Abstract
This study explores the effect of priming rhesus monkeys with an Ad5/35 vector expressing simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) gag and gp120, and then boosting the animals with an modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) vector encoding the same antigens after a 2-month interval. The animals were intravenously challenged with 100 TCID50 of highly pathogenic SIVmac239 virus 2 months after the booster vaccination. The priming vaccination induced robust SIV-specific cell-mediated and humoral immune responses, and boosting further enhanced the cellular immunity. Vaccination reduced peak and long-term viral loads by 1–2 logs for a period of >6 months, as reflected by a reduction in both the SIV RNA and DNA levels. Of considerable interest, the immunized monkeys did not suffer from loss of CD4 T cells, particularly central memory CD4 T cells. These results demonstrate that prophylactic vaccination with Ad5/35 followed by MVA reduces viral replication and prevents CD4 T-cell loss, and that these effects may decrease the likelihood of disease progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In the history of vaccine development, live-attenuated vaccines such as polio vaccine and vaccinia vaccine have been used successfully to prevent viral infections. Vaccination of rhesus monkeys with live-attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) vaccine was shown to provide protective immunity against disease after challenge with pathogenic SIV.1, 2, 3, 4 However, the live-attenuated SIV/HIV possesses the potential risk of the vaccine virus reverting to a pathogenic form. Indeed, a study in which 11 adult monkeys were vaccinated with SIVmac239Delta3 reported that in the 6.8-year period after vaccination, all the monkeys had signs of immune dysregulation, 64% of the monkeys had persistent recurrent viremia, and 18% of the monkeys developed AIDS.5 Furthermore, a recent study showed virus recombination between live-attenuated SIV (SIVmac239Deltanef) and a heterologous SIV that was used as the challenge virus.6 Hence, there is still uncertainty about the safety of the live-attenuated SIV/HIV vaccine for human use.
In the past decade, a number of novel vaccine platforms were studied for their use in the development of prophylactic vaccines against infection by viral pathogens, including HIV, hepatitis virus and influenza virus. Some of the most important studies have been those involving vector-based vaccines that use adenovirus (Ad) and vaccinia vectors. Human Ad viruses are classified into six subgroups from A to F.7 Most Ad serotypes belonging to subgroups A, C, D, E and F use the Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) as a cellular receptor.8 The Ad serum type 5 (Ad5, subgroup C) has well-defined biological properties and has been widely used as a vector in gene therapy and vaccine development. Results from human and nonhuman primate studies suggest that deficient Ad vectors induce antigen-specific cell-mediated immune responses in vivo.9, 10, 11 The Ad5 vector is particularly of interest because its safety has been proven in clinical trials, and it is of high quality and can be easily produced.9, 10, 11, 12, 13 Unfortunately, a recent large-scale phase IIb clinical trial demonstrated that subjects vaccinated three times with the Ad5 vector expressing HIV Gag, Pol and Nef were not protected against HIV infection. Vaccination did not reduce the HIV viral load or improve the CD4 T cell count once HIV infection occurred in the trial participants.14 Furthermore, a twofold viral increase was observed in the incidence of HIV acquisition among vaccinated recipients with increased Ad5-neutralizing antibody (Ab) titers compared with placebo recipients; this is probably because vaccination provides a more conducive environment for HIV replication through the activation of dendritic cells by the Ad5–Ab complex.15 In this study, we used a chimeric Ad5 vector with the Ad35 fiber (Ad5/35) (the Ad35 virus is classified as subgroup B). The Ad35 fiber was reported to show 25% amino-acid homology with the Ad5 fiber;16 moreover, cell entry of Ad35 is CAR independent and involves the CD46 receptor, which is expressed on most human cells.17 The Ad5/35 vector does not infect hepatocytes, but efficiently infects human dendritic cells; thus, Ad5/35 is expected to induce stronger immune responses than Ad5 in human trials.9
It was reported that the modified vaccine virus Ankara (MVA) derived from live vaccinia virus by more than 500 passages in chicken embryo fibroblast cells had lost 15% of the genome compared to its parent vaccinia virus, leading to severe restriction of its replication and virulence processes.18, 19 The absence of impaired gene expression shows that MVA is a replication-deficient virus in humans. Furthermore, MVA was safely administered to approximately 120 000 individuals as a smallpox vaccine,20 and clinically tested as a vaccine vector against other diseases, including HIV and cancer.21
Recent studies have shown that priming/boosting with different virus vector elicits higher immune responses than vaccination with an individual virus vector.22 In this study, we explored the protective efficacy of an Ad5/35 prime and MVA boost regimen against SIV challenge. Because clinical trials indicate that neither Ad nor MVA vectors induce strong protective immune responses against HIV individually, we tried to explore whether using these two vectors in a prime/boost combination might be more effective. We investigated this by vaccinating rhesus monkeys initially with Ad5/35 then with MVA vectors encoding SIV gag and SIV gp120, and then challenging them with SIVmac239. Results show that this prime/boost strategy led to a persistent more than 10-fold reduction in the SIV viral load, and the CD4 count (including central memory T cells, CM) was maintained in the infected animals. These findings suggest that such a combination vaccine may reduce the severity of retrovirus infection.
