Abstract
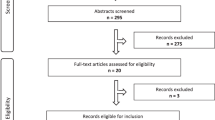
Genetic screening and health-care guidelines recommend that programmes should facilitate informed choice. It is therefore important that accurate measures of informed choice are available to evaluate such programmes. This review synthesises and appraises measures used to evaluate informed choice in population-based genetic screening programmes for reproductive risk. Databases were searched for studies offering genetic screening for the purpose of establishing reproductive risk to an adult population sample, in which aspects of informed choice were measured. Studies were included if, at a minimum, measures of uptake of screening and knowledge were used. Searches identified 1462 citations and 76 studies were reviewed in full text; 34 studies met the inclusion criteria. Over 20 different measures of informed choice were used. Many measures lacked adequate validity and reliability data. This systematic review will inform future evaluation of informed choice in population genetic screening programmes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Khoury MJ, McCabe LL, McCabe ERB : Genomic medicine - Population screening in the age of genomic medicine. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 50–58.
Godard B, ten Kate L, Evers-Kiebooms G, Ayme S : Population genetic screening programmes: principles, techniques, practices, and policies. Eur J Hum Genet 2003; 11: S49–S87.
World Health Organisation: Proposed International Guidelines on Ethical Issues in Medical Genetics and Genetic Services. Geneva, 1998.
Brehaut JC, O'Connor AM, Wood TJ et al: Validation of a decision regret scale. Med Decis Making 2003; 23: 281–292.
Wertz D, Fletcher J, Berg K, Boulyjenkov V : Guidelines on ethical issues in medical genetics and the provision of genetics services, Hereditary Diseases Program, Division of Noncommunicable Diseases Geneva: World Health Organisation, 1995.
Kohut RJ, Dewey D, Love EJ : Women’s knowledge of prenatal ultrasound and informed choice. J Genet Counsel 2002; 11: 265–276.
Bekker H, Thornton JG, Airey CM et al: Informed decision making: an annotated bibliography and systematic review. Health Technol Assess 1999; 3: 1–156.
Briss P, Rimer B, Reilley B et al: Promoting informed decisions about cancer screening in communities and healthcare systems. Am J Prev Med 2004; 26: 67–80.
Rimer BK, Briss PA, Zeller PK, Chan ECY, Woolf SH : Informed decision making: what is its role in cancer screening? Cancer 2004; 101: 1214–1228.
O'Connor AM : Validation of a decisional conflict scale. Med Decis Making 1995; 15: 25–30.
van den Berg M, Timmermans DRM, ten Kate LP, van Vugt JMG, van der Wal G : Informed decision making in the context of prenatal screening. Patient Educ Couns 2006; 63: 110–117.
Marteau TM, Dormandy E, Michie S : A measure of informed choice. Health Expect 2001; 4: 99–108.
van den Berg M, Timmermans DRM, Ten Kate LP, van Vugt JMG, van der Wal G : Are pregnant women making informed choices about prenatal screening? Genet Med 2005; 7: 332–338.
Jepson RG, Hewison J, Thompson AGH, Weller D : How should we measure informed choice? The case of cancer screening. J Med Ethics 2005; 31: 192–196.
Irwig L, McCaffery K, Salkeld G, Bossuyt P : Informed choice for screening: implications for evaluation. Br Med J 2006; 332: 1148–1150.
Mullen PD, Allen JD, Glanz K et al: Measures used in studies of informed decision making about cancer screening: a systematic review. Ann Behav Med 2006; 32: 188–201.
Foundation for Genetics and Population Health. Glossary of genetics terminology. 2012 (cited 08/09/2013); URL http://www.phgfoundation.org/pages/resources/glossary.htm.
Rostant K, Steed L, O'Leary P : Survey of the knowledge, attitudes and experiences of Western Australian women in relation to prenatal screening and diagnostic procedures. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2003; 43: 134–138.
De Vigan C, Vodovar V, Goujard J, Garel M, Vayssière C, Goffinet F : Mothers’ knowledge of screening for trisomy 21 in 1999: a survey in Paris maternity units. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2002; 104: 14–20.
Dahl K, Hvidman L, Jørgensen FS et al: First-trimester Down syndrome screening: pregnant women’s knowledge. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 38: 145–151.
