Abstract
Purpose
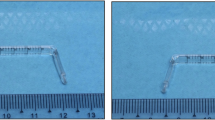
Evaluating anti-scarring therapies require objective assessment of scarring, and knowledge of normal fornix anatomy. Measurement of conjunctival scarring has focused on inferior fornix shortening, although the superior fornix is often overlooked. There are data on normal fornix depth (FD) in South Asians, but there are no studies investigating normal conjunctival FD in white Caucasians. We designed a fornix depth measurer (FDM) for objective measurement of upper and lower conjunctival FD. The purpose of this study was to evaluate intra- and inter-observer variability, and to establish a reference for normal conjunctival FD in an ethnically white Caucasian population.
Patients and methods
Prospective cross-sectional study evaluating conjunctival FD in 252 clinically normal white Caucasian participants aged 20–80. Paired observers evaluated inter- and intra-observer variability. Data was analyzed using Bland–Altman plots and analysis of variance.
Results
For white Caucasian subjects, mean upper and lower conjunctival fornix depths were 15.6 mm (95% confidence interval (CI), 12.5–18.8) and 10.9 mm (95% CI, 8.0–13.7), respectively. Females have smaller FDs (upper FD 15.3 mm±1.6 females, 16.2 mm±1.4 males, P<0.001; lower FD 10.6 mm±1.3 females, 11.3 mm±1.4 males, P<0.001). There was a progressive decline in FD with age (upper fornix depth 16.3 mm±1.2 at age 20–29, and 15.0 mm±1.8 at age 80+ (P=0.04)). There was 94–100% intra-observer and inter-observer agreement for upper and lower fornix measurements.
Conclusions
Using a slightly different custom-designed FDM, central conjunctival fornix depth in white Caucasian eyes appears to be similar to data previously reported in South Asian eyes. Fornix depth measurements were repeatable and reproducible.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Saw VP, Dart JK, Rauz S, Ramsay A, Bunce C, Xing W et al. Immunosuppressive therapy for ocular mucous membrane pemphigoid strategies and outcomes. Ophthalmology 2008; 115: 253–261.
Saw VP, Schmidt E, Offiah I, Galatowicz G, Zillikens D, Dart JK et al. Profibrotic phenotype of conjunctival fibroblasts from mucous membrane pemphigoid. Am J Pathol 2011; 178 (1): 187–197.
Mondino BJ, Brown SI . Immunosuppressive therapy in ocular cicatricial pemphigoid. Am J Ophthalmol 1983; 96 (4): 453–459.
Rowsey JJ, Macias-Rodriguez Y, Cukrowski C . A new method for measuring progression in patients with ocular cicatricial pemphigoid. Arch Ophthalmol 2004; 122 (2): 179–184.
Tauber J, Jabbur N, Foster CS . Improved detection of disease progression in ocular cicatricial pemphigoid. Cornea 1992; 11 (5): 446–451.
Foster CS . Cicatricial pemphigoid. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1986; 84: 527–663.
Williams GP, Saw VP, Saeed T, Evans ST, Cottrell P, Curnow SJ et al. Validation of a fornix depth measurer: a putative tool for the assessment of progressive cicatrising conjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol 2011; 95 (6): 842–847.
Kawakita T, Kawashima M, Murat D, Tsubota K, Shimazaki J . Measurement of fornix depth and area: a novel method of determining the severity of fornix shortening. Eye 2009; 23 (5): 1115–1119.
Reeves GM, Lloyd M, Rajlawat BP, Barker GL, Field EA, Kaye SB . Ocular and oral grading of mucous membrane pemphigoid. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2012; 250 (4): 611–618.
Schwab IR, Linberg JV, Gioia VM, Benson WH, Chao GM . Foreshortening of the inferior conjunctival fornix associated with chronic glaucoma medications. Ophthalmology 1992; 99 (2): 197–202.
Khan IJ, Ghauri AJ, Hodson J, Edmunds MR, Cottrell P, Evans S et al. Defining the limits of normal conjunctival fornix anatomy in a healthy South Asian population. Ophthalmology 2014; 121 (2): 492–497.
Rose GE . The giant fornix syndrome: an unrecognized cause of chronic, relapsing, grossly purulent conjunctivitis. Ophthalmology 2004; 111 (8): 1539–1545.
Acknowledgements
VS was supported by the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre at Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and the UCL Institute of Ophthalmology. The authors have been grateful for the support and advice of Professor John Dart (Moorfields Eye Hospital), Catey Bunce (Moorfields Eye Hospital), Darwin Minassian (Moorfields Eye Hospital), Saaeha Rauz (Birmingham & Midland Eye Centre) and Geraint Williams (Birmingham & Midland Eye Centre) during this study.
Author contributions
Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work: VS, DC and SH. Acquisition, analysis or interpretation of data: GJ, CD, SH, DB, HJ, ET, DC and VS. Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content: VS, GJ, SH, CD, DB, HJ, ET and DC. Final approval of the version published: GJ, DC, SH, DB, HJ, ET, CD and VS. Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved: GJ, DC, SH, DB, HJ, ET, CD and VS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jutley, G., Carpenter, D., Hau, S. et al. Upper and lower conjunctival fornix depth in healthy white caucasian eyes: a method of objective assessment. Eye 30, 1351–1358 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.128
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.128
This article is cited by
-
Klinik des okulären Schleimhautpemphigoids
Die Ophthalmologie (2023)
-
Ocular Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid: Current State of Pathophysiology, Diagnostics and Treatment
Ophthalmology and Therapy (2019)
-
Transconjunctival Müller’s muscle Tucking Method for Non-incisional Correction of Mild Ptosis: The Effectiveness and Maintenance
Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (2019)
-
A review of scoring systems for ocular involvement in chronic cutaneous bullous diseases
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018)
-
An alternative method for upper and lower conjunctival fornix measurement
Eye (2017)