Abstract
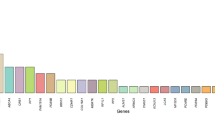
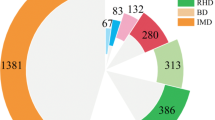
There are at least 38 mutant genes known to be associated with the ichthyosis phenotypes, and autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) is a specific subgroup caused by mutations in 13 different genes. Mutations in some of these genes, such as CERS3 with only two previous reports, are rare. In this study, we identified mutations in candidate genes in consanguineous families with ARCI with a next generation sequencing (NGS) array that incorporates 38 ichthyosis associated genes. We applied this sequencing array to DNA from 140 ichthyosis families with high prevalence of consanguinity. Among these patients we identified six distinct, previously unreported mutations in CERS3 in six Iranian families. These mutations in each family co-segregated with the ichthyosis phenotype. The patients demonstrated collodion membrane at birth, acrogeria, generalized scaling, and hyperlinearity of the palms and soles. The presence of a significant percentage of CERS3 mutations in our cohort depicts a marked difference between the etiology of ichthyoses in genetically poorly characterized regions and well-characterized western populations. Also, it shows that rare alleles are more prevalent in the gene pool of consanguineous populations and emphasizes the importance of these population studies for better understanding of ichthyosis pathogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Baden HP, Digiovanna JJ Ichthyosiform dermatoses. In:Rimoin DL(eds:)Emery and Rimoin's Principle and Practice of Medical Genetics. Academic Press: Philadelphia, 2013,pp 1–26.
Richard G, Bale SJ Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis; in: Pagon R, Adam MP, Ardinger HH et al(eds)GeneReviews. University of Washington: Seattle (WA), 2001, January 10, 2001; Last Update: August 28, 2014 edn.
Radner FP, Marrakchi S, Kirchmeier P et al: Mutations in CERS3 cause autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in humans. PLoS Genet 2013; 9: e1003536.
Eckl KM, Tidhar R, Thiele H et al: Impaired epidermal ceramide synthesis causes autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis and reveals the importance of ceramide acyl chain length. J Invest Dermatol 2013; 133: 2202–2211.
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF : A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1988; 16: 1215.
Jennemann R, Rabionet M, Gorgas K et al: Loss of ceramide synthase 3 causes lethal skin barrier disruption. Hum Mol Genet 2012; 21: 586–608.
Hamamy H, Antonarakis SE, Cavalli-Sforza LL et al: Consanguineous marriages, pearls and perils: Geneva International Consanguinity Workshop Report. Genet Med 2011; 13: 841–847.
Modell B, Darr A : Science and society: genetic counselling and customary consanguineous marriage. Nat Rev Genet 2002; 3: 225–229.
Saadat M, Ansari-Lari M, Farhud DD : Consanguineous marriage in Iran. Ann Hum Biol 2004; 31: 263–269.
Ben Halim N, Ben Alaya Bouafif N, Romdhane L et al: Consanguinity, endogamy, and genetic disorders in Tunisia. J Community Genet 2013; 4: 273–284.
Tuncbilek E, Koc I : Consanguineous marriage in Turkey and its impact on fertility and mortality. Ann Hum Genet 1994; 58: 321–329.
Saleheen D, Natarajan P, Armean IM et al: Human knockouts and phenotypic analysis in a cohort with a high rate of consanguinity. Nature 2017; 544: 235–239.
Vahidnezhad H, Youssefian L, Saeidian AH et al: Gene-targeted next generation sequencing identifies PNPLA1 mutations in patients with a phenotypic spectrum of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis: the impact of consanguinity. J Invest Dermatol 2017; 137: 678–685.
Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, Barzegar M et al: The Kindler syndrome: a spectrum of FERMT1 mutations in Iranian families. J Invest Dermatol 2015; 135: 1447–1450.
Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, Aghighi Y et al: Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome: a novel mutation and recurrent founder mutation in the CMG2/ANTXR2 gene. Acta Derm Venereol 2017; 96: 108–109.
Vahidnezhad H, Youssefian L, Saeidian AH et al: KRT5 and KRT14 mutations in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with phenotypic heterogeneity, and evidence of semi-dominant inheritance in a multiplex family. J Invest Dermatol 2016; 136: 1897–1901.
Vahidnezhad H, Youssefian L, Zeinali S et al: Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: COL7A1 mutation landscape in a multi-ethnic cohort of 152 extended families with high degree of customary consanguineous marriages. J Invest Dermatol 2017; 137: 660–669.
Rezaei N, Pourpak Z, Aghamohammadi A et al: Consanguinity in primary immunodeficiency disorders; the report from Iranian Primary Immunodeficiency Registry. Am J Reprod Immunol 2006; 56: 145–151.
Bademci G, Foster J 2nd, Mahdieh N et al: Comprehensive analysis via exome sequencing uncovers genetic etiology in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness in a large multiethnic cohort. Genet Med 2016; 18: 364–371.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Kaveh Khademhossein and Maryam Abiri for assistance in sample collection. Carol Kelly assisted in manuscript preparation. This study is in partial fulfillment of the PhD Thesis of Leila Youssefian.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youssefian, L., Vahidnezhad, H., Saeidian, A. et al. Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis: CERS3 mutations identified by a next generation sequencing panel targeting ichthyosis genes. Eur J Hum Genet 25, 1282–1285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2017.137
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2017.137
This article is cited by
-
Structural basis of the mechanism and inhibition of a human ceramide synthase
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2025)
-
Highlights of Gene and Cell Therapy for Epidermolysis Bullosa and Ichthyosis
Dermatology and Therapy (2024)
-
New developments in the molecular treatment of ichthyosis: review of the literature
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2022)
-
Mutation in ALOX12B likely cause of POI and also ichthyosis in a large Iranian pedigree
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2020)
-
Exacerbation of ichthyosis vulgaris phenotype by co-inheritance of STS and FLG mutations in a Chinese family with ichthyosis: a case report
BMC Medical Genetics (2018)