Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to investigate the difference of the clinical course in recurrent intermittent exotropia after second surgery compared with both recurrent intermittent exotropia after its first of two surgeries and intermittent exotropia after only a single surgery.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients diagnosed with intermittent exotropia who underwent lateral rectus recession and medial rectus resection (R&R) between January 1992 and January 2011 at Yeungnam University Hospital. Repeated measure ANOVA (rmANOVA) was used to compare the clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia before and after a second surgery with that of intermittent exotropia with a single surgery.
Results
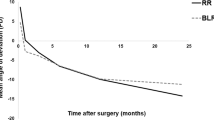
A total of 352 intermittent exotropia patients who underwent one R&R procedure and 77 recurrent intermittent exotropia patients who underwent a second R&R in the contralateral eye were included in this study. Although exodrift of recurrent intermittent exotropia was observed at 24 months of follow-up even after a second surgery, it was significantly lower than both intermittent exotropia with a single surgery and after its first of two surgeries (P<0.001, rmANOVA).
Conclusion
The clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia after a second surgery was improved compared with both recurrent intermittent exotropia after its first of two surgeries and intermittent exotropia after a single surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Leow P-L, Ko STC, Wu PKW, Chan CWN . Exotropic drift and ocular alignment after surgical correction for intermittent exotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 2010; 47 (1): 12–16.
Figueira EC, Hing S . Intermittent exotropia: comparison of treatments. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2006; 34 (3): 245–251.
Pineles SL, Ela-Dalman N, Zvansky AG, Yu F, Rosenbaum AL . Long-term results of the surgical management of intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS 2010; 14 (4): 298–304.
Maruo T, Kubota N, Sakaue T, Usui C . Intermittent exotropia surgery in children: long term outcome regarding changes in binocular alignment. A study of 666 cases. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q 2001; 16 (4): 265–270.
Ekdawi NS, Nusz KJ, Diehl NN, Mohney BG . Postoperative outcomes in children with intermittent exotropia from a population-based cohort. J AAPOS 2009; 13 (1): 4–7.
Hahm IR, Yoon SW, Baek S-H, Kong SM . The clinical course of recurrent exotropia after reoperation for exodeviation. Korean J Ophthalmol 2005; 19 (2): 140–144.
Kim WJ, Kim MM . The clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia after previous unilateral recess-resection surgery. J Korean Opthalmol Soc 2009; 50 (9): 1386–1391.
Lim SH, Hong JS, Kim MM . Prognostic factors for recurrence with unilateral recess-resect procedure in patients with intermittent exotropia. Eye (Lond) 2011; 25 (4): 449–454.
Hatsukawa Y, Nishina S, Sugasawa J, Kimura A, Yagasaki T, Fujikado T et al. Surgical results of unilateral recession-resection for intermittent exotropia in children: multicenter study in Japan. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 2011; 115 (5): 440–446.
Choi J, Chang JW, Kim SJ, Yu YS . The long-term survival analysis of bilateral lateral rectus recession versus unilateral recession-resection for intermittent exotropia. Am J Ophthalmol 2012; 153 (2): 343–351.e1.
Lim SH, Hwang BS, Kim MM . Prognostic factors for recurrence after bilateral rectus recession procedure in patients with intermittent exotropia. Eye (Lond) 2012; 26 (6): 846–852.
Rayner JW, Jampolsky A . Management of adult patients with large angle amblyopic exotropia. Ann Ophthalmol 1973; 5 (1): 95–99.
Beneish R, Flanders M . The role of stereopsis and early postoperative alignment in long-term surgical results of intermittent exotropia. Can J Ophthalmol 1994; 29 (3): 119–124.
Yildirim C, Mutlu FM, Chen Y, Altinsoy HI . Assessment of central and peripheral fusion and near and distance stereoacuity in intermittent exotropic patients before and after strabismus surgery. Am J Ophthalmol 1999; 128 (2): 222–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This study was presented as a free paper at the annual meeting of the Korean Ophthalmological Society in Seoul, 1–3 November 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W., Kim, M. The clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia following one or two surgeries over 24 months postoperatively. Eye 28, 819–824 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.93
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.93
This article is cited by
-
The subjective controllability of exotropia and its effect on surgical outcomes in patients with intermittent exotropia
BMC Ophthalmology (2023)
-
Effects of orthoptic therapy in children with intermittent exotropia after surgery: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Trials (2022)
-
Surgical success of lateral rectus resection for residual and recurrent esotropia
International Ophthalmology (2021)
-
Risk factors associated with poor outcome after medial rectus resection for recurrent intermittent exotropia
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2020)
-
The fast exodrift after the first surgical treatment of exotropia and its correlation with surgical outcome of second surgery
BMC Ophthalmology (2018)