Glazier R, Goel V, Holzapfel S, Summers A, Pugh P, Yeung M : Written patient information about triple-marker screening: a randomized, controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 1997; 90: 769–774.
Goel V, Glazier R, Holzapfel S, Pugh P, Summers A : Evaluating patient’s knowledge of maternal serum screening. Prenat Diagn 1996; 16: 425–430.
Kaiser AS, Ferris LE, Pastuszak AL et al: The effects of prenatal group genetic counselling on knowledge, anxiety and decisional conflict: issues for nuchal translucency screening. J Obstet Gynaecol 2002; 22: 246–255.
Smith DK, Shaw RW, Marteau TM : Informed consent to undergo serum screening for Down’s syndrome: the gap between policy and practice. Br Med J 1994; 309: 776.
Tschudin S, Huang D, Mor-Gultekin H, Alder J, Bitzer J, Tercanli S : Prenatal counseling-implications of the cultural background of pregnant women on information processing, emotional response and acceptance. Eur J Ultrasound 2011; 32 (Suppl 2): E100–E107.
Brown K, Dormandy E, Reid E, Gulliford M, Marteau T : Impact on informed choice of offering antenatal sickle cell and thalassaemia screening in primary care: a randomized trial. J Med Screen 2011; 18: 65–75.
Dormandy E, Bryan S, Gulliford MC et al: Antenatal screening for haemoglobinopathies in primary care: a cohort study and cluster randomised trial to inform a simulation model. The Screening for Haemoglobinopathies in First Trimester (SHIFT) trial. Health Technol Assess 2010; 14: 1–160.
Kuppermann M, Norton ME, Gates E et al: Computerized prenatal genetic testing decision-assisting tool: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2009; 113: 53–63.
Michie S, Smith D, McClennan A, Marteau TM : Patient decision making: an evaluation of two different methods of presenting information about a screening test. Br J Health Psychol 1997; 2: 317–326.
Miedzybrodzka ZH, Hall MH, Mollison J et al: Antenatal screening for carriers of cystic fibrosis: randomised trial of stepwise v couple screening. Br Med J 1995; 310: 353–357.
Nagle C, Gunn J, Bell R et al: Use of a decision aid for prenatal testing of fetal abnormalities to improve women’s informed decision making: a cluster randomised controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2008; 115: 339–347.
O'Cathain A, Walters SJ, Nicholl JP, Thomas KJ, Kirkham M : Use of evidence based leaflets to promote informed choice in maternity care: randomised controlled trial in everyday practice. Br Med J 2002; 324: 643–646.
Graham W, Smith P, Kamal A, Fitzmaurice A, Smith N, Hamilton N : Randomised controlled trial comparing effectiveness of touch screen system with leaflet for providing women with information on prenatal tests. Br Med J 2000; 320: 155–160.
Hewison J, Cuckle H, Baillie C et al: Use of videotapes for viewing at home to inform choice in Down syndrome screening: a randomised controlled trial. Prenat Diagn 2001; 21: 146–149.
Dormandy E, Michie S, Hooper R, Marteau TM : Informed choice in antenatal Down syndrome screening: a cluster-randomised trial of combined versus separate visit testing. Patient Educ Couns 2006; 61: 56–64.
Ames AG, Jaques A, Ukoumunne OC et al: Development of a fragile X syndrome (FXS) knowledge scale: towards a modified multidimensional measure of informed choice for FXS population carrier screening. Health Expect 2012, e-pub ahead of print 15 October 2012; doi:10.1111/hex.12009.
Chilaka VN, Konje JC, Stewart CR, Narayan H, Taylor DJ : Knowledge of Down syndrome in pregnant women from different ethnic groups. Prenat Diagn 2001; 21: 159–164.
Dahl K, Hvidman L, Jorgensen FS, Kesmodel US : Knowledge of prenatal screening and psychological management of test decisions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 38: 152–157.
Dormandy E, Hooper R, Michie S, Marteau T : Informed choice to undergo prenatal screening: a comparison of two hospitals conducting testing either as part of a routine visit or requiring a separate visit. J Med Screen 2002; 9: 109–114.
