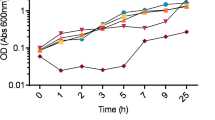
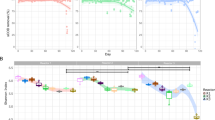
Abstract
Understanding adaptation of biological communities to environmental change is a central issue in ecology and evolution. Metagenomic analysis of a stressed groundwater microbial community reveals that prolonged exposure to high concentrations of heavy metals, nitric acid and organic solvents (∼50 years) has resulted in a massive decrease in species and allelic diversity as well as a significant loss of metabolic diversity. Although the surviving microbial community possesses all metabolic pathways necessary for survival and growth in such an extreme environment, its structure is very simple, primarily composed of clonal denitrifying γ- and β-proteobacterial populations. The resulting community is overabundant in key genes conferring resistance to specific stresses including nitrate, heavy metals and acetone. Evolutionary analysis indicates that lateral gene transfer could have a key function in rapid response and adaptation to environmental contamination. The results presented in this study have important implications in understanding, assessing and predicting the impacts of human-induced activities on microbial communities ranging from human health to agriculture to environmental management, and their responses to environmental changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Allen EE, Banfield JF . (2005). Community genomics in microbial ecology and evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol 3: 489–498.
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 25: 3389–3402.
Bearson S, Bearson B, Foster JW . (1997). Acid stress responses in enterobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 147: 173–180.
Brodie EL, DeSantis TZ, Joyner DC, Baek SM, Larsen JT, Andersen GL et al. (2006). Application of a high-density oligonucleotide microarray approach to study bacterial population dynamics during uranium reduction and reoxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 6288–6298.
Chou H-H, Holmes MH . (2001). DNA sequence quality trimming and vector removal. Bioinformatics 17: 1093–1104.
de Lipthay JR, Rasmussen LD, Oregaard G, Simonsen K, Bahl MI, Kroer N et al. (2008). Acclimation of subsurface microbial communities to mercury. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65: 145–155.
DeLong EF, Preston CM, Mincer T, Rich V, Hallam SJ, Frigaard N-U et al. (2006). Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean's interior. Science 311: 496–503.
DeMoss JA, Hsu PY . (1991). NarK enhances nitrate uptake and nitrite excretion in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 173: 3303–3310.
Dwernychuk L . (1972). Ducks nesting in association with gulls—an ecological trap. Can J Zool 50: 559.
Fields MW, Yan T, Rhee SK, Carroll SL, Jardine PM, Watson DB et al. (2005). Impacts on microbial communities and cultivable isolates from groundwater contaminated with high levels of nitric acid-uranium waste. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53: 417–428.
Fields MW, Bagwell CE, Carroll SL, Yan T, Liu X, Watson DB et al. (2006). Phylogenetic and functional biomakers as indicators of bacterial community responses to mixed-waste contamination. Environ Sci Technol 40: 2601–2607.
Fu YX . (1997). Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 147: 915–925.
Ge F, Wang L-S, Kim J . (2005). The cobweb of life revealed by genome-scale estimates of horizontal gene transfer. PLoS Biol 3: e316.
Gill SR, Pop M, DeBoy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS et al. (2006). Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 312: 1355–1359.
Handelsman J, Tiedje JM, Alvarez-Cohen L, Ashburner M, Cann IKO, DeLong EF et al. (2007). Committee on Metagenomics: Challenges and Functional Applications. National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC.
He Z, Gentry TJ, Schadt CW, Wu L, Liebich J, Chong SC et al. (2007). GeoChip: a comprehensive microarray for investigating biogeochemical, ecological and environmental processes. ISME J 1: 67–77.
Horvath RS . (1972). Microbial co-metabolism and the degradation of organic compounds in nature. Bacteriol Rev 36: 146–155.
Hwang C, Wu W, Gentry TJ, Carley J, Corbin GA, Carroll SL et al. (2009). Bacterial community succession during in situ uranium bioremediation: spatial similarities along controlled flow paths. ISME J 3: 47–64.
Langille M, Hsiao W, Brinkman F . (2008). Evaluation of genomic island predictors using a comparative genomics approach. BMC Bioinform 9: 329.
Lawrence JG, Ochman H . (1997). Amelioration of bacterial genomes: rates of change and exchange. J Mol Evol 44: 383–397.
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar AB et al. (2004). ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucl Acids Res 32: 1363–1371.
Markowitz VM, Ivanova NN, Szeto E, Palaniappan K, Chu K, Dalevi D et al. (2008). IMG/M: a data management and analysis system for metagenomes. Nucl Acids Res 36 (Database issue): D534–D538. gkm869.
Martinez RJ, Wang Y, Raimondo MA, Coombs JM, Barkay T, Sobecky PA . (2006). Horizontal gene transfer of PIB-type ATPases among bacteria isolated from radionuclide-and metal-contaminated subsurface soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 3111–3118.
McHardy AC, Martin HG, Tsirigos A, Hugenholtz P, Rigoutsos I . (2007). Accurate phylogenetic classification of variable-length DNA fragments. Nat Methods 4: 63–72.
Nei M, Kumar S . (2000). Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. Oxford University Press: New York, NY.
Palumbo AV, Schryver JC, Fields MW, Bagwell CE, Zhou JZ, Yan T et al. (2004). Coupling of functional gene diversity and geochemical data from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 6525–6534.
Petrie L, North NN, Dollhopf SL, Balkwill DL, Kostka JE . (2003). Enumeration and characterization of Iron(III)-reducing microbial communities from acidic subsurface sediments contaminated with Uranium(VI). Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 7467–7479.
