Abstract
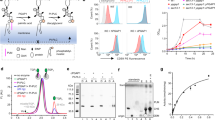
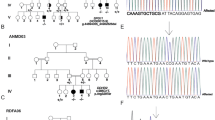
Homozygous variants in PGAP1 (post-GPI attachment to proteins 1) have recently been identified in two families with developmental delay, seizures and/or spasticity. PGAP1 is a member of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis and remodeling pathway and defects in this pathway are a subclass of congenital disorders of glycosylation. Here we performed whole-exome sequencing in an individual with cerebral visual impairment (CVI), intellectual disability (ID), and factor XII deficiency and revealed compound heterozygous variants in PGAP1, c.274_276del (p.(Pro92del)) and c.921_925del (p.(Lys308Asnfs*25)). Subsequently, PGAP1-deficient Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-cell lines were transfected with either mutant or wild-type constructs and their sensitivity to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) treatment was measured. The mutant constructs could not rescue the PGAP1-deficient CHO cell lines resistance to PI-PLC treatment. In addition, lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) of the affected individual showed no sensitivity to PI-PLC treatment, whereas the LCLs of the heterozygous carrier parents were partially resistant. In conclusion, we report novel PGAP1 variants in a boy with CVI and ID and a proven functional loss of PGAP1 and show, to our knowledge, for the first time this genetic association with CVI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Boonstra N, Limburg H, Tijmes N, van Genderen M, Schuil J, van Nispen R : Changes in causes of low vision between 1988 and 2009 in a Dutch population of children. Acta Ophthalmol 2012; 90: 277–286.
Rahi JS, Cable N : Severe visual impairment and blindness in children in the UK. Lancet 2003; 362: 1359–1365.
Dutton GN, Jacobson LK : Cerebral visual impairment in children. Semin Neonatol 2001; 6: 477–485.
Bosch DG, Boonstra FN, Willemsen MA, Cremers FP, de Vries BB : Low vision due to cerebral visual impairment: differentiating between acquired and genetic causes. BMC Ophthalmol 2014; 14: 59.
Bosch DG, Boonstra FN, Reijnders MR, Pfundt R, Cremers FP, de Vries BB : Chromosomal aberrations in cerebral visual impairment. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2014; 18: 677–684.
Bosch DG, Boonstra FN, Gonzaga-Jauregui C et al: NR2F1 mutations cause optic atrophy with intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet 2014; 94: 303–309.
Jensen H, Kjaergaard S, Klie F, Moller HU : Ophthalmic manifestations of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a. Ophthalmic Genet 2003; 24: 81–88.
Morava E, Wevers RA, Cantagrel V et al: A novel cerebello-ocular syndrome with abnormal glycosylation due to abnormalities in dolichol metabolism. Brain 2010; 133: 3210–3220.
Enns GM, Shashi V, Bainbridge M et al: Mutations in NGLY1 cause an inherited disorder of the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation pathway. Genet Med 2014; 16: 751–758.
Jaeken J : Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): it's (nearly) all in it!. J Inherit Metab Dis 2011; 34: 853–858.
Fujita M, Kinoshita T : GPI-anchor remodeling: potential functions of GPI-anchors in intracellular trafficking and membrane dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012; 1821: 1050–1058.
Tiede A, Bastisch I, Schubert J, Orlean P, Schmidt RE : Biosynthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositols in mammals and unicellular microbes. Biol Chem 1999; 380: 503–523.
McConville MJ, Menon AK : Recent developments in the cell biology and biochemistry of glycosylphosphatidylinositol lipids (review). Mol Membr Biol 2000; 17: 1–16.
Tanaka S, Maeda Y, Tashima Y, Kinoshita T : Inositol deacylation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins is mediated by mammalian PGAP1 and yeast Bst1p. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 14256–14263.
Murakami Y, Tawamie H, Maeda Y et al: Null mutation in PGAP1 impairing Gpi-anchor maturation in patients with intellectual disability and encephalopathy. PLoS Genet 2014; 10: e1004320.
Johnston JJ, Gropman AL, Sapp JC et al: The phenotype of a germline mutation in PIGA: the gene somatically mutated in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hum Genet 2012; 90: 295–300.
Ng BG, Hackmann K, Jones MA et al: Mutations in the glycosylphosphatidylinositol gene PIGL cause CHIME syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2012; 90: 685–688.
Maydan G, Noyman I, Har-Zahav A et al: Multiple congenital anomalies-hypotonia-seizures syndrome is caused by a mutation in PIGN. J Med Genet 2011; 48: 383–389.
Kvarnung M, Nilsson D, Lindstrand A et al: A novel intellectual disability syndrome caused by GPI anchor deficiency due to homozygous mutations in PIGT. J Med Genet 2013; 50: 521–528.
Krawitz PM, Schweiger MR, Rodelsperger C et al: Identity-by-descent filtering of exome sequence data identifies PIGV mutations in hyperphosphatasia mental retardation syndrome. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 827–829.
Krawitz PM, Murakami Y, Hecht J et al: Mutations in PIGO, a member of the GPI-anchor-synthesis pathway, cause hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2012; 91: 146–151.
