Abstract
Purpose
X-linked juvenile retinoschisis (XLRS), a leading cause of juvenile macular degeneration, is characterized by a spoke-wheel pattern in the macular region of the retina and splitting of the neurosensory retina. This study aimed to identify the underlying genetic defect in a Chinese family with XLRS.
Methods
The proband underwent complete ophthalmic examinations, including fundus examination, fundus autofluorescence, and optical coherence tomography. DNA extracted from proband and his younger brother was screened for mutations in RS1 gene. The detected RS1 mutation was tested in all available family members and 200 healthy controls.
Results
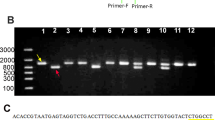
Reduced visual acuity, spoke-wheel pattern at the fovea, and split retina were observed in the proband. A novel frameshift mutation c.206-207delTG in the RS1 gene, leading to a truncated protein (p.L69fs16X), was identified in the proband and his younger brother. This mutation was not found in any unaffected member or in the healthy controls. The mother of the proband was hemizygous for this mutant allele.
Conclusions
We identified a novel causative mutation of RS1 in a Chinese family with XLRS. This finding expands the mutation spectrum of RS1 and provides evidence for a phenotype–genotype study in XLRS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Change history
13 November 2014
This article has been corrected since Advance Online Publication and an erratum is also printed in this issue
References
Sauer CG, Gehrig A, Warneke-Wittstock R, Marquardt A, Ewing CC, Gibson A et al. Positional cloning of the gene associated with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Nat Genet. 1997; 17: 164–170.
Sergeev YV, Caruso RC, Meltzer MR, Smaoui N, MacDonald IM, Sieving PA . Molecular modeling of retinoschisin with functional analysis of pathogenic mutations from human X-linked retinoschisis. Hum Mol Genet. 2010; 19 (7): 1302–1313.
Vijayasarathy C, Sui R, Zeng Y, Yang G, Xu F, Caruso RC et al. Molecular mechanisms leading lo null-protein product from retinoschisin(RS1) singal-sequence mutants in X-linked retinoschisis (XlRS) disease. Hum Mutat 2010; 31 (11): 1251–1260.
Reid SN, Akhmedov NB, Piriev NI, Kozak CA, Danciger M, Farber DB . The mouse X-linked juvenile retinoschisis cDNA: expression in photoreceptors. Gene 1999; 227 (2): 257–266.
Khan NW, Jamison JA, Kemp JA, Sieving PA . Analysis of photoreceptor function and inner retinal activity in juvenile X-linked retinoschisis. Vision Res. 2001; 41 (28): 3931–3942.
Molday LL, Hicks D, Sauer CG, Weber BH, Molday RS . Expression of X-linked retinoschisis protein RS1 in photoreceptor and bipolar cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2001; 42 (3): 816–825.
Tsang SH, Vaclavik V, Bird AC, Robson AG, Holder GE . Novel phenotypic and genotypic findings in X-linked retinoschisis. Arch Ophthalmol 2007; 125 (2): 259–267.
George ND, Yates JR, Moore AT . Clinical features in affected males with X-linked retinoschisis. Arch Ophthalmol 1996; 114 (3): 274–280.
Lesch B, Szabó V, Kánya M, Varsányi B, Somfai GM, Hargitai J et al. Truncation of retinoschisin protein associated with a novel splice site mutation in the RS1 gene. Mol Vis 2008; 14: 1549–1558.
Xu J, Gu H, Ma K, Liu X, Snellingen T, Sun E et al. R213W mutation in the retinoschisis 1 gene causes X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in a large Chinese family. Mol Vis 2010; 16: 1593–1600.
Grayson C, Reid SN, Ellis JA, Rutherford A, Sowden JC, Yates JR et al. Retinoschisin, the X-linked retinoschisis protein, is a secreted photoreceptor protein, and is expressed and released by Weri-Rb1 cells. Hum Mol Genet 2000; 9 (12): 1873–1879.
Tantri A, Vrabec TR, Cu-Unjieng A, Frost A, Annesley WH Jr, Donoso LA . X-linked retinoschisis: a clinical and molecular genetic review. Surv Ophthalmol 2004; 49 (2): 214–230.