Results
Immunization regimen
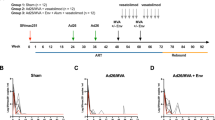
Preliminary experiments were conducted on mice to identify an immunization regimen that might be effective in rhesus monkeys. One week after a single immunization with Ad5/35-HIV or MVA-HIV (encoding full-length HIV gp160), the number of HIV-specific tetramer-positive CD8 T cells (derived from mouse peripheral blood mononuclear cells, PBMC) increased from background levels 0.05±0.01% to 5.2±0.4% or 3.2±0.3% (P<0.05; Figure 1). Priming and boosting with individual vectors induced a stronger response of 9.6±1.0 and 7.2±0.8% in the case of vaccination with Ad5/35-HIV and MVA-HIV, respectively (P<0.05 for both vectors; Figure 1). Priming with Ad5/35-HIV and boosting with MVA-HIV elicited a stronger response than priming/boosting with Ad5/35-HIV or MVA-HIV alone (14.5±1.2% for Ad5/35-HIV+MVA-HIV, P<0.05). Boosting with Ad5/35-GFP or MVA-GFP (encoding green fluorescent protein (GFP) without the H gene) did not alter the responses induced by the priming vaccination (data not shown). On the basis of these results, we studied the monkeys using an immunization regimen involving an Ad5/35 vector prime followed by an MVA vector boost.
Cell-mediated immunity in mice. BALB/c mice (n=10) were primed and boosted intramuscularly with 109 v.p. of Ad5/35-HIV and/or 106 PFU of MVA-HIV at 2-month intervals. An HIV-specific tetramer assay was performed 1 week after the final immunization. The panels show the representative data for each group. Upper panel, a single immunization; bottom panel, prime/boost with a different vector; right panel, Ad vector prime and MVA vector boost.
SIV viral load
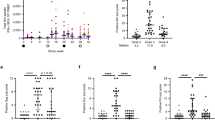
An Ad5/35 prime and MVA boost (encoding SIV gag and gp120) were administered to rhesus monkeys (n=5). After 2 months, these animals were challenged with 100 TCID50 (50% tissue culture infectious dose) of SIVmac239 (Figure 2). In both vaccinated and unvaccinated animals, the SIV viral load peaked on day 10. As seen in Figure 2, the mean plasma SIV RNA copy number on day 10 was 7.23±0.26 log10 in the unvaccinated monkeys compared to 5.13±0.62 log10 in the vaccinated monkeys (P=0.026). Over the ensuing 8 months, the SIV RNA load of the vaccinated monkeys averaged 4.21±1.73 log10 viral copies per ml, which is more than an order of magnitude lower than that of unvaccinated monkeys (P<0.0001).
A very similar pattern was observed in studies on SIV DNA load, which peaked on day 10 and then equilibrated (Figure 3). On day 10, the mean plasma SIV DNA copy number was 6.24±0.19 log10 in the unvaccinated monkeys compared to 4.92±0.33 log10 in the vaccinated monkeys (P=0.020). Over the ensuing 8 months, the SIV DNA load of the vaccinated monkeys averaged 3.77±0.23 log10 viral copies per million cells, which is more than two orders of magnitude lower than that of the unvaccinated monkeys (P<0.0001). After SIV challenge, the SIV RNA load showed a positive correlation with the SIV DNA load (R=0.575±0.02) from day 0 to 232.
SIV DNA copy number. Upper panel shows the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) SIV viral DNA copy number for individual monkeys, whereas the bottom panel shows the geometric means of PBMC SIV viral DNA copy number for the vaccinated vs unvaccinated monkeys. Vac, vaccinated monkey (n=5); Con, control monkey (n=4).
T-cell count
The number of CD4 T cells in peripheral circulation is an important index of SIV progression. Vaccination did not alter the CD4 T-cell count (Figure 4, upper panel). SIV infection resulted in a rapid reduction in the number of CD4 T cells in unvaccinated monkeys (it decreased from 1600 per μl to 500 per μl within 10 days; Figure 4, middle and bottom panels). In contrast, SIV challenge in the vaccinated group resulted in only a slight reduction in the number of CD4 T cells (P=0.006). The CD4 count of the vaccinated monkeys was similar to that of the unvaccinated monkeys on the day of challenge (P=0.8), but was significantly higher after SIV challenge (P<0.0001). The CD4 count was inversely correlated with the SIV RNA load (R=−0.343±0.03) and the SIV DNA load (R=−0.443±0.02) from days 10 to 232 after the SIV challenge. The effect of vaccination and challenge on the number of CD8 T cells was also investigated. However, none of these interventions had a significant impact (alone or in combination) on the CD8 cell count (data not shown). These data suggest that the Ad prime/MVA boost vaccination strategy enabled the control of CD4 cell loss after SIV infection in rhesus monkeys.
CD4 T-cell count. The upper and middle panels show CD4 T-cell counts for individual monkeys before and after SIV challenge, respectively; the bottom panel shows the geometric means of CD4 count for the vaccinated and naive monkeys after SIV challenge. Vac, vaccinated monkey (n=5); Con, control monkey (n=4).
