Abstract
Purpose
To determine the morphologic features of the optic disc and the location of visual field (VF) defect in relation to posterior staphyloma in normal tension glaucoma (NTG) eyes with myopia.
Methods
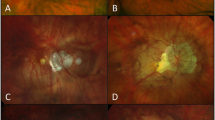
One hundred and thirty-four NTG patients with myopia were enrolled. B-scan ultrasonography was performed in enrolled patients. Disc tilt ratio, disc torsion, and area of peripapillary atrophy were measured from disc photographs. Patients were classified according to the presence of posterior staphyloma and its location: staphyloma involving the optic disc, staphyloma involving either the supero-temporal side of the optic disc or the infero-temporal side of the optic disc. The relationship between the location of the posterior staphyloma and that of the VF defect was analyzed.
Results
Among 134 eyes, 74 eyes (55.2%) had posterior staphyloma on B-scan ultrasonography. Mean torsion degree was significantly greater in eyes with staphyloma involving the temporal side of the optic disc (19.78±18.00°) compared with eyes with staphyloma involving the optic disc (4.65±4.92°, P=0.001). The frequency of the location of VF damage differed significantly between eyes with staphyloma involving the supero-temporal side and those involving the infero-temporal side of the optic disc (P=0.008), which was not significant in eyes with staphyloma involving the optic disc (P=0.813).
Conclusions
Optic disc torsion was a prominent finding in myopic NTG eyes when posterior staphyloma was located temporal to the optic disc. The location of posterior staphyloma was related to the direction of disc torsion and the location of VF defect.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Mitchell P, Hourihan F, Sandbach J, Wang JJ . The relationship between glaucoma and myopia: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology 1999; 106 (10): 2010–2015.
Xu L, Wang Y, Wang S, Jonas JB . High myopia and glaucoma susceptibility the Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2007; 114 (2): 216–220.
Wong TY, Klein BE, Klein R, Knudtson M, Lee KE . Refractive errors, intraocular pressure, and glaucoma in a white population. Ophthalmology 2003; 110 (1): 211–217.
Samarawickrama C, Mitchell P, Tong L, Gazzard G, Lim L, Wong TY et al. Myopia-related optic disc and retinal changes in adolescent children from Singapore. Ophthalmology 2011; 118: 2050–2057.
How AC, Tan GS, Chan YH, Wong TT, Seah SK, Foster PJ et al. Population prevalence of tilted and torted optic discs among an adult Chinese population in Singapore: the Tanjong Pagar Study. Arch Ophthalmol 2009; 127 (7): 894–899.
Doshi A, Kreidl KO, Lombardi L, Sakamoto DK, Singh K . Nonprogressive glaucomatous cupping and visual field abnormalities in young Chinese males. Ophthalmology 2007; 114 (3): 472–479.
Rada JA, Shelton S, Norton TT . The sclera and myopia. Exp Eye Res 2006; 82 (2): 185–200.
McBrien NA, Gentle A . Role of the sclera in the development and pathological complications of myopia. Prog Retin Eye Res 2003; 22 (3): 307–338.
Kim TW, Kim M, Weinreb RN, Woo SJ, Park KH, Hwang JM . Optic disc change with incipient myopia of childhood. Ophthalmology 2012; 119 (1): 21–26 e21-23.
Ohno-Matsui K, Shimada N, Yasuzumi K, Hayashi K, Yoshida T, Kojima A et al. Long-term development of significant visual field defects in highly myopic eyes. Am J Ophthalmol 2011; 152 (2): 256–265 e251.
Park HY, Lee K, Park CK . Optic disc torsion direction predicts the location of glaucomatous damage in normal-tension glaucoma patients with myopia. Ophthalmology 2012; 119 (9): 1844–1851.
Hsiang HW, Ohno-Matsui K, Shimada N, Hayashi K, Moriyama M, Yoshida T et al. Clinical characteristics of posterior staphyloma in eyes with pathologic myopia. Am J Ophthalmol 2008; 146 (1): 102–110.
Curtin BJ . Posterior staphyloma development in pathologic myopia. Ann Ophthalmol 1982; 14 (7): 655–658.
Pruett RC . Complications associated with posterior staphyloma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 1998; 9 (3): 16–22.
Steidl SM, Pruett RC . Macular complications associated with posterior staphyloma. Am J Ophthalmol 1997; 123 (2): 181–187.
Giuffre G . Chorioretinal degenerative changes in the tilted disc syndrome. Int Ophthalmol 1991; 15 (1): 1–7.
Vongphanit J, Mitchell P, Wang JJ . Population prevalence of tilted optic disks and the relationship of this sign to refractive error. Am J Ophthalmol 2002; 133 (5): 679–685.
Tay E, Seah SK, Chan SP, Lim AT, Chew SJ, Foster PJ et al. Optic disk ovality as an index of tilt and its relationship to myopia and perimetry. Am J Ophthalmol 2005; 139 (2): 247–252.
Cheng HM, Singh OS, Kwong KK, Xiong J, Woods BT, Brady TJ . Shape of the myopic eye as seen with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Optom Vis Sci 1992; 69 (9): 698–701.
Atchison DA, Pritchard N, Schmid KL, Scott DH, Jones CE, Pope JM . Shape of the retinal surface in emmetropia and myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46 (8): 2698–2707.
Moriyama M, Ohno-Matsui K, Hayashi K, Shimada N, Yoshida T, Tokoro T et al. Topographic analyses of shape of eyes with pathologic myopia by high-resolution three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Ophthalmology 2011; 118 (8): 1626–1637.
Ohno-Matsui K, Akiba M, Modegi T, Tomita M, Ishibashi T, Tokoro T et al. Association between shape of sclera and myopic retinochoroidal lesions in patients with pathologic myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012; 53 (10): 6046–6061.
Fledelius HC, Goldschmidt E . Eye shape and peripheral visual field recording in high myopia at approximately 54 years of age, as based on ultrasonography and Goldmann kinetic perimetry. Acta Ophthalmol 2010; 88 (5): 521–526.
Curtin BJ, Karlin DB . Axial length measurements and fundus changes of the myopic eye. I. The posterior fundus. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1970; 68: 312–334.
Choi JA, Park HY, Shin HY, Park CK . Optic disc characteristics in patients with glaucoma and combined superior and inferior retinal nerve fiber layer defects. JAMA Ophthalmol 2014; 132: 1068–1075.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Seoul St. Mary's Hospital Clinical Medicine Research Program year of 2013 through the Catholic University of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, HY., Jung, Y. & Park, C. Posterior staphyloma is related to optic disc morphology and the location of visual field defect in normal tension glaucoma patients with myopia. Eye 29, 333–341 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.256
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.256
This article is cited by
-
Impact of peripapillary staphylomas on the vascular and structural characteristics in myopic eyes: a propensity score matching analysis
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2023)
-
The prevalance of congenital optic disc anomalies in Turkey: a hospital-based study
International Ophthalmology (2022)
-
Vertical disc tilt and features of the optic nerve head anatomy are related to visual field defect in myopic eyes
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Posterior Pole and Optic Nerve Head in Myopes with Glaucoma
Scientific Reports (2017)