Abstract
Purpose
To estimate the prevalence of myopia among primary and middle school-aged students in Guangzhou and to explore the potentially contributing factors to myopia.
Methods
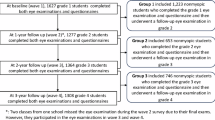
This cross-sectional study was based on a sample of students in grades 1–6 and grades 7–9. Data were collected from refractive error measurements and a structured questionnaire.
Results
A total of 3055 participants were involved in this analysis, and the overall prevalence of myopia was 47.4% (95% confidence interval (CI)= 45.6–49.2%). The prevalence of myopia in students increased along with the growth of grade level; the prevalence of myopia in students in grade 1 was only 0.2%, as it increased to 38.8% in students in grade 3, and the rate was the highest (68.4%) in students in grade 9. Girls were at a higher risk of myopia than boys (adjusted odds ratio=1.22, 95% CI=1.04–1.44). Both male and female students whose distance of reading was longer than 25 cm were less likely to have myopia and who have one or two myopic parents were at a higher risk of myopia. In addition, reading for pleasure more than 2 h per day (adjusted odds ratio=1.84, 95% CI=1.09–3.12) was only positively associated with myopia in boys and spending time watching television per week was only positively associated with myopia in girls.
Conclusion
Myopia in students is a significant public health problem in Guangzhou. Female gender, higher grade, longer time spent for near work, shorter distance of near work, and parental myopia were shown to be associated with the increasing risk of myopia in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Morgan IG, Ohno-Matsui K, Saw SM . Myopia. LANCET 2012; 379 (9827): 1739–1748.
Lin LL, Shih YF, Hsiao CK, Chen CJ . Prevalence of myopia in Taiwanese schoolchildren: 1983 to 2000. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2004; 33 (1): 27–33.
Wu HM, Seet B, Yap EP, Saw SM, Lim TH, Chia KS . Does education explain ethnic differences in myopia prevalence? A population-based study of young adult males in Singapore. Optom Vis Sci 2001; 78 (4): 234–239.
Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Mariotti SP, Pokharel GP . Global magnitude of visual impairment caused by uncorrected refractive errors in 2004. Bull World Health Organ 2008; 86 (1): 63–70.
Goldschmidt E, Jacobsen N . Genetic and environmental effects on myopia development and progression. Eye (Lond) 2014; 28 (2): 126–133.
Feldkamper M, Schaeffel F . Interactions of genes and environment in myopia. Dev Ophthalmol 2003; 37: 34–49.
Wu LJ, You QS, Duan JL, Luo YX, Liu LJ, Li X et al. Prevalence and associated factors of myopia in high-school students in Beijing. PLoS One 2015; 10 (3): e0120764.
Lim HT, Yoon JS, Hwang SS, Lee SY . Prevalence and associated sociodemographic factors of myopia in Korean children: the 2005 third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III). Jpn J Ophthalmol 2012; 56 (1): 76–81.
Saw SM, Chua WH, Hong CY, Wu HM, Chan WY, Chia KS et al. Nearwork in early-onset myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2002; 43 (2): 332–339.
McBrien NA, Moghaddam HO, Reeder AP . Atropine reduces experimental myopia and eye enlargement via a nonaccommodative mechanism. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993; 34 (1): 205–215.
Irving EL, Sivak JG, Callender MG . Refractive plasticity of the developing chick eye. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 1992; 12 (4): 448–456.
French AN, Morgan IG, Mitchell P, Rose KA . Risk factors for incident myopia in Australian schoolchildren: the Sydney adolescent vascular and eye study. Ophthalmology 2013; 120 (10): 2100–2108.
Mutti DO, Mitchell GL, Moeschberger ML, Jones LA, Zadnik K . Parental myopia, near work, school achievement, and children's refractive error. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2002; 43 (12): 3633–3640.
Jones LA, Sinnott LT, Mutti DO, Mitchell GL, Moeschberger ML, Zadnik K . Parental history of myopia, sports and outdoor activities, and future myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48 (8): 3524–3532.
Rose KA, Morgan IG, Ip J, Kifley A, Huynh S, Smith W et al. Outdoor activity reduces the prevalence of myopia in children. Ophthalmology 2008; 115 (8): 1279–1285.
Zadnik K, Satariano WA, Mutti DO, Sholtz RI, Adams AJ . The effect of parental history of myopia on children's eye size. JAMA 1994; 271 (17): 1323–1327.
Lim LT, Gong Y, Ah-Kee EY, Xiao G, Zhang X, Yu S . Impact of parental history of myopia on the development of myopia in mainland China school-aged children. Ophthalmol Eye Dis 2014; 6: 31–35.
Reports on the physical fitness and health research of chinese school students. 2010 The Ministry Of Education of China, (in Chinese).
Zhao J, Pan X, Sui R, Munoz SR, Sperduto RD, Ellwein LB . Refractive error study in children: results from Shunyi District, China. Am J Ophthalmol 2000; 129 (4):427–435.
Tay MT, Au EK, Ng CY, Lim MK . Myopia and educational attainment in 421,116 young Singaporean males. Ann Acad Med Singapore 1992; 21 (6): 785–791.
Statistical Annual Report of Guangzhou in the Sixth National Population Census in 2010. 2011 Guangzhou Bureau of Statistics, (in Chinese).