Central memory T cells
On days 0, 14 and 232 after SIV challenge, we detected CD4 subset cells. Approximately 41.7 and 59.3% of naive CD4 T cells, 10.5 and 14.0% of effector memory (EM) CD4 T cells, and 47.2 and 25.2% of CM CD4 T cells were detected in the vaccine and control groups, respectively, on day 232 after SIV infection (Figure 5, upper panel). No significant difference was found between the groups about the number of naive, EM and CM CD4 T cells before the SIV challenge (P<0.05; Figure 5, bottom panel), but a significant difference was found in the number of CM CD4 T cells after the SIV infection (532 vs 194 on day 14, P<0.05; 450 vs 175 on day 232, P<0.05). The data obtained from this study show that the vaccination failed to control SIV replication completely, but prevented CM CD4 T-cell loss to a remarkable extent, which may greatly influence disease progression.23
Memory T cells. Memory CD4 T cells derived from monkey peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were studied before and after SIV challenge. Naive CD4 T cells (Naive), effector memory CD4 T cells (EM) and central memory CD4 T cells (CM) were identified as CD3+CD4+CD95–CD28+, CD3+CD4+CD95+CD28– and CD3+CD4+CD95+CD28+, respectively. Vac, vaccinated monkey (n=5); Con, control monkey (n=4).
SIV-specific cell-mediated immunity
Cell-mediated immunity was monitored by the interferon-γ (IFNγ) ELISpot assay. Ad vaccine elicited a strong SIV-specific IFNγ response (Figure 6, top panel). MVA vaccination further enhanced the magnitude of their responses. Two monkeys (Vac1 and Vac3) mounted strong memory responses, whereas other two monkeys (Vac4 and Vac5) mounted much weaker responses after the MVA boost. After the SIV challenge, the control group showed an increase of approximately 10-fold in the SIV-specific IFNγ response, which was sustained for 8 months (Figure 6, bottom panel). The response was also increased in the vaccine group; it was 10-fold higher than that in the control group until the end of the study (P<0.05). The IFNγ response without peptide stimulation in the vaccine group and with peptide stimulation in the control group was less than 50 spots per million cells. We found that the IFNγ response was inversely correlated with the SIV RNA viral load (R=−0.430±0.03) and SIV DNA load (R=−0.425±0.02) and positively correlated with the CD4 count (R=0.430±0.02) from days 10 to 232.
Ag-specific IFNγ-secreting T cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were stimulated using a pool of overlapping 15 amino-acid peptides from SIVmac239 gag and gp120. The upper and middle panels show IFNγ-secreting cells per million PBMC for each monkey before and after simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) challenge, whereas the bottom panel shows the geometric means (±s.e.) of antigen-specific IFNγ-secreting T cells for the vaccinated and unvaccinated monkeys after SIV infection. Vac, vaccinated monkey (n=5); Con, control monkey (n=4).
SIV-specific antibody
The SIV-specific anti-gag and anti-env Ab levels were monitored by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anti-gag Abs were first detected 2 weeks after vaccination (Figure 7, top panel) and increased on days 45 and 60. Unlike the cell-mediated immune response, boosting with MVA did not enhance humoral immunity. After SIV infection, the anti-SIVgag Ab levels increased further in the vaccinated animals. A lower SIVgag-specific Ab response also developed after SIV challenge in the unvaccinated monkeys (Figure 7, middle and bottom panels). Indeed, the titers in the vaccinated monkeys remained significantly higher than those in the unvaccinated monkeys at all time points after SIV infection (P<0.05). The SIV gag-specific Ab was positively correlated with the SIV-IFNγ response (R=0.620±0.03) and CD4 count (R=0.655±0.02), and inversely correlated with the SIV RNA load (R=−0.662±0.02) and the SIV DNA load (R=−0.714±0.03). A similar pattern was observed in the anti-SIVenv Ab response (Figure 8). SIV infection increased SIVenv-specific Ab levels in both vaccinated and unvaccinated monkeys, with the former producing higher and more long-lasting anti-env Ab titers. Similar to the SIV gag-specific Ab, the anti-env Ab was also positively correlated with the SIV-IFNγ response (R=0.577±0.02) and CD4 count (R=0.632±0.02), and inversely correlated with the SIV RNA load (R=−0.610±0.03) and SIV DNA load (R=−0.662±0.02).
Anti-SIVgag Ab titer. Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-specific Ab titers were examined at the indicated times. The upper and middle panels show the anti-SIVgag Ab titer for individual monkeys before and after SIV challenge, whereas the bottom panel shows the geometric means of the titers for the vaccinated and unvaccinated monkeys. Vac, vaccinated monkey (n=5); Con, control monkey (n=4).
Anti-SIVenv Ab titer and neutralizing Ab. Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-specific Ab titers were examined at the indicated times. The upper and middle panels show anti-SIVenv Ab titer for individual monkeys, whereas the bottom panel shows the geometric means of the titers for the vaccinated and unvaccinated monkeys. Vac, vaccinated monkey (n=5); Con, control monkey (n=4).
Discussion
This study explores the effect of a vaccine regimen involving an Ad prime/MVA boost on the induction of protective immunity against SIVmac239 infection in rhesus monkeys. The results of this study show that this vaccination regimen significantly reduced both the SIV RNA and the DNA viral loads. Furthermore, the vaccinated monkeys maintained their total and CM CD4 T-cell numbers, suggesting that vaccination may reduce susceptibility to the detrimental manifestations of progressive retrovirus infection.
