined. To further investigate the genetic cause of this disease, we sequenced all previously reported genetic alterations in 166 patients and 473 Filipino controls. Singly occurring variants in our ethnically matched controls would have allowed us to define these as polymorphisms, but none were found. Instead, we identified five patients carrying none of the disease-associated variants, and one male control carrying all of them. In parallel, we searched for novel single-nucleotide variants using next-generation sequencing. We did not identify any shared variants in coding regions of the X chromosome. However, by validating intergenic variants discovered via genome sequencing, we were able to define the boundaries of the disease-specific haplotype and narrow the disease locus to a 294-kb region that includes four known genes. Using microarray-based analyses, we ruled out the presence of disease-linked copy number variants within the implicated region. Finally, we utilized in silico analysis and detected no strong evidence of regulatory regions surrounding the disease-associated variants. In conclusion, our finding of disease-specific variants occurring in complete linkage disequilibrium raises new insights and intriguing questions about the origin of the disease haplotype, the existence of phenocopies and of reduced penetrance, and the causative genetic alteration in XDP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Klein C : Genetics in dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2014; 20 (Suppl 1): S137–S142.
Lee LV, Rivera C, Teleg RA et al: The unique phenomenology of sex-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (XDP, DYT3, "Lubag"). Int J Neurosci 2011; 121(Suppl): 3–11.
Németh AH, Nolte D, Dunne E et al: Refined linkage disequilibrium and physical mapping of the gene locus for X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (DYT3). Genomics 1999; 60: 320–329.
Peters U, Haberhausen G, Kostrzewa M : PFX1 and p54nrb: fine mapping, genomic structure, and exclusion as candidate genes of X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Hum Genet 1997; 100: 569–572.
Nolte D, Ramser J, Niemann S, Lehrach H, Sudbrak R, Müller U : ACRC codes for a novel nuclear protein with unusual acidic repeat tract and maps to DYT3 (dystonia parkinsonism) critical interval in Xq13.1. Neurogenetics 2001; 3: 207–213.
Deng H, Le WD : Joseph Jankovic: Genetic study of an American family with DYT3 dystonia (lubag). Neurosci Lett 2008; 448: 180–183.
Nolte D, Niemann S, Müller U : Specific sequence changes in multiple transcript system DYT3 are associated with X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 10347–10352.
Makino S, Kaji R, Ando S et al: Reduced neuron-specific expression of the TAF1 gene is associated with X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 80: 393–406.
Herzfeld T, Nolte D, Grznarova M, Hofmann A, Schultze JL, Müller U : X-linked dystonia parkinsonism syndrome (XDP, lubag): disease-specific sequence change DSC3 in TAF1/DYT3 affects genes in vesicular transport and dopamine metabolism. Hum Mol Genet 2013; 22: 941–951.
Müller U, Herzfeld T, Nolte D : The TAF1/DYT3 multiple transcript system in X-linked dystonia parkinsonism (letters to the editor). Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 415–417.
Tamiya G, Makino S, Kaji R : TAF1 as the most plausible disease gene for XDP/DYT3 (letters to the editor). Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 417–418.
Sako W, Morigaki R, Kaji R et al: Identification and localization of a neuron-specific isoform of TAF1 in rat brain: implications for neuropathology of DYT3 dystonia. Neuroscience 2011; 189: 100–107.
Domingo A, Lee LV, Brüggemann N et al: Case report of a female with X-linked recessive dystonia-parkinsonism: a clue to the epidemiology of parkinsonism in Filipino women? JAMA Neurol 2014; 71: 1177–1180.
Westenberger A, Rosales R, Heinitz S et al: X-linked Dystonia-Parkinsonism manifesting in a female patient due to atypical turner syndrome. Mov Disord 2013; 28: 675–678.
Kawarai T, Pasco PMD, Teleg RA et al: Application of long-range polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Neurogenetics 2013; 14: 167–169.
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H : ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nuc Acids Res 2010; 38: e164.
Boyle AP, Hong EL, Hariharan M et al: Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res 2012; 22: 1790–1797.
Scott WH : Cracks in the parchment curtain and other essays in Philippine history. Manila, Quezon City New Day Publishers, 1982; 300, pp.
Drmanac R, Sparks AB, Callow MJ et al: Human genome sequencing using unchained base reads on self-assembling DNA nanoarrays. Science 2010; 327: 78–81.
Wong LP, Ong RTH, Poh WT et al: Deep whole-genome sequencing of 100 southeast Asian Malays. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 92: 52–66.
Subramony SH, Advincula J, Perlman S et al: Comprehensive phenotype of the p.Arg420his allelic form of spinocerebellar ataxia type 13. Cerebellum 2013; 12: 932–936.
Saunders-Pullman R, Fuchs T et al: Heterogeneity in primary dystonia: lessons from THAP1, GNAL, and TOR1A in Amish-Mennonites. Mov Disord 2014; 29: 812–818.
Mazars R, Gonzalez-de-Peredo A, Cayrol C et al: The THAP-zinc finger protein THAP1 associates with coactivator HCF-1 and O-GlcNAc transferase: a link between DYT6 and DYT3 dystonias. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 13364–13371.
Levy S, Sutton G, Ng P et al: The diploid genome sequence of an individual human. PLoS Biol 2007; 5: e254.
Villard L, Briault S, Am Lossi et al: Two unrelated patients with inversions of the X-chromosome and non-specific mental retardation: physical and transcriptional mapping of their common breakpoint region in Xq13.1. J Med Genet 1999; 36: 754–758.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Bachmann-Strauss Dystonia & Parkinson Foundation through a Jake’s Ride for Dystonia Research Grant (to AW) and the Fritz Thyssen Foundation (to AW) for funding our experiments. AD is the recipient of a scholarship from the German Academic Exchange Program (DAAD). CK is a Schilling Professor of Neurogenetics (Herman and Lilly Schilling Foundation). We would like to thank the following members of the XDP Study Group of the Philippines who assisted in collecting XDP patients and assembling control cohorts: Dr Abundio Balgos, Dr Cid Czarina Diesta, Dr Criscely Go, Dr Arlene Ng, Dr Anthony Piano, Dr Marita VT Reyes, Dr Sonia Sarcia, and Mercy Joyce Monding-Yabres.
Abbreviations
XDP, X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism; DSC, disease-specific single-nucleotide change; SNV, single-nucleotide variation; CNV, copy number variant; STR, Short-tandem repeat; NGS, next-generation sequencing, in this text refers to genome sequencing; TAF1, TATA box-binding protein-associated factor 1 gene; OGT, O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase gene; ACRC, acidic repeat-containing protein gene; CXCR3, chemokine receptor 3 gene; SVA, SINE-VNTR-Alu element.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
CK is a medical counselor to Centogene, a commercial genetic testing center based in Rostock, Germany. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domingo, A., Westenberger, A., Lee, L. et al. New insights into the genetics of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (XDP, DYT3). Eur J Hum Genet 23, 1334–1340 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.292
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.292
This article is cited by
-
X-linked dystonia parkinsonism: epidemiology, genetics, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment
Acta Neurologica Belgica (2023)
-
Tissue-specific and repeat length-dependent somatic instability of the X-linked dystonia parkinsonism-associated CCCTCT repeat
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2022)
-
Combined dystonias: clinical and genetic updates
Journal of Neural Transmission (2021)
-
Tremor in Primary Monogenic Dystonia
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2021)
-
The importance of genetic testing for dystonia patients and translational research
Journal of Neural Transmission (2021)