Abstract
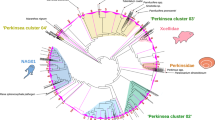
Protist parasites are ecologically important, as they can have great impact on host population dynamics and functioning of entire ecosystems. Nevertheless, little is known about their prevalence in aquatic habitats. Here, we investigate the diversity and distributional patterns of the protist parasites Perkinsus and Parvilucifera (Perkinsea). Our approach included 454 pyrosequencing of the 18S rDNA gene obtained from a high-altitude lake (Lake Finsevatn, Norway) and phylogenetic analyses of all publicly available sequences related to Perkinsea. The applied PCR primers target a 450 bp region that encompass the variable V4 region of the 18S rDNA gene and have been optimized for the Titanium upgrade of the 454 technology. Nearly 5000 sequences longer than 150 bp were recovered from nearly all eukaryotic supergroups, and of those, 13 unique sequences were affiliated to Perkinsea. Thus, our new strategy for 454 amplicon sequencing was able to recover a large diversity of distantly related eukaryotes and previously unknown species of Perkinsea. In addition, we identified 40 Perkinsea sequences in GenBank generated by other recent diversity surveys. Importantly, phylogenetic analyses of these sequences identified 17 habitat-specific marine and freshwater clades (PERK 1-17). Hence, only a few successful transitions between these habitats have taken place over the entire history of Perkinsea, suggesting that the boundary between marine and fresh waters may constitute a barrier to cross-colonizations for intracellular parasites.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25: 3389–3402.
Amaral-Zettler LA, McCliment EA, Ducklow HW, Huse SM . (2009). A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes. PLoS ONE 4: e6372.
Behnke A, Bunge J, Barger K, Breiner H-W, Alla V, Stoeck T . (2006). Microeukaryote community patterns along an O2/H2S gradient in a supersulfidic anoxic fjord (Framvaren, Norway). Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 3626–3636.
Berney C, Fahrni J, Pawlowski J . (2004). How many novel eukaryotic ‘kingdoms’? Pitfalls and limitations of environmental DNA surveys. BMC Biol 2: 13.
Brugerolle G . (2002). Cryptophagus subtilis: a new parasite of cryptophytes affiliated with the Perkinsozoa lineage. Eur J Protistol 37: 379–390.
Brugerolle G . (2003). Apicomplexan parasite Cryptophagus renamed Rastrimonas gen. nov. Eur J Protistol 39: 101–101.
Burki F, Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Pawlowski J . (2008). Phylogenomics reveals a new ‘megagroup’ including most photosynthetic eukaryotes. Biol Lett 4: 366–369.
Cavalier-Smith T . (2004). Chromalveolate diversity and cell megaevolution: interplay of membranes, genomes and cytoskeleton. In: Hirt RP, Horner DS (eds). Organelles Genomes and Eukaryotic Phylogeny. CRC Press: New York, pp 75–108.
Cavalier-Smith T, Chao EE . (2004). Protalveolate phylogeny and systematics and the origins of Sporozoa and dinoflagellates (phylum Myzozoa nom. nov.). Eur J Protistol 40: 185–212.
Cavalier-Smith T, Lewis R, Chao EE, Oates B, Bass D . (2009). Helkesimastix marina n. sp. (Cercozoa: Sainouroidea superfam. n.) a Gliding zooflagellate of novel ultrastructure and unusual ciliary behaviour. Protist 160: 452–479.
Chambouvet A, Morin P, Marie D, Guillou L . (2008). Control of toxic marine dinoflagellate blooms by serial parasitic killers. Science 322: 1254–1257.
Davis AK, Yabsley MJ, Keel MK, Maerz JC . (2007). Discovery of a novel alveolate pathogen affecting southern leopard frogs in Georgia: description of the disease and host effects. Ecohealth 4: 310–317.
Delgado M . (1999). A new ‘diablillo parasite’ in the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella as a possibility to control harmful algal blooms. Harmful Algae News 19: 1–3.
Dolven JK, Lindqvist C, Albert VA, Bjorklund KR, Yuasa T, Takahashi O et al. (2007). Molecular diversity of alveolates associated with neritic North Atlantic radiolarians. Protist 158: 65–76.
