Abstract
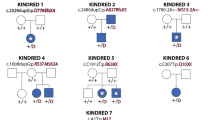
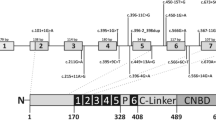
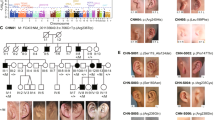
Nager syndrome is a rare preaxial acrofacial dysostosis that is caused by heterozygous loss-of-function variants in SF3B4. This gene encodes for a protein required for the assembly of spliceosomal complexes, being a master gene for splicing regulation. The main clinical features of Nager syndrome include facial-mandibular and preaxial limb malformations, with normal cognitive functioning. Most Nager patients are sporadic, but few familial cases with a highly variable phenotype have been reported. In this work, we report a novel synonymous variant within exon 3 of the SF3B4 gene in a family with three members affected by Nager syndrome. No pathogenic variants have been detected in other 24 genes associated with syndromes characterized by mandibulo-facial anomalies. The pathogenicity of the mutation was demonstrated through a hybrid minigene assay, which confirmed an aberrant splicing with the creation of a cryptic splice site, and showed that this allele is hypomorphic. Our findings emphasize the importance to perform functional analyses to assess the possible consequences of synonymous variants and confirmed that hybrid minigenes represent an effective tool to evaluate the effects of variants on splicing, particularly when RNA is not available.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Chemke J, Mogilner BM, Ben-Itzhak I, Zurkowski L, Ophir D : Autosomal recessive inheritance of Nager acrofacial dysostosis. J Med Genet 1988; 25: 230–232.
Hall BD : Nager acrofacial dysostosis: autosomal dominant inheritance in mild to moderately affected mother and lethally affected phocomelic son. Am J Med Genet 1989; 33: 394–397.
Aylsworth AS, Lin AE, Friedman PA : Nager acrofacial dysostosis: male-to-male transmission in 2 families. Am J Med Genet 1991; 41: 83–88.
Bernier FP, Caluseriu O, Ng S et al :Haploinsufficiency of SF3B4, a component of the pre-mRNA spliceosomal complex, causes Nager syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2012; 90: 925–933.
Petit F, Escande F, Jourdain AS et al :Nager syndrome: confirmation of SF3B4 haploinsufficiency as the major cause. Clin Genet 2014; 86: 246–251.
Czeschik JC, Voigt C, Alanay Y et al :Clinical and mutation data in 12 patients with the clinical diagnosis of Nager syndrome. Hum Genet 2013; 132: 885–898.
Castori M, Bottillo I, D’Angelantonio D et al :A 22-week-old fetus with Nager syndrome and congenital diaphragmatic hernia due to a novel SF3B4 mutation. Mol Syndromol 2014; 5: 241–244.
McPherson E, Zaleski C, Ye Z, Lin S : Rodriguez syndrome with SF3B4 mutation: a severe form of Nager syndrome? Am J Med Genet A 2014; 164A: 1841–1845.
Lund IC, Vestergaard EM, Christensen R, Uldbjerg N, Becher N : Prenatal diagnosis of Nager syndrome in a 12-week-old fetus with a whole gene deletion of SF3B4 by chromosomal microarray. Eur J Med Genet 2016; 59: 48–51.
Waggoner DJ, Ciske DJ, Dowton SB, Watson MS : Deletion of 1q in a patient with acrofacial dysostosis. Am J Med Genet 1999; 82: 301–304.
Forzan M, Salviati L, Pertegato V et al :Is CFTR 621+3A>G a cystic fibrosis causing mutation? J Hum Genet 2010; 55: 23–26.
Giorgi G, Casarin A, Trevisson E et al :Validation of CFTR intronic variants identified during cystic fibrosis population screening by a minigene splicing assay. Clin Chem Lab Med 2015; 53: 1719–1723.
Sharma N, Sosnay PR, Ramalho AS et al :Experimental assessment of splicing variants using expression minigenes and comparison with in silico predictions. Hum Mutat 2014; 35: 1249–1259.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Italian Ministry of Health [GR-2009-1578914 to ET], by University of Padova [CPDA140508/14 to ET] and by a grant from Fondazione Cariparo [to LS].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassina, M., Cerqua, C., Rossi, S. et al. A synonymous splicing mutation in the SF3B4 gene segregates in a family with highly variable Nager syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 25, 371–375 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.176
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.176