Abstract
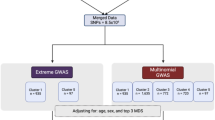
Neuropathic pain-like joint symptoms (NP) are seen in a proportion of individuals diagnosed with osteoarthritis (OA) and post total joint replacement (TJR). In this study, we performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) using NP as defined by the painDETECT questionnaire (score >12 indicating possible NP) in 613 post-TJR participants recruited from Nottinghamshire (UK). The prevalence of possible NP was 17.8%. The top four hits from the GWAS and two other biologically relevant single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were replicated in individuals with OA and post TJR from an independent study in the same area (N=908) and in individuals from the Rotterdam Study (N=212). Three of these SNPs showed effect sizes in the same direction as in the GWAS results in both replication cohorts. The strongest association upon meta-analysis of a recessive model was for the variant allele in rs887797 mapping to the protein kinase C alpha (PRKCA) gene odds ratio (OR)possNP=2.41 (95% CI 1.74–3.34, P=1.29 × 10−7). This SNP has been found to be associated with multiple sclerosis and encodes a functional variant affecting splicing and expression of the PRKCA gene. The PRKCA gene has been associated with long-term potentiation, synaptic plasticity, chronic pain and memory in the literature, making this a biologically relevant finding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hochman JR, Gagliese L, Davis AM, Hawker GA : Neuropathic pain symptoms in a community knee OA cohort. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2011; 19: 647–654.
Wylde V, Hewlett S, Learmonth ID, Dieppe P : Persistent pain after joint replacement: prevalence, sensory qualities, and postoperative determinants. Pain 2011; 152: 566–572.
Buvanendran A, Kroin JS, Della Valle CJ et al: Perioperative oral pregabalin reduces chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Anesth Analg 2010; 110: 199–207.
Haroutiunian S, Nikolajsen L, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS : The neuropathic component in persistent postsurgical pain: a systematic literature review. Pain 2013; 154: 95–102.
Treede R-D, Jensen TS, Campbell J et al: Neuropathic pain redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008; 70: 1630–1635.
Kehlet H, Jensen TS, Woolf CJ : Persistent postsurgical pain: risk factors and prevention. Lancet 2006; 367: 1618–1625.
Valdes AM, Suokas AK, Doherty SA, Jenkins W, Doherty M : History of knee surgery is associated with higher prevalence of neuropathic pain-like symptoms in patients with severe osteoarthritis of the knee. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2013; 43: 588–592.
van Hecke O, Austin SK, Khan RA, Smith BH, Torrance N : Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014; 155: 654–662.
Dualé C, Ouchchane L, Schoeffler P et al: Neuropathic aspects of persistent postsurgical pain: a French multicenter survey with a 6-month prospective follow-up. J Pain 2014; 15: p 24.e1–24.e20.
Graven-Nielsen T, Wodehouse T, Langford RM, Arendt-Nielsen L, Kidd BL : Normalization of widespread hyperesthesia and facilitated spatial summation of deep-tissue pain in knee osteoarthritis patients after knee replacement. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64: 2907–2916.
Novak JC, Lovell JA, Stuesse SL, Cruce WLR, McBurney DL, Crisp T : Aging and neuropathic pain. Brain Res 1999; 833: 308–310.
Momi SK, Fabiane SM, Lachance G, Livshits G, Williams FM : Neuropathic pain as part of chronic widespread pain: environmental and genetic influences. Pain 2015; 156: 2100–2106.
Honkasalo ML, Kaprio J, Winter T et al: Migraine and concomitant symptoms among 8167 adult twin pairs. Headache 1995; 35: 70–78.
Ziegler DK, Hur YM, Bouchard TJ, Hassanein RS, Barter R : Migraine in twins raised together and apart. Headache 1998; 38: 417–422.
Heikkila JK, Koskenvuo M, Heliovaara M et al: Genetic and environmental factors in sciatica. Evidence from a nationwide panel of 9365 adult twin pairs. Ann Med 1989; 21: 393–398.
Larsson B, Bille B, Pedersen NL : Genetic influence in headaches: a Swedish twin study. Headache 1995; 35: 513–519.
Bengtsson B, Thorson J : Back pain: a study of twins. Acta Genet Med Gemellol 1991; 40: 83–90.
