Abstract
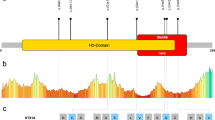
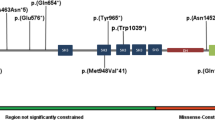
AIMP1/p43 is a multifunctional non-catalytic component of the multisynthetase complex. The complex consists of nine catalytic and three non-catalytic proteins, which catalyze the ligation of amino acids to their cognate tRNA isoacceptors for use in protein translation. To date, two allelic variants in the AIMP1 gene have been reported as the underlying cause of autosomal recessive primary neurodegenerative disorder. Here, we present two consanguineous families from Pakistan and Iran, presenting with moderate to severe intellectual disability, global developmental delay, and speech impairment without neurodegeneration. By the combination of homozygosity mapping and next generation sequencing, we identified two homozygous missense variants, p.(Gly299Arg) and p.(Val176Gly), in the gene AIMP1 that co-segregated with the phenotype in the respective families. Molecular modeling of the variants revealed deleterious effects on the protein structure that are predicted to result in reduced AIMP1 function. Our findings indicate that the clinical spectrum for AIMP1 defects is broader than witnessed so far.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Quevillon S, Agou F, Robinson JC, Mirande M : The p43 component of the mammalian multi-synthetase complex is likely to be the precursor of the endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II cytokine. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 32573–32579.
Quevillon S, Mirande M : The p18 component of the multisynthetase complex shares a protein motif with the beta and gamma subunits of eukaryotic elongation factor 1. FEBS Lett 1996; 395: 63–67.
Quevillon S, Robinson JC, Berthonneau E, Siatecka M, Mirande M : Macromolecular assemblage of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: identification of protein-protein interactions and characterization of a core protein. J Mol Biol 1999; 285: 183–195.
Lee SW, Cho BH, Park SG, Kim S : Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complexes: beyond translation. J Cell Sci 2004; 117: 3725–3734.
Zhu X, Liu Y, Yin Y et al: MSC p43 required for axonal development in motor neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 15944–15949.
Feinstein M, Markus B, Noyman I et al: Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease caused by AIMP1/p43 homozygous mutation. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 87: 820–828.
Armstrong L, Biancheri R, Shyr C et al: AIMP1 deficiency presents as a cortical neurodegenerative disease with infantile onset. Neurogenetics 2014; 15: 157–159.
Hamdan FF, Gauthier J, Spiegelman D et al: Mutations in SYNGAP1 in autosomal nonsyndromic mental retardation. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 599–605.
Chelly J, Khelfaoui M, Francis F, Cherif B, Bienvenu T : Genetics and pathophysiology of mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 701–713.
Garshasbi M, Hadavi V, Habibi H et al: A defect in the TUSC3 gene is associated with autosomal recessive mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 1158–1164.
Kuss AW, Garshasbi M, Kahrizi K et al: Autosomal recessive mental retardation: homozygosity mapping identifies 27 single linkage intervals, at least 14 novel loci and several mutation hotspots. Hum genet 2010; 129: 141–148.
Leonard H, Wen X : The epidemiology of mental retardation: challenges and opportunities in the new millennium. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2002; 8: 117–134.
Musante L, Ropers HH : Genetics of recessive cognitive disorders. Trends Genet 2014; 30: 32–39.
Iqbal Z, Neveling K, Razzaq A et al: Targeted next generation sequencing reveals a novel intragenic deletion of the TPO gene in a family with intellectual disability. Arch Med Res 2012; 43: 312–316.
Iqbal Z, van Bokhoven H : Identifying genes responsible for intellectual disability in consanguineous families. Hum Hered 2014; 77: 150–160.
Bittles A : Consanguinity and its relevance to clinical genetics. Clin Genet 2001; 60: 89–98.
Al-Ansari A : Etiology of mild mental retardation among Bahraini children: a community-based case control study. Ment Retard 1993; 31: 140–143.
Bundey S, Alam H, Kaur A, Mir S, Lancashire R : Why do UK born Pakistani babies have high perinatal and neonatal mortality rates? Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 1991; 5: 101–114.
Grimberg J, Nawoschik S, Belluscio L, McKee R, Turck A, Eisenberg A : A simple and efficient non-organic procedure for the isolation of genomic DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res 1989; 17: 8390.
Lindner TH, Hoffmann K : easyLINKAGE: a PERL script for easy and automated two-/multi-point linkage analyses. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 405–407.
Broman KW, Murray JC, Sheffield VC, White RL, Weber JL : Comprehensive human genetic maps: individual and sex-specific variation in recombination. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 63: 861–869.
Vissers LE, de Ligt J, Gilissen C et al: A de novo paradigm for mental retardation. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 1109–1112.
Najmabadi H, Hu H, Garshasbi M et al: Deep sequencing reveals 50 novel genes for recessive cognitive disorders. Nature 2011; 478: 57–63.
Reuter MS, Musante L, Hu H et al: NDST1 missense mutations in autosomal recessive intellectual disability. Am J Med Genet A 2014; 164A: 2753–2763.
Hu H, Wienker TF, Musante L et al: Integrated sequence analysis pipeline provides one-stop solution for identifying disease-causing mutations. Hum Mutat 2014; 35: 1427–1435.
Rozen S, Skaletsky H : Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 2000; 132: 365–386.
Venselaar H, Te Beek TA, Kuipers RK, Hekkelman ML, Vriend G : Protein structure analysis of mutations causing inheritable diseases. An e-Science approach with life scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinformatics 2010; 11: 548.
Biancheri R, Rossi A, Zara F, Filocamo M : AIMP1/p43 mutation and PMLD. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 391, author reply 393-395.
Boespflug-Tanguy O, Aubourg P, Dorboz I et al: Neurodegenerative disorder related to AIMP1/p43 mutation is not a PMLD. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 392–393, author reply 393-395.
Laser-Azogui A, Kornreich M, Malka-Gibor E, Beck R : Neurofilament assembly and function during neuronal development. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2015; 32C: 92–101.
Lepinoux-Chambaud C, Eyer J : Review on intermediate filaments of the nervous system and their pathological alterations. Histochem Cell Biol 2013; 140: 13–22.
Abou Jamra R, Wohlfart S, Zweier M et al: Homozygosity mapping in 64 Syrian consanguineous families with non-specific intellectual disability reveals 11 novel loci and high heterogeneity. Eur J Hum Genet 2011; 19: 1161–1166.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the members of the families PKMR60 and M105 who voluntarily participated in this study. We thank Bettina Lipkowitz, Melanie Bienek, Sabine Otto and Vanessa Suckow for expert technical assistance. This research has received funding from the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program under grant agreement number 241995 (project GENCODYS). H-HR was funded by the Max-Planck Society, and AR, MYZ and ZI were supported by the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (HEC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, Z., Püttmann, L., Musante, L. et al. Missense variants in AIMP1 gene are implicated in autosomal recessive intellectual disability without neurodegeneration. Eur J Hum Genet 24, 392–399 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.148
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.148
This article is cited by
-
The recurrent missense mutation p.(Arg367Trp) in YARS1 causes a distinct neurodevelopmental phenotype
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Roles of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multi-functional proteins in physiology and cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases as therapeutic targets
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2019)
-
Pathogenic variants in AIMP1 cause pontocerebellar hypoplasia
neurogenetics (2019)