SIV and chimeric SHIV are used to model HIV infection in monkeys. SIV induces a chronic infection similar to that induced by HIV-1 in humans, whereas SHIV causes a more rapidly progressive disease characterized by the loss of CD4 T cells and death.10, 24 Recent studies show that vaccination is more effective against SHIV infections than against SIV infections.10, 25, 26 Live and live-attenuated vaccines have been used successfully to prevent many infectious diseases (see review by Koff et al.26). A live-attenuated vaccine with minor modifications (SIVDeltanef) may induce sterile protection, but may eventually result in disease. In contrast, increased attenuation of the live-attenuated vaccine makes the vaccines less pathogenic, but results in significantly reduced protection. Till date, no live-attenuated vaccines have been found well tolerated and result in sterile protection. Because of the safety concerns and inadequate protection of the more attenuated live-attenuated vaccine, the vaccine field is currently not actively pursuing live-attenuated vaccines for use in humans.1, 4, 6, 27, 28, 29, 30 Previously, the efficacy of various Ad- and MVA-based vaccines about the susceptibility to SHIV infection in monkeys has been examined by our research group and other scientists.10, 24 This study investigates whether a combination of these vaccines can prevent SIV infection.
Considerable research has been conducted using DNA vaccines (individually or with proteins and/or cytokines),25 Ad-based vaccines (replication competent or replication deficient), vaccinia virus-based vaccines (MVA, canarypox virus (ALVAC) and attenuated vaccinia (NYVAC))31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, and other vectors37, 38 alone or in combination to induce antigen-specific anti-retroviral responses in animals. Administration of a recombinant viral vector can induce strong humoral and cell-mediated immune responses against both transgene and viral vectors. A different viral vector can be used as a boost to generate the immunity induced by a priming vector, and it is expected to elicit a high response. This work first evaluated the immune response induced when mice were immunized and boosted with an Ad vaccine, MVA vaccine and a staggered combination of both vaccines. The results showed that the combination of an Ad prime and MVA boost in a mouse model elicited a stronger CTL response than any other regimen (Figure 1). Double-stranded viral DNA genome (such as Ad and vaccinia virus)39, 40, 41, 42 and their viral proteins43, 44 can induce innate immunity in vitro, resulting in type I IFN secretion following activation of adaptive immunity. However, no remarkable alteration of HIV-specific cell-mediated immune response was observed when a null virus vector was used as a boost (data not shown); this indicated that the adjuvant effect of the null virus vector when used as the boost was limited to a great extent in vivo. This finding is consistent with that for a similar prime/boost regimen reported by Draper et al.;45 their study focused on humoral immunity against malaria; it is also in agreement with the finding reported by Santra et al.,22 who focused on cell-mediated immunity against HIV in a monkey model.
Detailed studies performed on rhesus monkeys showed that this vaccination strategy significantly reduced both peak and persistent viral loads after SIV challenge (Figure 2), and prevented CD4 T-cell loss (Figure 4). Unfortunately, the replication of the SIV challenge virus was not completely controlled, and further studies should be conducted to explore monkey mortality and to examine whether SIV replication can be controlled for a long period by antigen-specific immunity. Taking into consideration the recent failure of a large-scale clinical trial that involved the use of an Ad5 vector14 and a recent study that compared the immunogenicity and protective immunity of a combination of the Ad26, Ad35 and Ad5 vectors, in which partial protection against SIV was observed,46 we conclude that the current replication-deficient viral vector needs further improvement.
Infection by HIV/SIV causes the biphasic destruction of CD4 T cells. Rapid loss of a considerable amount of memory CD4 T cells is mediated by early viral infection;47, 48, 49 this is followed by a slow but progressive loss of CD4 T cells mediated by chronic processes.50, 51 The memory CD4 T cells that survive the initial virus-mediated purge may subsequently expand, and several studies have suggested that prophylactic vaccination may help preserve and maintain these memory CD4 T cells.13, 23, 52 Numerous studies have verified the importance of CM CD4 T cells in suppressing viral replication and mortality after viral infections.13, 23, 46 In the current study, memory CD4 T cells were present in the PBMC before and after SIV infection. After SIV infection, no significant difference was observed in the number of naive CD4 T cells and EM CD4 T cells between the vaccine and control groups (Figure 5). The vaccinated group also showed some loss of CM CD4 T cells when infected with SIV (Figure 5); however, there was a dramatic loss of CM T cells in the control group. This was previously shown to correlate with survival in SIV-infected monkeys.13, 23
Vaccination induced both anti-SIVgag- and anti-SIVenv-specific Ab production (Figures 7 and 8). Like any other current HIV vaccine, this vaccine may not be expected to elicit humoral immune responses that can broadly neutralize HIV/SIV isolates for a prolonged period of time. However, recent studies show that vaccination with viral vectors such as Ad vectors can elicit Ab-dependent cell-mediated virus inhibition by non-neutralizing antibodies.46, 53 Therefore, antibodies, including non-neutralizing antibodies, will be helpful for the control of HIV/SIV replication.