Ziccardi L, Vijayasarathy C, Bush RA, Sieving PA . Loss of retinoschisin (RS1) cell surface protein in maturing mouse rod photoreceptors elevates the luminance threshold for light-driven translocation of transducin but not arrestin. J Neurosci 2012; 32 (38): 13010–13021.
Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT et al. X-Linked Juvenile Retinoschisis. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle 1993-2014.
Kortüm K, Kernt M, Reznicek L . Significance of ophthalmological imaging in common hereditary retinal diseases. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd 2013; 230 (3): 223–231.
Apushkin MA, Fishman GA, Janowicz MJ . Correlation of optical coherence tomography findings with visual acuity and macular lesions in patients with X-linked retinoschisis. Ophthalmology 2005; 112 (3): 495–501.
Pierro L, Fogliato G, Gagliardi M, Codenotti M . Correspondence to: Use of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography to differentiate acquired retinoschisis from retinal detachment in difficult cases. Retina 2013; 33 (6): 1290–1291.
Li X, Ma X, Tao Y . Clinical features of X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in Chinese families associated with novel mutations in the RS1 gene. Mol Vis 2007; 13: 804–812.
Wu WW, Wong JP, Kast J, Molday RS . RS1, a discoidin domain-containing retinal cell adhesion protein associated with X-linked retinoschisis, exists as a novel disulfide-linked octamer. J Biol Chem 2005; 280 (11): 10721–10730.
Wu WW, Molday RS . Defective discoidin domain structure, subunit assembly, and endoplasmic reticulum processing of retinoschisin are primary mechanisms responsible for X-linked retinoschisis. J Biol Chem 2003; 278 (30): 28139–28146.
Skorczyk A, Krawczyński MR . Four novel RS1 gene mutations in Polish patients with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Mol Vis 2012; 18: 3004–3012.
Takada Y, Vijayasarathy C, Zeng Y, Kjellstrom S, Bush RA, Sieving PA . Synaptic pathology in retinoschisis knockout (Rs1-/y) mouse retina and modification by rAAV-Rs1 gene delivery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008; 49 (8): 3677–3686.
Wang T, Zhou A, Waters CT, O'Connor E, Read RJ, Trump D . Molecular pathology of X linked retinoschisis: mutations interfere with retinoschisin secretion and oligomerisation. Br J Ophthalmol 2006; 90 (1): 81–86.
Kjellstrom S, Bush RA, Zeng Y, Takada Y, Sieving PA . Retinoschisin gene therapy and natural history in the Rs1h-KO mouse: long-term rescue from retinal degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48 (8): 3837–3845.
Hiriyanna KT, Bingham EL, Yashar BM, Ayyagari R, Fishman G, Small KW et al. Novel mutations in XLRS1 causing retinoschisis, including first evidence of putative leader sequence change. Hum Mutat 1999; 14 (5): 423–427.
Inoue Y, Yamamoto S, Okada M, Tsujikawa M, Inoue T, Okada AA et al. X-linked retinoschisis with point mutations in the XLRS1 gene. Arch Ophthalmol 2000; 118 (1): 93–96.
The Retinoschisis Consortium. Functional implications of the spectrum of mutations found in 234 cases with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Hum Mol Genet 1998; 7 (7): 1185–1192.
Vincent A, Robson AG, Neveu MM, Wright GA, Moore AT, Webster AR et al. A phenotype-genotype correlation study of X-linked retinoschisis. Ophthalmology 2013; 120 (7): 1454–1464.
Bowles K, Cukras C, Turriff A, Sergeev Y, Vitale S, Bush RA et al. X-linked retinoschisis: RS1 mutation severity and age affect the ERG phenotype in a cohort of 68 affected male subjects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52 (12): 9250–9256.
Sergeev YV, Vitale S, Sieving PA, Vincent A, Robson AG, Moore AT et al. Molecular modeling indicates distinct classes of missense variants with mild and severe XLRS phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet 2013; 22 (23): 4756–4767.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients’ families and healthy controls for their participation in our study. We also thank Ranhui Duan for manuscript revising. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270706) and (81271944).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Mei, L., Gui, B. et al. A novel deletion mutation in RS1 gene caused X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in a Chinese family. Eye 28, 1364–1369 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.196
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.196