Saw SM, Nieto FJ, Katz J, Chew SJ . Estimating the magnitude of close-up work in school-age children: a comparison of questionnaire and diary instruments. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 1999; 6 (4): 291–301.
Saw SM, Zhang MZ, Hong RZ, Fu ZF, Pang MH, Tan DT . Near-work activity, night-lights, and myopia in the Singapore–China study. Arch Ophthalmol 2002; 120 (5): 620–627.
Xiang F, He M, Morgan IG . The impact of parental myopia on myopia in Chinese children: population-based evidence. Optom Vis Sci 2012; 89 (10): 1487–1496.
Mirshahi A, Ponto KA, Hoehn R, Zwiener I, Zeller T, Lackner K et al. Myopia and level of education: results from the Gutenberg Health Study. Ophthalmology 2014; 121 (10): 2047–2052.
Saxena R, Vashist P, Tandon R, Pandey RM, Bhardawaj A, Menon V et al. Prevalence of myopia and its risk factors in urban school children in Delhi: the North India Myopia Study (NIM Study). PLoS One 2015; 10 (2): e0117349.
Villarreal GM, Ohlsson J, Cavazos H, Abrahamsson M, Mohamed JH . Prevalence of myopia among 12- to 13-year-old schoolchildren in northern Mexico. Optom Vis Sci 2003; 80 (5): 369–373.
Xiang F, He M, Morgan IG . The impact of severity of parental myopia on myopia in Chinese children. Optom Vis Sci 2012; 89 (6): 884–891.
He M, Zeng J, Liu Y, Xu J, Pokharel GP, Ellwein LB . Refractive error and visual impairment in urban children in southern china. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004; 45 (3): 793–799.
Wen G, Tarczy-Hornoch K, McKean-Cowdin R, Cotter SA, Borchert M, Lin J et al. Prevalence of myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism in non-Hispanic white and Asian children: multi-ethnic pediatric eye disease study. Ophthalmology 2013; 120 (10): 2109–2116.
Czepita D, Mojsa A, Ustianowska M, Czepita M, Lachowicz E . Role of gender in the occurrence of refractive errors. Ann Acad Med Stetin 2007; 53 (2): 5–7.
Demissie Z, Lowry R, Eaton DK, Park S, Kann L . Electronic media and beverage intake among United States high school students—2010. J Nutr Educ Behav 2013; 45 (6):756–760.
Ip JM, Saw SM, Rose KA, Morgan IG, Kifley A, Wang JJ et al. Role of near work in myopia: findings in a sample of Australian school children. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008; 49 (7): 2903–2910.
Lee YY, Lo CT, Sheu SJ, Yin LT . Risk factors for and progression of myopia in young Taiwanese men. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2015; 22 (1): 66–73.
Ling SL, Chen AJ, Rajan U, Cheah WM . Myopia in ten year old children—a case control study. Singapore Med J 1987; 28 (4): 288–292.
He M, Xiang F, Zeng Y, Mai J, Chen Q, Zhang J et al. Effect of time spent outdoors at school on the development of myopia among children in china: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015; 314 (11): 1142–1148.
Low W, Dirani M, Gazzard G, Chan YH, Zhou HJ, Selvaraj P et al. Family history, near work, outdoor activity, and myopia in Singapore Chinese preschool children. Br J Ophthalmol 2010; 94 (8): 1012–1016.
Zhou Z, Ma X, Yi H, Pang X, Shi Y, Chen Q et al. Factors underlying different myopia prevalence between middle- and low-income provinces in China. Ophthalmology 2015; 122 (5): 1060–1062.
Lu B, Congdon N, Liu X, Choi K, Lam DS, Zhang M et al. Associations between near work, outdoor activity, and myopia among adolescent students in rural China: the Xichang Pediatric Refractive Error Study report no. 2. Arch Ophthalmol 2009; 127 (6): 769–775.
Cheng D, Schmid KL, Woo GC . Myopia prevalence in Chinese–Canadian children in an optometric practice. Optom Vis Sci 2007; 84 (1): 21–32.
French AN, Ashby RS, Morgan IG, Rose KA . Time outdoors and the prevention of myopia. Exp Eye Res 2013; 114: 58–68.
Funarunart P, Tengtrisorn S, Sangsupawanich P, Siangyai P . Accuracy of noncycloplegic refraction in primary school children in southern Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai 2009; 92 (6): 806–811.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the contribution of the Guangdong Education Bureau and its participating schools. Funding: This study was supported by Health Promotion Centre for Primary and Secondary Schools of Guangzhou Municipality. The funders had no role in study design and data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, L., Yang, J., Mai, J. et al. Prevalence and associated factors of myopia among primary and middle school-aged students: a school-based study in Guangzhou. Eye 30, 796–804 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.39
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.39
This article is cited by
-
The Current and Future Landscape of the Childhood Myopia Epidemic in China—A Review
Ophthalmology and Therapy (2024)
-
Association between whole-grain intake and myopia in chinese children: a cross-sectional epidemiological study
BMC Ophthalmology (2023)
-
Comparing the effects of highly aspherical lenslets versus defocus incorporated multiple segment spectacle lenses on myopia control
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Myopia prediction for children and adolescents via time-aware deep learning
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Epidemiological investigation of the status of myopia in children and adolescents in Fujian Province in 2020
Japanese Journal of Ophthalmology (2023)