This study was conducted on Chinese rhesus monkeys rather than the more commonly studied Indian rhesus monkeys. We were unable to determine the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) type of the Chinese monkeys with the currently available reagents.54 These reagents are thus effective only for MHC type of Indian monkeys, suggesting that these populations are genetically distinct. In this context, Ling et al.55 reported that Chinese rhesus monkeys more closely resemble humans than Indian monkeys do in terms of viral load and CD4 T-cell count following retroviral infection. In Indian rhesus monkeys, certain MHC-I alleles (including Mamu-B*0849, Mamu-B*1750 and to a lesser extent, Manu A*01) and MHC-II alleles (such as Mamu-DRB1*1003 and -DRB1*030651) are associated with improved control of viral replication and progress independent of immunization history. Thus, it is possible that protective alleles also exist in Chinese rhesus monkeys. Because the MHC of the rhesus monkeys used in this study is different from that of the majority of humans infected with HIV-1, the findings obtained in this particular strain of rhesus monkey may have implications when conducting research on humans. However, because available reagents failed to MHC-type monkeys used in this study, there is no reason to expect that the consistent improvement observed in all vaccinated animals was a consequence of such an effect.
In summary, this work explored the use of an Ad5/35 prime/MVA boost regimen in providing protection against SIV challenge in a relevant primate model. Vaccination induced robust SIV-specific CTL and humoral immunity that significantly reduced both the peak and set points of the SIV viral load. In addition, this vaccination prevented the loss of total CD4 and CM CD4 T cells, which is typically observed after SIV infection of rhesus monkeys. These findings suggest that such a vaccination strategy may have a beneficial impact on disease severity, even though it currently cannot provide sterilizing immunity.
Materials and methods
Animals
BALB/c mice (8-week old) and male Chinese rhesus monkeys (4- to 6-year old) were used in the vaccination/challenge studies. The monkeys were maintained according to standard operating procedures established for the evaluation of human vaccines at the Animal Center, Chinese Medical Scientific Institute, Beijing, China. The study was permitted by the Animal Administer Community of Chinese Medical Scientific Institute and was in accordance with requirements specified in the laboratory biosafety manual of the World Health Organization.
Viruses
In murine studies, an Ad5/35 expressing HIVIIIB gp160 (Ad5/35-HIV9) and MVA expressing HIVBH2 gp160 (MVA-HIV, kind gift from Dr Bernard Moss, National Institutes of Health, Rockville, MD, USA) were used. Two viral vectors were used in the monkey study as vaccines. In monkey studies, an Ad5/35 vector11 expressing SIVmac239 full length of Gag and gp120 (Ad5/35-SIV) and an MVA vector expressing SIVmac239 full length of Gag and gp120 (MVA-SIV) was used, as described previously.11 The Ad5/35 virus was propagated in HEK293 cells and purified over CsCl as described elsewhere.10 The total concentration of virions in each preparation was calculated by the formula 1 OD260=1012 viral particle (v.p.) per ml. MVA virus was propagated in the BHK21 cell line and purified by one round of ultracentrifuge over 36% sucrose. The MVA virus was titrated in the BHK21 cells to determine the number of plaque-forming units (PFU). The SIVmac239 virus lot (named SIVman239/nef prepared in CEMx174 cells)54 was used in challenge experiments, which was kindly provided by Dr Thomas Friedrich (Wisconsin National Primate Research Center, Madison, WI, USA).
Immunizations
Mice (n=10) were immunized intramuscularly with 109 v.p. of Ad5/35-HIV, 106 PFU of MVA-HIV alone or a combination of both at 2-month intervals. Monkeys (n=5) were immunized intramuscularly with 1012 v.p. of Ad5/35-SIV and 109 PFU of MVA-SIV vaccine on days 0 and 60, respectively. Control monkeys (n=4) were not immunized but like the vaccinated animals were challenged intravenously with 100 TCID50 of SIVmac239 virus 60 days after MVA-SIV vaccination.
Antibodies and flow cytometry
All antibodies were purchased from BD Pharmingen (San Diego, CA, USA). Anti-mouse CD8-FITC (Ly-2) Ab was used for mouse tetramer staining. Anti-human CD3-PerCP/Cy5.5, CD4-FITC and CD8-PE antibodies were used to stain monkey CD4 and CD8 cells. Anti-human CD3-APC, CD4-PerCP/Cy5.5, CD95-PE and CD28-FITC antibodies were used to stain memory T cells. Naive CD4 T cells, EM CD4 T cells and CM CD4 T cells were identified as CD3+CD4+CD95−CD28+, CD3+CD4+CD95+CD28− and CD3+CD4+CD95+CD28+, respectively.13, 23, 46
Tetramer assay
These assays were performed as described previously.9 The H-2Dd/p18 tetramer (RGPGRAFVTI, synthesized by NIH Tetramer Core Facility, Atlanta, GA, USA) labeled with PE was used for tetramer assay. Briefly, 100 μl of heparin-preserved whole mouse blood was stained with 0.5 μg of FITC-conjugated anti-mouse CD8 Ab and 0.05 μg of tetramer reagent at room temperature for 30 min. The cells were then fixed with 100 μl of OptiLyse B-Lysing solution (Beckman Coulter, Marseille Cedex, France) at room temperature for 10 min. Erythrocytes were lysed by adding 1 ml of H2O and twice washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) followed by flow cytometric analysis.
