Abstract
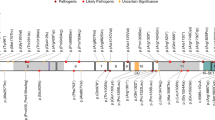
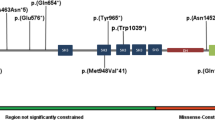
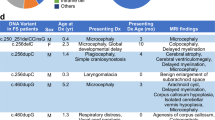
FOXP1 (forkhead box protein P1) is a transcription factor involved in the development of several tissues, including the brain. An emerging phenotype of patients with protein-disrupting FOXP1 variants includes global developmental delay, intellectual disability and mild to severe speech/language deficits. We report on a female child with a history of severe hypotonia, autism spectrum disorder and mild intellectual disability with severe speech/language impairment. Clinical exome sequencing identified a heterozygous de novo FOXP1 variant c.1267_1268delGT (p.V423Hfs*37). Functional analyses using cellular models show that the variant disrupts multiple aspects of FOXP1 activity, including subcellular localization and transcriptional repression properties. Our findings highlight the importance of performing functional characterization to help uncover the biological significance of variants identified by genomics approaches, thereby providing insight into pathways underlying complex neurodevelopmental disorders. Moreover, our data support the hypothesis that de novo variants represent significant causal factors in severe sporadic disorders and extend the phenotype seen in individuals with FOXP1 haploinsufficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Shu W, Yang H, Zhang L, Lu MM, Morrisey EE : Characterization of a new subfamily of winged-helix/forkhead (Fox) genes that are expressed in the lung and act as transcriptional repressors. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 27488–27497.
Shu W, Lu MM, Zhang Y, Tucker PW, Zhou D, Morrisey EE : Foxp2 and Foxp1 cooperatively regulate lung and esophagus development. Development 2007; 134: 1991–2000.
Wang B, Weidenfeld J, Lu MM et al: Foxp1 regulates cardiac outflow tract, endocardial cushion morphogenesis and myocyte proliferation and maturation. Development 2004; 131: 4477–4487.
Rousso DL, Gaber ZB, Wellik D, Morrisey EE, Novitch BG : Coordinated actions of the forkhead protein Foxp1 and Hox proteins in the columnar organization of spinal motor neurons. Neuron 2008; 59: 226–240.
Dasen JS, De Camilli A, Wang B, Tucker PW, Jessell TM : Hox repertoires for motor neuron diversity and connectivity gated by a single accessory factor, FoxP1. Cell 2008; 134: 304–316.
Bacon C, Schneider M, Le Magueresse C et al: Brain-specific Foxp1 deletion impairs neuronal development and causes autistic-like behaviour. Mol Psychiatry 2015; 20:632–639.
Le Fevre AK, Taylor S, Malek NH et al: FOXP1 mutations cause intellectual disability and a recognizable phenotype. Am J Med Genet A 2013; 161A: 3166–3175.
Bacon C, Rappold GA : The distinct and overlapping phenotypic spectra of FOXP1 and FOXP2 in cognitive disorders. Hum Genet 2012; 131: 1687–1698.
Pariani MJ, Spencer A, Graham JM Jr., Rimoin DL : A 785kb deletion of 3p14.1p13, including the FOXP1 gene, associated with speech delay, contractures, hypertonia and blepharophimosis. Eur J Med Genet 2009; 52: 123–127.
Carr CW, Moreno-De-Luca D, Parker C et al: Chiari I malformation, delayed gross motor skills, severe speech delay, and epileptiform discharges in a child with FOXP1 haploinsufficiency. Eur J Hum Genet 2010; 18: 1216–1220.
Horn D, Kapeller J, Rivera-Brugues N et al: Identification of FOXP1 deletions in three unrelated patients with mental retardation and significant speech and language deficits. Hum Mutat 2010; 31: E1851–E1860.
Palumbo O, D'Agruma L, Minenna AF et al: 3p14.1 de novo microdeletion involving the FOXP1 gene in an adult patient with autism, severe speech delay and deficit of motor coordination. Gene 2013; 516: 107–113.
Talkowski ME, Rosenfeld JA, Blumenthal I et al: Sequencing chromosomal abnormalities reveals neurodevelopmental loci that confer risk across diagnostic boundaries. Cell 2012; 149: 525–537.
Hamdan FF, Daoud H, Rochefort D et al: De novo mutations in FOXP1 in cases with intellectual disability, autism, and language impairment. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 87: 671–678.