Erard-Le Denn E, ChrÈtiennot-Dinet MJ, Probert I . (2000). First report of parasitism on the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum Halim. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 50: 109–113.
Figueroa RI, Garcés E, Massana R, Camp J . (2008). Description, host-specificity, and strain selectivity of the dinoflagellate parasite Parvilucifera sinerae sp. nov. (Perkinsozoa). Protist 159: 563–578.
Gestal C, Novoa B, Posada D, Figueras A, Azevedo C . (2006). Perkinsoide chabelardi n. gen., a protozoan parasite with an intermediate evolutionary position: possible cause of the decrease of sardine fisheries? Environ Microbiol 8: 1105–1114.
Green DE, Feldman SH, Wimsatt J . (2003). Emergence of a Perkinsus-like agent in anuran liver during die-offs of local populations: PCR detection and phylogenetic characterization. Proc Am Assoc Zoo Vet, 120–121.
Groisillier A, Massana R, Valentin K, Vaulotl D, Guilloul L . (2006). Genetic diversity and habitats of two enigmatic marine alveolate lineages. Aquat Microb Ecol 42: 277–291.
Guillou L, Viprey M, Chambouvet A, Welsh RM, Kirkham AR, Massana R et al. (2008). Widespread occurrence and genetic diversity of marine parasitoids belonging to Syndiniales (Alveolata). Environ Microbiol 10: 3349–3365.
Harada A, Ohtsuka S, Horiguchi T . (2006). Species of the parasitic genus duboscquella are members of the enigmatic marine alveolate group I. Protist 158: 337–347.
Katoh K, Kuma K-I, Toh H, Miyata T . (2005). MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucl Acids Res 33: 511–518.
Kumar S, Skjaeveland A, Orr R, Enger P, Ruden T, Mevik B-H et al. (2009). AIR: A batch-oriented web program package for construction of supermatrices ready for phylogenomic analyses. BMC Bioinformatics 10: 357.
Kuvardina ON, Leander BS, Aleshin VV, Myl’nikov AP, Keeling PJ, Simdyanov TG . (2002). The phylogeny of colpodellids (Alveolata) using small subunit rRNA gene sequences suggests they are the free-living sister group to apicomplexans. J Eukaryot Microbiol 49: 498–504.
Leander BS, Clopton RE, Keeling PJ . (2003a). Phylogeny of gregarines (Apicomplexa) as inferred from small-subunit rDNA and beta-tubulin. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53: 345–354.
Leander BS, Kuvardina ON, Aleshin VV, Mylnikov AP, Keeling PJ . (2003b). Molecular phylogeny and surface morphology of Colpodella edax (Alveolata): insights into the phagotrophic ancestry of apicomplexans. J Eukaryot Microbiol 50: 334–340.
Leander BS, Hoppenrath M . (2008). Ultrastructure of a novel tube-forming, intracellular parasite of dinoflagellates: Parvilucifera prorocentri sp. nov. (Alveolata, Myzozoa). Eur J Protistol 44: 55–70.
Lefèvre E, Roussel B, Amblard C, Sime-Ngando T . (2008). The molecular diversity of freshwater picoeukaryotes reveals high occurrence of putative parasitoids in the plankton. PLoS ONE 3: e2324.
Lepère C, Domaizon I, Debroas D . (2008). Unexpected importance of potential parasites in the composition of the freshwater small-eukaryote community. Appl Environ Microbiol 74: 2940–2949.
Logares R, Bråte J, Bertilsson S, Clasen JL, Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Rengefors K . (2009). Infrequent marine-freshwater transitions in the microbial world. Trends Microbiol 17: 414–422.
López-García P, Moreira D . (2008). Tracking microbial biodiversity through molecular and genomic ecology. Res Microbiol 159: 67–73.
Lozupone C, Knight R . (2005). UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 8228–8235.
Maddison D, Maddison W . (2000). MacClade 4: Analysis of Phylogeny and Character Evolution, 4 edn. Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.