ELISpot analysis
Ninety-six-well flat-bottom plates (Millipore) were coated overnight with 10 μg ml−1 of anti-human IFNγ Ab (B27; BD Pharmingen), washed and blocked with 5% fetal calf serum (FCS) in PBS. PBMC were isolated by density-gradient centrifugation from EDTA-preserved rhesus monkey blood. The unfractionated PBMC were washed in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FCS and seeded into the Ab-coated wells at 2 × 105 cells per well. Cells were stimulated in vitro with 1 μg ml−1 of SIVmac239 gp120 and a Gag peptide pool (overlapping 15 amino-acid peptides provided by the AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Program, NIH, Rockville, MD, USA), 5 μg ml−1 PHA-M (Sigma-Aldrich Japan, Tokyo, Japan) or medium alone. Cells were cultured for 18 h at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 in air incubator. Plates were developed with 2 μg ml−1 of biotinylated rabbit polyclonal anti-human IFNγ antiserum (BioSource International, Camarillo, CA, USA), washed and incubated with streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase (Southern Biotechnology, Birmingham, AL, USA). After a final rinse, NBT/BCIP (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) was added for 10–15 min, and the plates were washed and air-dried. Developed wells were imaged, and spot-forming cells were counted using the KS ELISPOT compact system (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). Spot-forming cells were defined as a large black spot with a fuzzy border.
Competitive PCR
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated by density-gradient centrifugation from EDTA-preserved rhesus monkey blood. Total viral genomic RNA was extracted from 200 μl of the plasma using TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Quantitative, competitive RT-PCR was performed using a QuantiTect SYBR Green RT-PCR kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with sense primer sequence (GTAACTATGTCCACCTGCCATTA, binding to SIV genome no. 554–576) and anti-sense primer sequence (CAGCCTCCTCGTTTATGATGT, binding to SIV genome no 763–742 of gag region). Total cellular genomic DNA was extracted from monkey PBMC. Quantitative, competitive PCR was performed using a QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR kit (Qiagen) with above primer pair.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was performed as described elsewhere. To summarize, 96-well microtiter plates were coated with 200 ng ml−1 of SIVmac239 Gag or gp120 peptide pool. The plate was incubated overnight at 4 °C and blocked with PBS 1%–bovine serum albumin for 2 h at room temperature. Diluted anti-sera were added and incubated for 2 h at 37 °C, and bound Ig was quantified using an affinity-purified horseradish-peroxidase-labeled anti-human Ab (Sigma-Aldrich, Tokyo, Japan). Ab titer was measured by OD450 and compared to a standard high-titered anti-serum.
Data analysis
All values were expressed as means±s.e. Statistical analysis was performed between the vaccine group and control group using nonparametric Mann–Whitney U-test. P-values of <0.05 were considered significant. Simple linear regression analysis was used to estimate the relationship between vaccine group and control group. Analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel Statistics 2004 for Windows (SSRI Co Ltd, Tokyo, Japan).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Daniel MD, Kirchhoff F, Czajak SC, Sehgal PK, Desrosiers RC . Protective effects of a live attenuated SIV vaccine with a deletion in the nef gene. Science 1992; 258: 1938–1941.
Joag SV, Liu ZQ, Stephens EB, Smith MS, Kumar A, Li Z et al. Oral immunization of macaques with attenuated vaccine virus induces protection against vaginally transmitted AIDS. J Virol 1998; 72: 9069–9078.
Koff WC, Johnson PR, Watkins DI, Burton DR, Lifson JD, Hasenkrug KJ et al. HIV vaccine design: insights from live attenuated SIV vaccines. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 19–23.
Wyand MS, Manson K, Montefiori DC, Lifson JD, Johnson RP, Desrosiers RC . Protection by live, attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus against heterologous challenge. J Virol 1999; 73: 8356–8363.
Hofmann-Lehmann R, Vlasak J, Williams AL, Chenine AL, McClure HM, Anderson DC et al. Live attenuated, nef-deleted SIV is pathogenic in most adult macaques after prolonged observation. AIDS 2003; 17: 157–166.
Reynolds MR, Weiler AM, Weisgrau KL, Piaskowski SM, Furlott JR, Weinfurter JT et al. Macaques vaccinated with live-attenuated SIV control replication of heterologous virus. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 2537–2550.
Havenga MJ, Lemckert AA, Ophorst OJ, van Meijer M, Germeraad WT, Grimbergen J et al. Exploiting the natural diversity in adenovirus tropism for therapy and prevention of disease. J Virol 2002; 76: 4612–4620.
Roelvink PW, Lizonova A, Lee JG, Li Y, Bergelson JM, Finberg RW et al. The Coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor protein can function as a cellular attachment protein for adenovirus serotypes from subgroups A, C, D, E, and F. J Virol 1998; 72: 7909–7915.
Xin KQ, Jounai N, Someya K, Honma K, Mizuguchi H, Naganawa S et al. Prime-boost vaccination with plasmid DNA and a chimeric adenovirus type 5 vector with type 35 fiber induces protective immunity against HIV. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 1769–1777.
Shiver JW, Fu TM, Chen L, Casimiro DR, Davies ME, Evans RK et al. Replication-incompetent adenoviral vaccine vector elicits effective anti-immunodeficiency-virus immunity. Nature 2002; 415: 331–335.
Shimada M, Wang HB, Kondo A, Xu XP, Yoshida A, Shinoda K et al. Effect of therapeutic immunization using Ad5/35 and MVA vectors on SIV infection of rhesus monkeys undergoing antiretroviral therapy. Gene Therapy 2009; 16: 218–228.
Roberts DM, Nanda A, Havenga MJ, Abbink P, Lynch DM, Ewald BA et al. Hexon-chimaeric adenovirus serotype 5 vectors circumvent pre-existing anti-vector immunity. Nature 2006; 441: 239–243.
