Abstract
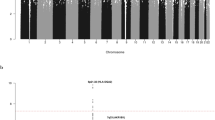
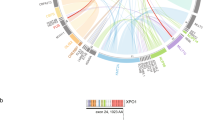
An inherited predisposition to acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is exceedingly rare, but the investigation of these families will aid in the delineation of the underlying mechanisms of the more common, sporadic cases. Three AML predisposition genes, RUNX1, CEBPA and GATA2, have been recognised, but the culprit genes in the majority of AML pedigrees remain obscure. We applied a combined strategy of linkage analysis and next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology in an autosomal-dominant AML Chinese family with 11 cases in four generations. A genome-wide linkage scan using a 500K SNP genotyping array was conducted to identify a previously unreported candidate region on 20p13 with a maximum multipoint heterogeneity LOD (HLOD) score of 3.56 (P=0.00005). Targeted NGS within this region and whole-exome sequencing (WES) revealed a missense mutation in TGM6 (RefSeq, NM_198994.2:c.1550T>G, p.(L517W)), which cosegregated with the phenotype in this family, and was absent in 530 healthy controls. The mutated amino acid was located in a highly conserved position, which may be deleterious and affect the activation of TGM6. Our results strongly support the candidacy of TGM6 as a novel familial AML-associated gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Song WJ, Sullivan MG, Legare RD et al: Haploinsufficiency of CBFA2 causes familial thrombocytopenia with propensity to develop acute myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Genet 1999; 23: 166–175.
Hahn CN, Chong CE, Carmichael CL et al: Heritable GATA2 mutations associated with familial myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 1012–1017.
Smith ML, Cavenagh JD, Lister TA, Fitzgibbon J : Mutation of CEBPA in familial acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2403–2407.
Kirwan M, Vulliamy T, Marrone A et al: Defining the pathogenic role of telomerase mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Mutat 2009; 30: 1567–1573.
Holme H, Hossain U, Kirwan M, Walne A, Vulliamy T, Dokal I : Marked genetic heterogeneity in familial myelodysplasia/acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2012; 158: 242–248.
Quintana-Bustamante O, Lan-Lan Smith S, Griessinger E et al: Overexpression of wild-type or mutants forms of CEBPA alter normal human hematopoiesis. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1537–1546.
He LZ, Lu LH, Chen ZZ : Genetic mechanism of leukemia predisposition in a family with 7 cases of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1994; 76: 65–69.
Matsuzaki H, Loi H, Dong S et al: Parallel genotyping of over 10 000 SNPs using a one-primer assay on a high-density oligonucleotide array. Genome Res 2004; 14: 414–425.
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR : Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 2002; 30: 97–101.
Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve-Daly MP, Lander ES : Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 1347–1363.
Rehman AU, Morell RJ, Belyantseva IA et al: Targeted capture and next-generation sequencing identifies C9orf75, encoding taperin, as the mutated gene in nonsyndromic deafness DFNB79. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 86: 378–388.
Hedges DJ, Burges D, Powell E et al: Exome sequencing of a multigenerational human pedigree. PLoS One 2009; 4: e8232.
Ng PC, Henikoff S : Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions. Genome Res 2001; 11: 863–874.
Sunyaev S, Ramensky V, Koch I, Lathe W 3rd, Kondrashov AS, Bork P : Prediction of deleterious human alleles. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 591–597.
Wang JL, Yang X, Xia K et al: TGM6 identified as a novel causative gene of spinocerebellar ataxias using exome sequencing. Brain 2010; 133: 3510–3518.
Iismaa SE, Mearns BM, Lorand L, Graham RM : Transglutaminases and disease: lessons from genetically engineered mouse models and inherited disorders. Physiol Rev 2009; 89: 991–1023.
Carmichael CL, Wilkins EJ, Bengtsson H et al: Poor prognosis in familial acute myeloid leukaemia with combined biallelic CEBPA mutations and downstream events affecting the ATM, FLT3 and CDX2 genes. Br J Haematol 2010; 150: 382–385.
Horwitz M, Goode EL, Jarvik GP : Anticipation in familial leukemia. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 59: 990–998.
Grossmann V, Kohlmann A, Klein HU et al: Targeted next-generation sequencing detects point mutations, insertions, deletions and balanced chromosomal rearrangements as well as identifies novel leukemia-specific fusion genes in a single procedure. Leukemia 2011; 25: 671–680.
Liu W, Yu ZC, Cao WF, Ding F, Liu ZH : Functional studies of a novel oncogene TGM3 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: 3929–3932.
Palumbo JS, Barney KA, Blevins EA et al: Factor XIII transglutaminase supports hematogenous tumor cell metastasis through a mechanism dependent on natural killer cell function. J Thromb Haemost 2008; 6: 812–819.
Davies PJ, Murtaugh MP, Moore WT Jr, Johnson GS, Lucas D : Retinoic acid-induced expression of tissue transglutaminase in human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Biol Chem 1985; 260: 5166–5174.
Suedhoff T, Birckbichler PJ, Lee KN, Conway E, Patterson MK Jr : Differential expression of transglutaminase in human erythroleukemia cells in response to retinoic acid. Cancer Res 1990; 50: 7830–7834.
Mehta K, Lopez-Berestein G : Expression of tissue transglutaminase in cultured monocytic leukemia (THP-1) cells during differentiation. Cancer Res 1986; 46: 1388–1394.
Singh US, Kunar MT, Kao YL, Baker KM : Role of transglutaminase II in retinoic acid-induced activation of RhoA-associated kinase-2. EMBO J 2001; 20: 2413–2423.
Lentini A, Provenzano B, Tabolacci C, Beninati S : Protein-polyamine conjugates by transglutaminase 2 as potential markers for antineoplastic screening of natural compounds. Amino Acids 2009; 36: 701–708.
Savitsky K, Bar-Shira A, Gilad S et al: A single ataxia telangiectasia gene with a product similar to PI-3 kinase. Science 1995; 268: 1749–1753.
Tsangaris E, Adams SL, Yoon G et al: Ataxia and pancytopenia caused by a mutation in TINF2. Hum Genet 2008; 124: 507–513.
Acknowledgements
We thank all of the family members and volunteers for their participation in this study. We further thank Dr Jiucun Wang and Dr Qiang Huang (School of Life Sciences, Fudan University) for their technology support. Thanks are also due to Dr Zuwei Qian of the Affymetrix Company for offering 8 sets of the 500K SNP array. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270609, 30770909) and the Major Science and Technology Project of Fujian Province (2003F003, 2012Y4012) and Fujian Medical University (09ZD008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Ll., Huang, Ym., Wang, M. et al. Positional cloning and next-generation sequencing identified a TGM6 mutation in a large Chinese pedigree with acute myeloid leukaemia. Eur J Hum Genet 23, 218–223 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.67
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.67
This article is cited by
-
The role of gene variants in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders as revealed by next generation sequencing studies: a review
Translational Neurodegeneration (2017)
-
Familial Leukemias
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2015)