Dormandy E, Michie S, Hooper R, Marteau TM : Low uptake of prenatal screening for Down syndrome in minority ethnic groups and socially deprived groups: a reflection of women’s attitudes or a failure to facilitate informed choices? Int J Epidemiol 2005; 34: 346–352.
Dormandy E, Tsui EYL, Marteau TM : Development of a measure of informed choice suitable for use in low literacy populations. Patient Educ Couns 2007; 66: 278–295.
Farrell RM, Nutter B, Agatisa PK : Meeting patients’ education and decision-making needs for first trimester prenatal aneuploidy screening. Prenat Diagn 2011; 31: 1222–1228.
Favre R, Moutel G, Duchange N et al: What about informed consent in first-trimester ultrasound screening for Down syndrome? Fetal Diagn Ther 2008; 23: 173–184.
Fransen MP, Essink-Bot ML, Vogel I, Mackenbach JP, Steegers EAP, Wildschut HIJ : Ethnic differences in informed decision-making about prenatal screening for Down’s syndrome. J Epidemiol Community Health 2010; 64: 262–268.
Gourounti K, Sandal J : The validation and translation of Multidimensional Measure of Informed Choice in Greek. Midwifery 2011; 27: 170–173.
Gourounti K, Sandall J : Do pregnant women in Greece make informed choices about antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome? A questionnaire survey. Midwifery 2008; 24: 153–162.
Hwa HL, Huang LH, Hsieh FJ, Chow SN : Informed consent for antenatal serum screening for Down syndrome. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2010; 49: 50–56.
Jaques AM, Halliday JL, Bell RJ : Do women know that prenatal testing detects fetuses with Down syndrome? J Obstet Gynaecol 2004; 24: 647–651.
Jaques AM, Sheffield LJ, Halliday JL : Informed choice in women attending private clinics to undergo first-trimester screening for Down syndrome. Prenat Diagn 2005; 25: 656–664.
Metcalfe S, Jacques A, Archibald A et al: A model for offering carrier screening for fragile X syndrome to nonpregnant women: results from a pilot study. Genet Med 2008; 10: 525–535.
Michie S, Smith D, Marteau TM : Prenatal tests: how are women deciding? Prenat Diagn 1999; 19: 743–748.
Rowe HJ, Fisher JRW, Quinlivan JA : Are pregnant Australian women well informed about prenatal genetic screening? A systematic investigation using the Multidimensional Measure of Informed Choice. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2006; 46: 433–439.
Stefansdottir V, Skirton H, Jonasson K, Hardardottir H, Jonsson JJ : Effects of knowledge, education, and experience on acceptance of first trimester screening for chromosomal anomalies. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2010; 89: 931–938.
Watson EK, Mayall E, Chapple J et al: Screening for carriers of cystic fibrosis through primary health care services. Br Med J 1991; 303: 504–507.
Wynter KH, Rowe HJ, Fisher JR, Lee M, Quinlivan JA : Are adolescents’ decisions about prenatal screening for Down syndrome informed? A controlled, prospective study. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2011; 24: 29–34.
Kuppermann M, Learman LA, Gates E et al: Beyond race or ethnicity and socioeconomic status: predictors of prenatal testing for Down syndrome. Obstet Gynecol 2006; 107: 1087–1097.
Ajzen I : The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 1991; 50: 179–211.
Green JM, Hewison J, Bekker HL, Bryant LD, Cuckle HS : Psychosocial aspects of genetic screening of pregnant women and newborns: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess 2004; 8: 1–128.
Bekker HL, Hewison J, Thornton JG : Understanding why decision aids work: linking process with outcome. Patient Educ Couns 2003; 50: 323–329.
Holmes-Rovner M, Kroll J, Schmitt N et al: Patient satisfaction with health care decisions: the satisfaction with decision scale. Med Decis Making 1996; 16: 58–64.
Tversky A, Kahneman D : Judgment under uncertainty: heuristics and biases. Science 1974; 185: 1124–1131.
Dawson NV, Weiss R : Dichotomizing continuous variables in statistical analysis. Med Decis Making 2012; 32: 225–226.
O'Connor AM, O'Brien-Pallas L : Decisional conflict (specify); in Mcfarland GK, Mcfarlane EA (eds): Nursing Diagnosis & Intervention: Planning for Patient Care. St Louis, MO: Mosby Incorporated, 1993, pp 468–478.