Mattapallil JJ, Douek DC, Buckler-White A, Montefiori D, Letvin NL, Nabel GJ et al. Vaccination preserves CD4 memory T cells during acute simian immunodeficiency virus challenge. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1533–1541.
Sekaly RP . The failed HIV Merck vaccine study: a step back or a launching point for future vaccine development? J Exp Med 2008; 205: 7–12.
Perreau M, Pantaleo G, Kremer EJ . Activation of a dendritic cell–T cell axis by Ad5 immune complexes creates an improved environment for replication of HIV in T cells. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 2717–2725.
Gao W, Robbins PD, Gambotto A . Human adenovirus type 35: nucleotide sequence and vector development. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 1941–1949.
Gaggar A, Shayakhmetov DM, Lieber A . CD46 is a cellular receptor for group B adenoviruses. Nat Med 2003; 9: 1408–1412.
Meyer H, Sutter G, Mayr A . Mapping of deletions in the genome of the highly attenuated vaccinia virus MVA and their influence on virulence. J Gen Virol 1991; 72 (Part 5): 1031–1038.
Carroll MW, Moss B . Host range and cytopathogenicity of the highly attenuated MVA strain of vaccinia virus: propagation and generation of recombinant viruses in a nonhuman mammalian cell line. Virology 1997; 238: 198–211.
Stickl H, Hochstein-Mintzel V, Mayr A, Huber HC, Schafer H, Holzner A . [MVA vaccination against smallpox: clinical tests with an attenuated live vaccinia virus strain (MVA) (author's translation)]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 1974; 99: 2386–2392.
Amara RR, Villinger F, Altman JD, Lydy SL, O’Neil SP, Staprans SI et al. Control of a mucosal challenge and prevention of AIDS by a multiprotein DNA/MVA vaccine. Science 2001; 292: 69–74.
Santra S, Sun Y, Parvani JG, Philippon V, Wyand MS, Manson K et al. Heterologous prime/boost immunization of rhesus monkeys by using diverse poxvirus vectors. J Virol 2007; 81: 8563–8570.
Letvin NL, Mascola JR, Sun Y, Gorgone DA, Buzby AP, Xu L et al. Preserved CD4+ central memory T cells and survival in vaccinated SIV-challenged monkeys. Science 2006; 312: 1530–1533.
Amara RR, Villinger F, Staprans SI, Altman JD, Montefiori DC, Kozyr NL et al. Different patterns of immune responses but similar control of a simian-human immunodeficiency virus 89.6P mucosal challenge by modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) and DNA/MVA vaccines. J Virol 2002; 76: 7625–7631.
Barouch DH, Craiu A, Kuroda MJ, Schmitz JE, Zheng XX, Santra S et al. Augmentation of immune responses to HIV-1 and simian immunodeficiency virus DNA vaccines by IL-2/Ig plasmid administration in rhesus monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 4192–4197.
Koff WC, Parks CL, Berkhout B, Ackland J, Noble S, Gust ID . Replicating viral vectors as HIV vaccines Summary Report from IAVI Sponsored Satellite Symposium, International AIDS Society Conference, July 22, 2007. Biologicals 2008; 36: 277–286.
Johnson RP, Lifson JD, Czajak SC, Cole KS, Manson KH, Glickman R et al. Highly attenuated vaccine strains of simian immunodeficiency virus protect against vaginal challenge: inverse relationship of degree of protection with level of attenuation. J Virol 1999; 73: 4952–4961.
Wyand MS, Manson KH, Garcia-Moll M, Montefiori D, Desrosiers RC . Vaccine protection by a triple deletion mutant of simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 1996; 70: 3724–3733.
Baba TW, Liska V, Khimani AH, Ray NB, Dailey PJ, Penninck D et al. Live attenuated, multiply deleted simian immunodeficiency virus causes AIDS in infant and adult macaques. Nat Med 1999; 5: 194–203.
Baba TW, Jeong YS, Pennick D, Bronson R, Greene MF, Ruprecht RM . Pathogenicity of live, attenuated SIV after mucosal infection of neonatal macaques. Science 1995; 267: 1820–1825.
Amara RR, Smith JM, Staprans SI, Montefiori DC, Villinger F, Altman JD et al. Critical role for Env as well as Gag-Pol in control of a simian-human immunodeficiency virus 89.6P challenge by a DNA prime/recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara vaccine. J Virol 2002; 76: 6138–6146.
Autran B, Murphy RL, Costagliola D, Tubiana R, Clotet B, Gatell J et al. Greater viral rebound and reduced time to resume antiretroviral therapy after therapeutic immunization with the ALVAC-HIV vaccine (vCP1452). Aids 2008; 22: 1313–1322.
Liu J, Yu Q, Stone GW, Yue FY, Ngai N, Jones RB et al. CD40L expressed from the canarypox vector, ALVAC, can boost immunogenicity of HIV-1 canarypox vaccine in mice and enhance the in vitro expansion of viral specific CD8+ T cell memory responses from HIV-1-infected and HIV-1-uninfected individuals. Vaccine 2008; 26: 4062–4072.