Clarke H, Katz J, Flor H et al: Genetics of chronic post-surgical pain: a crucial step toward personal pain medicine. Can J Anesth 2015; 62: 294–303.
Belfer I, Shnol H, Finelli P: Molecular genetics of variability in human pain; in eLS. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2013.
Nissenbaum J, Devor M, Seltzer Z et al: Susceptibility to chronic pain following nerve injury is genetically affected by CACNG2. Genome Res 2010; 20: 1180–1190.
Tsuda M, Kuboyama K, Inoue T, Nagata K, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K : Behavioral phenotypes of mice lacking purinergic P2X4 receptors in acute and chronic pain assays. Mol Pain 2009; 5: 28.
Valdes AM, De Wilde G, Doherty SA et al: The Ile585Val TRPV1 variant is involved in risk of painful knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 1556–1561.
Young EE, Costigan M, Herbert TA, Lariviere WR : Heritability of nociception IV: neuropathic pain assays are genetically distinct across methods of peripheral nerve injury. Pain 2014; 155: 868–880.
Meng W, Deshmukh HA, van Zuydam NR et al: A genome-wide association study suggests an association of Chr8p21.3 (GFRA2) with diabetic neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain 2015; 19: 392–399.
Meng W, Deshmukh HA, Donnelly LA et al: A genome-wide association study provides evidence of sex-specific involvement of Chr1p35.1 (ZSCAN20-TLR12P) and Chr8p23.1 (HMGB1P46) with diabetic neuropathic pain. EBioMedicine 2015; 2: 1386–1393.
Krishna SS, Majumdar I, Grishin NV : Structural classification of zinc fingers: survey and summary. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 532–550.
Anttila V, Stefansson H, Kallela K, Unda Todt U, Terwindt GM, Calafato MS et al: Genome-wide association study of migraine implicates a common susceptibility variant on 8q22.1. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 869–873.
Peters MJ, Broer L, Willemen HLDM et al: Genome-wide association study meta-analysis of chronic widespread pain: evidence for involvement of the 5p15.2 region. Ann Rheum Dis 2013; 72: 427–436.
Kim H, Ramsay E, Lee H, Wahl S, Dionne RA : Genome-wide association study of acute post-surgical pain in humans. Pharmacogenomics 2009; 10: 171–179.
Hofman A, Breteler MB, van Duijn C et al: The Rotterdam Study: objectives and design update. Eur J Epidemiol 2007; 22: 819–829.
Zeggini E, Panoutsopoulou K, Southam L et al: Identification of new susceptibility loci for osteoarthritis (arcOGEN): a genome-wide association study. Lancet 2012; 380: 815–823.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al: PLINK: a toolset for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Huang, da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA : Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 44–57.
Han B, Eskin E : Random-effects model aimed at discovering associations in meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 586–598.
Freynhagen R, Baron R, Gockel U, Tolle TR : painDETECT: a new screening questionnaire to identify neuropathic components in patients with back pain. Curr Med Res Opin 2006; 22: 1911–1920.
Kawasaki Y, Kohno T, Zhuang ZY, Brenner GJ, Wang H, Van Der Meer C et al: Ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, protein kinase A, protein kinase C, and Src contribute to C-fiber-induced ERK activation and cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation in dorsal horn neurons, leading to central sensitization. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 8310–8321.
Price TJ, Inyang KE : Commonalities between pain and memory mechanisms and their meaning for understanding chronic pain. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2015; 131: 409–434.
de Quervain DJF, Kolassa I-T, Ackermann S et al: PKCα is genetically linked to memory capacity in healthy subjects and to risk for posttraumatic stress disorder in genocide survivors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 8746–8751.
MacLeod CA, Donaldson DI : PRKCA polymorphism changes the neural basis of episodic remembering in healthy individuals. PLoS One 2014; 9: e98018.
Welter D, MacArthur J, Morales J et al: The NHGRI GWAS Catalog, a curated resource of SNP-trait associations. Nucleic Acids Research 2014; 42 (Database issue): D1001–D1006.
Olah Z, Karai L, Iadarola MJ : Protein kinase Cα is required for vanilloid receptor 1 activation: evidence for multiple signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 35752–35759.