Srivastava S, Cohen JS, Vernon H et al: Clinical whole exome sequencing in child neurology practice. Ann Neurol 2014; 76: 473–483.
O'Roak BJ, Deriziotis P, Lee C et al: Exome sequencing in sporadic autism spectrum disorders identifies severe de novo mutations. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 585–589.
Lee H, Deignan JL, Dorrani N et al: Clinical exome sequencing for genetic identification of rare mendelian disorders. JAMA 2014; 312: 1880–1887.
Devanna P, Middelbeek J, Vernes SC : FOXP2 drives neuronal differentiation by interacting with retinoic acid signaling pathways. Front Cell Neurosci 2014; 8: 305.
Deriziotis P, O’Roak BJ, Graham SA et al: De novo TBR1 mutations in sporadic autism disrupt protein functions. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 4954.
Deriziotis P, Graham SA, Estruch SB, Fisher SE : Investigating protein-protein interactions in live cells using Bioluminescence Resonance. J Vis Exp 2014, e-pub ahead of print 26 May 2014; doi:10.3791/51438.
Buxbaum JD, Daly MJ, Devlin B, Lehner T, Roeder K, State MW : The autism sequencing consortium: large-scale, high-throughput sequencing in autism spectrum disorders. Neuron 2012; 76: 1052–1056.
Li S, Weidenfeld J, Morrisey EE : Transcriptional and DNA binding activity of the Foxp1/2/4 family is modulated by heterotypic and homotypic protein interactions. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 809–822.
Ferland RJ, Cherry TJ, Preware PO, Morrisey EE, Walsh CA : Characterization of Foxp2 and Foxp1 mRNA and protein in the developing and mature brain. J Comp Neurol 2003; 460: 266–279.
Teramitsu I, Kudo LC, London SE, Geschwind DH, White SA : Parallel FoxP1 and FoxP2 expression in songbird and human brain predicts functional interaction. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 3152–3163.
Vernes SC, Newbury DF, Abrahams BS et al: A functional genetic link between distinct developmental language disorders. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 2337–2345.
MacDermot KD, Bonora E, Sykes N et al: Identification of FOXP2 truncation as a novel cause of developmental speech and language deficits. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 1074–1080.
Lai CS, Fisher SE, Hurst JA, Vargha-Khadem F, Monaco AP : A forkhead-domain gene is mutated in a severe speech and language disorder. Nature 2001; 413: 519–523.
Watkins KE, Dronkers NF, Vargha-Khadem F : Behavioural analysis of an inherited speech and language disorder: comparison with acquired aphasia. Brain 2002; 125: 452–464.
Fisher SE, Scharff C : FOXP2 as a molecular window into speech and language. Trends Genet 2009; 25: 166–177.
Vernes SC, MacDermot KD, Monaco AP, Fisher SE : Assessing the impact of FOXP1 mutations on developmental verbal dyspraxia. Eur J Hum Genet 2009; 17: 1354–1358.
Acknowledgements
We thank the family for taking part in the research. This work was supported by the Max Planck Society, the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (P30AG043097) and the NIH diversity supplement (HD036071). We also thank Dr Joshua Deignan, Hane Lee and the UCLA Clinical Genomics Centre for clinical exome sequencing and data interpretation, Dr Pedro Rodenas-Cuadrado and Paolo Devanna for technical advice and Dr Randi J Hagerman and Dr Sarah A Graham for useful discussions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lozano, R., Vino, A., Lozano, C. et al. A de novo FOXP1 variant in a patient with autism, intellectual disability and severe speech and language impairment. Eur J Hum Genet 23, 1702–1707 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.66
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.66
This article is cited by
-
Possible roles of deep cortical neurons and oligodendrocytes in the neural basis of human sociality
Anatomical Science International (2024)
-
FOXP1 syndrome: a review of the literature and practice parameters for medical assessment and monitoring
Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (2021)
-
Speech, language and communication phenotyping in rare genetic syndromes: Commentary on Speech and language deficits are central to SETBP1 haploinsufficiency disorder
European Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
Autism spectrum disorders: autistic phenotypes and complicated mechanisms
World Journal of Pediatrics (2019)
-
A De Novo FOXP1 Truncating Mutation in a Patient Originally Diagnosed as C Syndrome
Scientific Reports (2018)