Thongcharoen P, Suriyanon V, Paris RM, Khamboonruang C, de Souza MS, Ratto-Kim S et al. A phase 1/2 comparative vaccine trial of the safety and immunogenicity of a CRF01_AE (subtype E) candidate vaccine: ALVAC-HIV (vCP1521) prime with oligomeric gp160 (92TH023/LAI-DID) or bivalent gp120 (CM235/SF2) boost. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2007; 46: 48–55.
Gomez CE, Najera JL, Krupa M, Esteban M . The poxvirus vectors MVA and NYVAC as gene delivery systems for vaccination against infectious diseases and cancer. Curr Gene Ther 2008; 8: 97–120.
Ferrier-Rembert A, Drillien R, Tournier JN, Garin D, Crance JM . Short- and long-term immunogenicity and protection induced by non-replicating smallpox vaccine candidates in mice and comparison with the traditional 1st generation vaccine. Vaccine 2008; 26: 1794–1804.
Xin KQ, Urabe M, Yang J, Nomiyama K, Mizukami H, Hamajima K et al. A novel recombinant adeno-associated virus vaccine induces a long-term humoral immune response to human immunodeficiency virus. Hum Gene Ther 2001; 12: 1047–1061.
Xin KQ, Hoshino Y, Toda Y, Igimi S, Kojima Y, Jounai N et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of orally administered recombinant Lactococcus lactis expressing surface-bound HIV Env. Blood 2003; 102: 223–228.
Ishii KJ, Kawagoe T, Koyama S, Matsui K, Kumar H, Kawai T et al. TANK-binding kinase-1 delineates innate and adaptive immune responses to DNA vaccines. Nature 2008; 451: 725–729.
Ishii KJ, Coban C, Kato H, Takahashi K, Torii Y, Takeshita F et al. A Toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 40–48.
Zhu J, Huang X, Yang Y . Innate immune response to adenoviral vectors is mediated by both Toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. J Virol 2007; 81: 3170–3180.
Martinez J, Huang X, Yang Y . Direct action of type I IFN on NK cells is required for their activation in response to vaccinia viral infection in vivo. J Immunol 2008; 180: 1592–1597.
Nociari M, Ocheretina O, Murphy M, Falck-Pedersen E . Adenovirus induction of IRF3 occurs through a binary trigger targeting Jun N-terminal kinase and TBK1 kinase cascades and type I interferon autocrine signaling. J Virol 2009; 83: 4081–4091.
Agrawal S, Gupta S, Agrawal A . Vaccinia virus proteins activate human dendritic cells to induce T cell responses in vitro. Vaccine 2009; 27: 88–92.
Draper SJ, Moore AC, Goodman AL, Long CA, Holder AA, Gilbert SC et al. Effective induction of high-titer antibodies by viral vector vaccines. Nat Med 2008; 14: 819–821.
Liu J, O’Brien KL, Lynch DM, Simmons NL, La Porte A, Riggs AM et al. Immune control of an SIV challenge by a T-cell-based vaccine in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2009; 457: 87–91.
Mattapallil JJ, Douek DC, Hill B, Nishimura Y, Martin M, Roederer M . Massive infection and loss of memory CD4+ T cells in multiple tissues during acute SIV infection. Nature 2005; 434: 1093–1097.
Song K, Rabin RL, Hill BJ, De Rosa SC, Perfetto SP, Zhang HH et al. Characterization of subsets of CD4+ memory T cells reveals early branched pathways of T cell differentiation in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 7916–7921.
Picker LJ, Watkins DI . HIV pathogenesis: the first cut is the deepest. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 430–432.
Douek DC . Disrupting T-cell homeostasis: how HIV-1 infection causes disease. AIDS Rev 2003; 5: 172–177.
Douek DC, Picker LJ, Koup RA . T cell dynamics in HIV-1 infection. Annu Rev Immunol 2003; 21: 265–304.
Kawada M, Tsukamoto T, Yamamoto H, Iwamoto N, Kurihara K, Takeda A et al. Gag-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-based control of primary simian immunodeficiency virus replication in a vaccine trial. J Virol 2008; 82: 10199–10206.
Hidajat R, Xiao P, Zhou Q, Venzon D, Summers LE, Kalyanaraman VS et al. Correlation of vaccine-elicited systemic and mucosal nonneutralizing antibody activities with reduced acute viremia following intrarectal simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251 challenge of rhesus macaques. J Virol 2009; 83: 791–801.
O’Connor DH, Mothe BR, Weinfurter JT, Fuenger S, Rehrauer WM, Jing P et al. Major histocompatibility complex class I alleles associated with slow simian immunodeficiency virus disease progression bind epitopes recognized by dominant acute-phase cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte responses. J Virol 2003; 77: 9029–9040.
Ling B, Veazey RS, Luckay A, Penedo C, Xu K, Lifson JD et al. SIV(mac) pathogenesis in rhesus macaques of Chinese and Indian origin compared with primary HIV infections in humans. AIDS 2002; 16: 1489–1496.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Chuan Qin, Dr Hong Gao and Dr Li-San Pan (Institute of Laboratory Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences) for animal care and treatment. This work was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan; a grant for the Strategic Research Project of Yokohama City University, Japan; a grant from Research Foundation for Advanced Medical Research Center and a grant from the Japanese National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (no. 05-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HB., Kondo, A., Yoshida, A. et al. Partial protection against SIV challenge by vaccination of adenovirus and MVA vectors in rhesus monkeys. Gene Ther 17, 4–13 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2009.122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2009.122