Paraboschi EM, Rimoldi V, Soldà G et al: Functional variations modulating PRKCA expression and alternative splicing predispose to multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 2014; 23: 6746–6761.
NCBI. FOXL1 forkhead box L1 [Homo sapiens (human)]. Gene 2014. Available at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2300.
Jiang D, Hwang KS, Bordelon Y, Apostolova LG : Plenary paper - cortical atrophy and gene expression in Parkinson's disease with mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 2013; 61: S3.
Zhang Y-K, Huang Z-J, Liu S et al: WNT signaling underlies the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rodents. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 2268–2286.
Castaño Betancourt MC, Cailotto F, Kerkhof HJ et al: Genome-wide association and functional studies identify the DOT1L gene to be involved in cartilage thickness and hip osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2012; 109: 8218–8223.
Penza P, Lombardi R, Camozzi F, Ciano C, Lauria G : Painful neuropathy in subclinical hypothyroidism: clinical and neuropathological recovery after hormone replacement therapy. Neurol Sci 2009; 30: 149–151.
Ioannidis JP : Why most discovered true associations are inflated. Epidemiology 2008; 19: 640–648.
Garner C : Upward bias in odds ratio estimates from genome-wide association studies. Genet Epidemiol 2007; 31: 288–295.
Gwilym SE, Keltner JR, Warnaby CE, Carr AJ, Chizh B, Chessell I, Tracey I : Psychophysical and functional imaging evidence supporting the presence of central sensitization in a cohort of osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Care Res 2009; 61: 1226–1234.
Acknowledgements
SCW was funded by a PhD studentship awarded by the University of Nottingham. This work was supported by a EULAR project grant to AMV (grant no. 108239) and by the Arthritis Research UK Pain Centre (grant no. 18769). We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of Sally Doherty and Maggie Wheeler to patient assessments at baseline, data collection and entry. JM was funded by The Netherlands Society for Scientific Research (NWO) VIDI Grant 917103521. The generation and management of GWAS genotype data for the Rotterdam Study (RS I, RS II, RS III) was executed by the Human Genotyping Facility of the Genetic Laboratory of the Department of Internal Medicine, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. The GWAS data sets are supported by the Netherlands Organisation of Scientific Research NWO Investments (no. 175.010.2005.011, 911-03-012), the Genetic Laboratory of the Department of Internal Medicine, Erasmus MC, the Research Institute for Diseases in the Elderly (014-93-015; RIDE2), the Netherlands Genomics Initiative (NGI)/Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) Netherlands Consortium for Healthy Aging (NCHA), project nr. 050-060-810. We thank Pascal Arp, Mila Jhamai, Marijn Verkerk, Lizbeth Herrera and Marjolein Peters, MSc, and Carolina Medina-Gomez, MSc, for their help in creating the GWAS database, and Karol Estrada, PhD, Yurii Aulchenko, PhD, and Carolina Medina-Gomez, MSc, for the creation and analysis of imputed data. The Rotterdam Study is funded by Erasmus Medical Center and Erasmus University, Rotterdam, Netherlands Organization for the Health Research and Development (ZonMw), the Research Institute for Diseases in the Elderly (RIDE), the Ministry of Education, Culture and Science, the Ministry for Health, Welfare and Sports, the European Commission (DG XII), and the Municipality of Rotterdam. We are grateful to the study participants, the staff from the Rotterdam Study and the participating general practitioners and pharmacists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Warner, S., van Meurs, J., Schiphof, D. et al. Genome-wide association scan of neuropathic pain symptoms post total joint replacement highlights a variant in the protein-kinase C gene. Eur J Hum Genet 25, 446–451 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.196
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.196
This article is cited by
-
Die EAN-NeuPSIG-Leitlinie zur Diagnostik bei neuropathischen Schmerzen – eine Kurzfassung
Der Schmerz (2026)
-
Cost-effective non-additive GWAS across 2329 diseases in 500,349 individuals
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty: a narrative review
Perioperative Medicine (2024)
-
Genome-wide enriched pathway analysis of acute post-radiotherapy pain in breast cancer patients: a prospective cohort study
Human Genomics (2019)
-
The Rotterdam Study: 2018 update on objectives, design and main results
European Journal of Epidemiology (2017)