Massana R, Karniol B, Pommier T, Bodaker I, Oded B . (2008). Metagenomic retrieval of a ribosomal DNA repeat array from an uncultured marine alveolate. Environ Microbiol 10: 1335–1343.
Moore RB, Obornik M, Janouskovec J, Chrudimsky T, Vancova M, Green DH et al. (2008). A photosynthetic alveolate closely related to apicomplexan parasites. Nature 451: 959–963.
Noren F, Moestrup O, Rehnstam-Holm AS . (1999). Parvilucifera infectans Noren et Moestrup gen. et sp nov (Perkinsozoa phylum nov.): a parasitic flagellate capable of killing toxic microalgae. Eur J Protistol 35: 233–254.
Quince C, Lanzen A, Curtis TP, Davenport RJ, Hall N, Head IM et al. (2009). Accurate determination of microbial diversity from 454 pyrosequencing data. Nat Methods 6: 639–641.
Richards TA, Vepritskiy AA, Gouliamova DE, Nierzwicki-Bauer SA . (2005). The molecular diversity of freshwater picoeukaryotes from an oligotrophic lake reveals diverse, distinctive and globally dispersed lineages. Environ Microbiol 7: 1413–1425.
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP . (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19: 1572–1574.
Saldarriaga JF, Max’ Taylor FJR, Cavalier-Smith T, Menden-Deuer S, Keeling PJPJ . (2004). Molecular data and the evolutionary history of dinoflagellates. Eur J Protistol 40: 85–111.
Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Minge MA, Cavalier-Smith T, Nedreklepp JM, Klaveness D, Jakobsen KS (2006). Combined Heat Shock Protein 90 and Ribosomal RNA Sequence Phylogeny Supports Multiple Replacements of Dinoflagellate Plastids. J Eukaryot Microbiol 53: 217–224.
Siddall ME, Reece KS, Nerad TA, Burreson EM . (2001). Molecular determination of the phylogenetic position of a species in the genus colpodella (Alveolata). Am Mus Novit 3314: 1–12.
Silberman JD, Collins AG, Gershwin LA, Johnson PJ, Roger AJ . (2004). Ellobiopsids of the genus Thalassomyces are alveolates. J Eukaryot Microbiol 51: 246–252.
Stamatakis A . (2006). RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22: 2688–2690.
Stoeck T, Behnke A, Christen R, Amaral-Zettler L, Rodriguez-Mora M, Chistoserdov A et al. (2009). Massively parallel tag sequencing reveals the complexity of anaerobic marine protistan communities. BMC Biology 7: 72.
Villalba A, Reece KS, Ordás MC, Casas SM, Figueras A . (2004). Perkinsosis in molluscs: a review. Aquat Living Resour 17: 411–432.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Bioportal team for implementing bioinformatics applications on the Bioportal (http://www.bioportal.uio.no). This work has been supported by the University of Oslo grants to KST, PhD fellowship to JB and travel funds to RL. The Swedish Research Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning (FORMAS) via Uppsala Microbiomics Centre (UMC; http://www.microbiomics.se) has given financial support to RL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The ISME Journal website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bråte, J., Logares, R., Berney, C. et al. Freshwater Perkinsea and marine-freshwater colonizations revealed by pyrosequencing and phylogeny of environmental rDNA. ISME J 4, 1144–1153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.39
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.39
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
DNA metabarcoding reveals the diversity of small-sized macroalgae ignored by traditional monitoring in a coastal ecosystem
Marine Biology (2024)
-
Taxonomic composition, community structure and molecular novelty of microeukaryotes in a temperate oligomesotrophic lake as revealed by metabarcoding
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Environmental drivers of soil microbial activity and diversity along an elevational gradient
Journal of Mountain Science (2022)
-
Comparison of Deep-Sea Picoeukaryotic Composition Estimated from the V4 and V9 Regions of 18S rRNA Gene with a Focus on the Hadal Zone of the Mariana Trench
Microbial Ecology (2022)
-
Diversity and community structure of eukaryotic microalgae in surface sediments in the central Bohai Sea, China, based on a metabarcoding approach
Journal of Oceanology and Limnology (2022)