Krawitz PM, Murakami Y, Riess A et al: PGAP2 mutations, affecting the GPI-anchor-synthesis pathway, cause hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 92: 584–589.
Hansen L, Tawamie H, Murakami Y et al: Hypomorphic mutations in PGAP2, encoding a GPI-anchor-remodeling protein, cause autosomal-recessive intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 92: 575–583.
Howard MF, Murakami Y, Pagnamenta AT et al: Mutations in PGAP3 impair GPI-anchor maturation, causing a subtype of hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2014; 94: 278–287.
Chiyonobu T, Inoue N, Morimoto M, Kinoshita T, Murakami Y : Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor deficiency caused by mutations in PIGW is associated with West syndrome and hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome. J Med Genet 2014; 51: 203–207.
Martin HC, Kim GE, Pagnamenta AT et al: Clinical whole-genome sequencing in severe early-onset epilepsy reveals new genes and improves molecular diagnosis. Hum Mol Genet 2014; 23: 3200–3211.
Swoboda KJ, Margraf RL, Carey JC et al: A novel germline PIGA mutation in Ferro-Cerebro-Cutaneous syndrome: a neurodegenerative X-linked epileptic encephalopathy with systemic iron-overload. Am J Med Genet A 2014; 164A: 17–28.
Nakashima M, Kashii H, Murakami Y et al: Novel compound heterozygous PIGT mutations caused multiple congenital anomalies-hypotonia-seizures syndrome 3. Neurogenetics 2014; 15: 193–200.
Novarino G, Fenstermaker AG, Zaki MS et al: Exome sequencing links corticospinal motor neuron disease to common neurodegenerative disorders. Science 2014; 343: 506–511.
Lupski JR, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Yang Y et al: Exome sequencing resolves apparent incidental findings and reveals further complexity of SH3TC2 variant alleles causing Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. Genome Med 2013; 5: 57.
de Ligt J, Willemsen MH, van Bon BW et al: Diagnostic exome sequencing in persons with severe intellectual disability. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1921–1929.
Roberts WL, Myher JJ, Kuksis A, Low MG, Rosenberry TL : Lipid analysis of the glycoinositol phospholipid membrane anchor of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Palmitoylation of inositol results in resistance to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Biol Chem 1988; 263: 18766–18775.
Zoltewicz JS, Plummer NW, Lin MI, Peterson AS : oto is a homeotic locus with a role in anteroposterior development that is partially redundant with Lim1. Development 1999; 126: 5085–5095.
Ueda Y, Yamaguchi R, Ikawa M et al: PGAP1 knock-out mice show otocephaly and male infertility. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 30373–30380.
Zoltewicz JS, Ashique AM, Choe Y et al: Wnt signaling is regulated by endoplasmic reticulum retention. PloS One 2009; 4: e6191.
McKean DM, Niswander L : Defects in GPI biosynthesis perturb Cripto signaling during forebrain development in two new mouse models of holoprosencephaly. Biol Open 2012; 1: 874–883.
Sparks SE, Krasnewich DM et al: Congenital disorders of n-linked glycosylation pathway overview; in Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH (eds): GeneReviews. Seattle, WA, USA: University of Washington, 1993.
Schloesser M, Hofferbert S, Bartz U, Lutze G, Lammle B, Engel W : The novel acceptor splice site mutation 11396(G—>A) in the factor XII gene causes a truncated transcript in cross-reacting material negative patients. Hum Mol Genet 1995; 4: 1235–1237.
Schloesser M, Zeerleder S, Lutze G et al: Mutations in the human factor XII gene. Blood 1997; 90: 3967–3977.
Tashima Y, Taguchi R, Murata C, Ashida H, Kinoshita T, Maeda Y : PGAP2 is essential for correct processing and stable expression of GPI-anchored proteins. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 1410–1420.
Murakami Y, Kanzawa N, Saito K et al: Mechanism for release of alkaline phosphatase caused by glycosylphosphatidylinositol deficiency in patients with hyperphosphatasia mental retardation syndrome. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 6318–6325.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the individual involved and his family for their support and cooperation. We thank the technical ophthalmological assistant P. Rison for his assistance during the ophthalmological examination. This work has been supported by grants from Stichting ODAS (to FNB and FPMC), Vereniging Bartiméus-Sonneheerdt (5781251 to FNB and FPMC), and the Dutch Organization for Health Research and Development (917-86-319 and 912-12-109 to BBAdV). In addition, this study was accomplished in part through the Center for Mendelian Genomics research effort funded by the National Institutes of Health and supported by the National Human Genome Research Institute grant U54HG006542 to the Baylor-Hopkins Center for Mendelian Genomics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosch, D., Boonstra, F., Kinoshita, T. et al. Cerebral visual impairment and intellectual disability caused by PGAP1 variants. Eur J Hum Genet 23, 1689–1693 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.42
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.42
This article is cited by
-
Compound heterozygous variants in PGAP1 causing severe psychomotor retardation, brain atrophy, recurrent apneas and delayed myelination: a case report and literature review
BMC Neurology (2016)
-
Molecular subtyping and improved treatment of neurodevelopmental disease
Genome Medicine (2016)
-
Novel genetic causes for cerebral visual impairment
European Journal of Human Genetics (2016)