Phillips DH, Watson DB, Kelly SD, Ravel B, Kemner KM . (2008). Deposition of uranium precipitates in dolomitic gravel fill. Environ Sci Technol 42: 7104–7110.
Rensing C, Newby DT, Pepper IL . (2002). The role of selective pressure and selfish DNA in horizontal gene transfer and soil microbial community adaptation. Soil Biol Biochem 34: 285–296.
Riesenfeld CS, Schloss PD, Handelsman J . (2004). Metagenomics: genomic analysis of microbial communities. Annu Rev Genet 38: 525–552.
Rozas J, Rozas R . (1999). DnaSP version 3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15: 174–175.
Rozas J, Gullaud M, Blandin G, Aguade M . (2001). DNA variation at the rp49 gene region of drosophila simulans: evolutionary inferences from an unusual haplotype structure. Genetics 158: 1147–1155.
Silver S, Phung LT . (1996). Bacterial heavy metal resistance: new surprises. Annu Rev Microbiol 50: 753–789.
Sluis MK, Ensign SA . (1997). Purification and characterization of acetone carboxylase from Xanthobacter strain Py2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 8456–8461.
Smets BF, Barkay T . (2005). Horizontal gene transfer: perspectives at a crossroads of scientific disciplines. Nat Rev Microbiol 3: 675–678.
Sokurenko EV, Feldgarden M, Trintchina E, Weissman SJ, Avagyan S, Chattopadhyay S et al. (2004). Selection footprint in the fimh adhesin shows pathoadaptive niche differentiation in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol 21: 1373–1383.
Stajich JE, Block D, Boulez K, Brenner SE, Chervitz SA, Dagdigian C et al. (2002). The bioperl toolkit: perl modules for the life sciences. Genome Res 12: 1611–1618.
Tajima F . (1989). Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123: 585–595.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S . (2007). MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (mega) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24: 1596–1599. msm092..
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Hamady M, Fraser-Liggett CM, Knight R, Gordon JI . (2007). The human microbiome project. Nature 449: 804–810.
Tyson GW, Chapman J, Hugenholtz P, Allen EE, Ram RJ, Richardson PM et al. (2004). Community structure and metabolism through reconstruction of microbial genomes from the environment. Nature 428: 37–43.
Voget S, Steele HL, Streit WR . (2006). Characterization of a metagenome-derived halotolerant cellulase. J Biotechnol 126: 26–36.
Waack S, Keller O, Asper R, Brodag T, Damm C, Fricke W et al. (2006). Score-based prediction of genomic islands in prokaryotic genomes using hidden Markov models. BMC Bioinform 7: 142.
Whitman WB, Coleman DC, Wiebe WJ . (1998). Prokaryotes: the unseen majority. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 6578–6583.
Wu D, Daugherty SC, Van Aken SE, Pai GH, Watkins KL, Khouri H et al. (2006). Metabolic complementarity and genomics of the dual bacterial symbiosis of sharpshooters. PLoS Biol 4: e188.
Yan T, Fields MW, Wu L, Zu Y, Tiedje JM, Zhou J . (2003). Molecular diversity and characterization of nitrite reductase gene fragments (nirK and nirS) from nitrate- and uranium-contaminated groundwater. Environ Microbiol 5: 13–24.
Yang Z . (1997). PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci 13: 555–556.
Yang Z . (2003). Adaptive molecular evolution. In: Balding DJ, Bishop M, Cannings C (eds) Handbook of Statistical Genetics, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd: New York, NY, pp 229–254.
Yooseph S, Sutton G, Rusch DB, Halpern AL, Williamson SJ, Remington K et al. (2007). The sorcerer ii global ocean sampling expedition: expanding the universe of protein families. PLoS Biol 5: e16.
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM . (1996). DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 316–322.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Fares Najar and Dr Bruce Roe for providing sequencing services, and Dr Tommy Phelps and Dr Christopher W Schadt for assisting groundwater sampling. This research was supported by The United States Department of Energy under the Environmental Remediation Sciences Program (ERSP), and Genomics: GTL program through the Virtual Institute of Microbial Stress and Survival (VIMSS; http://vimss.lbl.gov), Office of Biological and Environmental Research, Office of Science, and by the University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344, and Los Alamos National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06NA25396. Oak Ridge National Laboratory is managed by University of Tennessee UT-Battelle LLC for the Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725. All authors contributed intellectual input and assistance to this study and paper preparation. The original concept and experimental strategy were developed by JZ and MWF. Sampling collections and DNA preparation were performed by TG and LW. DW performed chemical analysis of the groundwater sample. KB and SGT oversaw metagenomic sequencing and assembly. CH performed all sequence and evolutionary analysis. YD assisted in computational analysis of metagenome sequences. SB performed PCR experiments for population genetics analysis and LGT confirmation. JZ and CH performed data synthesis, and took the lead in writing the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemme, C., Deng, Y., Gentry, T. et al. Metagenomic insights into evolution of a heavy metal-contaminated groundwater microbial community. ISME J 4, 660–672 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.154
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.154
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mixed heavy metal stress induces global iron starvation response
The ISME Journal (2023)
-
Impact of soil supplemented with pig manure on the abundance of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their associated genes
The Journal of Antibiotics (2023)
-
Fungal community diversity of heavy metal contaminated soils revealed by metagenomics
Archives of Microbiology (2022)
-
Culture-dependent to culture-independent approaches for the bioremediation of paints: a review
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2021)
-
Stress-related ecophysiology of members of the genus Rhodanobacter isolated from a mixed waste contaminated subsurface
Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering (2021)