Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the structural relationship between the cornea and the optic disc in normal subjects.
Methods
This hospital-based observational study included 205 eyes from 205 individuals who were diagnosed as normal at our glaucoma clinic. The subjects underwent an eye examination, optic disc imaging with optic disc photography, optical coherence tomography, IOL master, specular microscopy, and ultrasound corneal pachymetry.
Results
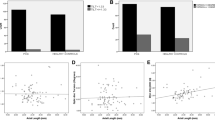
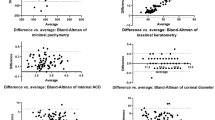
In univariate regression models (Pearson's correlation coefficient), the cup-to-disc (CD) ratio showed a negative correlation with corneal curvature (r=−0.315, P<0.001) and central corneal thickness (r=−0.206, P=0.005), and a positive correlation with white-to-white diameter (horizontal limbus to limbus distance, r=0.215, P=0.003). In multiple linear regression models with CD ratio as the dependant parameter, the CD ratio was still significantly associated with corneal curvature (β=−0.205, P=0.011) and white-to-white diameter (β=0.207, P=0.010). The central corneal thickness failed to show statistical significance, but did show a negative correlation with borderline significance (β=−0.133, P=0.075).
Conclusions
Eyes with a large CD ratio have large and flat corneas; this may suggest that there is a structural relationship between the cornea and the optic disc. These results can be helpful in analysing the anatomical relationship between the cornea and the optic disc.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Sellheyer K, Spitznas M . Development of the human sclera. A morphological study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1988; 226: 89–100.
Jonas JB, Kling F, Gründler AE . Optic disc shape, corneal astigmatism, and amblyopia. Ophthalmology 1997; 104: 1934–1937.
Bozkurt B, Irkec M, Gedik S, Orhan M, Erdener U . Topographical analysis of corneal astigmatism in patients with tilted-disc syndrome. Cornea 2002; 21: 458–462.
Apple DJ . New aspects of colobomas and optic nerve anomalies. Int Ophthalmol Clin 1984; 24: 109–121.
Lempert P, Porter L . Dysversion of the optic disc and axial length measurements in a presumed amblyopic population. J AAPOS 1998; 2: 207–213.
Young SE, Walsh FB, Knox DL . The tilted disk syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 1976; 82: 16–23.
Pakravan M, Parsa A, Sanagou M, Parsa CF . Central corneal thickness and correlation to optic disc size: a potential link for susceptibility to glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol 2007; 91: 26–28.
Cankaya AB, Elgin U, Batman A, Acaroglu G . Relationship between central corneal thickness and parameters of optic nerve head topography in healthy subjects. Eur J Ophthalmol 2008; 18: 32–38.
Herndon LW, Weizer JS, Stinnett SS . Central corneal thickness as a risk factor for advanced glaucoma damage. Arch Ophthalmol 2004; 122: 17–21.
Leske MC, Heijl A, Hussein M, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, Komaroff E, Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial Group. Factors for glaucoma progression and the effect of treatment: the early manifest glaucoma trial. Arch Ophthalmol 2003; 121: 48–56.
Wells AP, Garway-Heath DF, Poostchi A, Wong T, Chan KC, Sachdev N et al. Corneal hysteresis but not corneal thickness correlates with optic nerve surface compliance in glaucoma patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008; 49: 3380–3386.
Jonas JB, Martus P, Budde WM, Jünemann A, Hayler J . Small neuroretinal rim and large parapapillary atrophy as predictive factors for progression of glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology 2002; 109: 1561–1567.
Jonas JB, Holbach L . Central corneal thickness and thickness of the lamina cribrosa in human eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46: 1275–1279.
Jonas JB, Berenshtein E, Holbach L . Anatomic relationship between lamina cribrosa, intraocular space, and cerebrospinal fluid space. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003; 44: 5189–5195.
Jonas JB, Berenshtein E, Holbach L . Lamina cribrosa thickness and spatial relationships between intraocular space and cerebrospinal fluid space in highly myopic eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004; 45: 2660–2665.
Jonas JB, Gusek GC, Guggenmoos-Holzmann I, Naumann GO . Size of the optic nerve scleral canal and comparison with intravital determination of optic disc dimensions. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1988; 226: 213–215.
Parsa CF . Congenital optic disc anomalies. In: Albert DM, Miller JW (eds). Albert and Jacobiec's Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology, 3rd edn. Saunders/Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 2008; 4271–4275.
Choi HJ, Kim DM, Hwang SS . Relationship between central corneal thickness and localized retinal nerve fiber layer defect in normal-tension glaucoma. J Glaucoma 2006; 15: 120–123.
Araie M, Sekine M, Suzuki Y, Koseki N . Factors contributing to the progression of visual field damage in eyes with normal-tension glaucoma. Ophthalmology 1994; 101: 1440–1444.
Jonas JB, Hayreh SS, Tao Y . Central corneal thickness and thickness of the lamina cribrosa and peripapillary sclera in monkeys. Arch Ophthalmol 2009; 127: 1395–1396.
Larsen JS . The sagittal growth of the eye. 3. Ultrasonic measurement of the posterior segment (axial length of the vitreous) from birth to puberty. Acta Opthalmol 1971; 49: 873–886.
Atchison DA, Jones CE, Schmid KL, Pritchard N, Pope JM, Strugnell WE et al. Eye shape in emmetropia and myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004; 45: 3380–3386.
Oliveira C, Harizman N, Girkin CA, Tello C, Liebmann JM, Ritch R . Axial length and optic disc size in normal eyes. Br J Ophthalmol 2007; 91: 37–39.
Park SH, Park KH, Kim JM, Choi CY . The relation between axial length and ocular parameters. Ophthalmologica 2010; 224: 188–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Park, K., Kim, S. et al. The relationship between the cornea and the optic disc. Eye 24, 1653–1657 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2010.98
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2010.98
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Can we trust intraocular pressure measurements in eyes with intracameral air?
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2014)