Archibald AD, Jaques AM, Wake S, Collins VR, Cohen J, Metcalfe SA : “It’s something I need to consider”: decisions about carrier screening for fragile X syndrome in a population of non-pregnant women. Am J Med Genet A 2009; 149A: 2731–2738.
Kasparian NA, Wakefield CE, Meiser B : Assessment of psychosocial outcomes in genetic counseling research: an overview of available measurement scales. J Genet Counsel 2007; 16: 693–712.
Bunnik EM, Janssens ACJ, Schermer MH : A tiered-layered-staged model for informed consent in personal genome testing. Eur J Hum Genet 2012; 21: 596–601.
Counsyl. Genetic testing as the first step to a healthy pregnancy. 2013 (cited 21 November 2013); URL www.counsyl.com.
General Medical Council: Consent: patients and doctors making decisions together. General Medical Council: London, 2008.
Deans Z, Newson A : Should non-invasiveness change informed consent procedures for prenatal diagnosis? Health Care Anal 2011; 19: 122–132.
van den Heuvel A, Chitty L, Dormandy E et al: Will the introduction of non-invasive prenatal diagnostic testing erode informed choices? An experimental study of health care professionals. Patient Educ Couns 2010; 78: 24–28.
Michie S, Dormandy E, Marteau TM : The multi-dimensional measure of informed choice: a validation study. Patient Educ Couns 2002; 48: 87–91.
General Medical Council: Consent: patients and doctors making decisions together. General Medical Council: London, 1998.
Marteau TM, Johnston M, Plenicar M, Shaw RW, Slack J : Development of a self-administered questionnaire to measure women's knowledge of prenatal screening and diagnostic tests. J Psychosom Res 1988; 32: 403–408.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee: ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 77: screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Obstet Gynecol 2007; 109: 217–227.
Farrell RM, Dolgin N, Flocke SA, Winbush V, Mercer MB, Simon C : Risk and uncertainty: shifting decision making for aneuploidy screening to the first trimester of pregnancy. Genet Med 2011; 13: 429–436.
Thornton JG, Hewison J, Lilford RJ, Vail A : A randomised trial of three methods of giving information about prenatal testing. Br Med J 1995; 311: 1127–1130.
Priest JH, FitzGerald JM, Haag MM, Streets K, Vanisko M, Johnson JP : Acceptance of amniocentesis by women in the state of Montana (USA) who are screen positive for Down’s syndrome. J Med Screen 1998; 5: 178–182.
Houts PS, Bachrach R, Witmer JT, Tringali CA, Bucher JA, Localio RA : Using pictographs to enhance recall of spoken medical instructions. Patient Educ Couns 1998; 35: 83–88.
Houts PS, Witmer JT, Egeth HE, Loscalzo MJ, Zabora JR : Using pictographs to enhance recall of spoken medical instructions II. Patient Educ Couns 2001; 43: 231–242.
US National Cancer Institute. Simplification of Informed Consent Documents. 2006 URL http://www.nci.nih.gov/clinicaltrials/understanding/simplification-of-informed-consent-docs.
Acknowledgements
We thank Pho Chua, librarian at the Royal Children’s Hospital, for her assistance. We acknowledge the funding enabling this research from the Murdoch Childrens Research Institute, Australian Postgraduate Award, and the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ames, A., Metcalfe, S., Archibald, A. et al. Measuring informed choice in population-based reproductive genetic screening: a systematic review. Eur J Hum Genet 23, 8–21 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.89
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.89
This article is cited by
-
Educational tools support informed decision-making for genetic carrier screening in a heterogenic Israeli population
Journal of Community Genetics (2023)
-
Couples’ experiences with expanded carrier screening: evaluation of a university hospital screening offer
European Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
Current attitudes and preconceptions towards expanded carrier screening in the Eastern Chinese reproductive-aged population
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2021)
-
Experiences of a High‐Risk Population with Prenatal Hemoglobinopathy Carrier Screening in a Primary Care Setting: a Qualitative Study
Journal of Genetic Counseling (2018)
-
The effect of a decision aid on informed decision-making in the era of non-invasive prenatal testing: a randomised controlled trial
European Journal of Human Genetics (2016)