Abstract
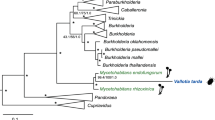
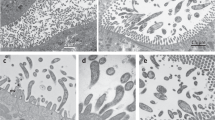
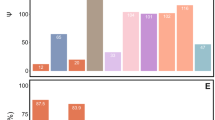
Adelgids (Insecta: Hemiptera: Adelgidae) are known as severe pests of various conifers in North America, Canada, Europe and Asia. Here, we present the first molecular identification of bacteriocyte-associated symbionts in these plant sap-sucking insects. Three geographically distant populations of members of the Adelges nordmannianae/piceae complex, identified based on coI and ef1alpha gene sequences, were investigated. Electron and light microscopy revealed two morphologically different endosymbionts, coccoid or polymorphic, which are located in distinct bacteriocytes. Phylogenetic analyses of their 16S and 23S rRNA gene sequences assigned both symbionts to novel lineages within the Gammaproteobacteria sharing <92% 16S rRNA sequence similarity with each other and showing no close relationship with known symbionts of insects. Their identity and intracellular location were confirmed by fluorescence in situ hybridization, and the names ‘Candidatus Steffania adelgidicola’ and ‘Candidatus Ecksteinia adelgidicola’ are proposed for tentative classification. Both symbionts were present in all individuals of all investigated populations and in different adelgid life stages including eggs, suggesting vertical transmission from mother to offspring. An 85 kb genome fragment of ‘Candidatus S. adelgidicola’ was reconstructed based on a metagenomic library created from purified symbionts. Genomic features including the frequency of pseudogenes, the average length of intergenic regions and the presence of several genes which are absent in other long-term obligate symbionts, suggested that ‘Candidatus S. adelgidicola’ is an evolutionarily young bacteriocyte-associated symbiont, which has been acquired after diversification of adelgids from their aphid sister group.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Akman L, Yamashita A, Watanabe H, Oshima K, Shiba T, Hattori M et al. (2002). Genome sequence of the endocellular obligate symbiont of tsetse flies, Wigglesworthia glossinidia. Nat Genet 32: 402–407.
Altschul S, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E, Lipman D . (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410.
Balch RE . (1952). Studies of the balsam woolly aphid Adelges piceae (Ratz.) and its effects on balsam fir, Abies balsamea (L.) Mill. Can Dep Agric Pub 867: 1–76.
Baumann P . (2005). Biology bacteriocyte-associated endosymbionts of plant sap-sucking insects. Annu Rev Microbiol 59: 155–189.
Baumann P . (2006). Diversity of prokaryote-insect associations within the Sternorrhyncha (psyllids, whiteflies, aphids, mealybugs). In: Bourtzis K, Miller TA (eds) Insect Symbiosis. CRC Press: Boca Raton, pp 1–24.
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M . (2001). GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucl Acids Res 29: 2607–2618.
Binazzi A . (2000). Notes on and key to winged forms of adelgids recorded from Italy (Homoptera, Aphidoidea, Adelgidae). Redia 83: 187–215.
Blackman RL, Eastop VF . (1994). Aphids of the World's Trees: An Identification and Information Guide. CAB International: Wallingford.
Bryant DG . (1971). Balsam woolly aphid Adelges piceae (Homoptera: Phylloxeridae) seasonal and spatial development in crowns of balsam fir, Abies balsamea. Can Entomol 103: 1411–1420.
Buchner P . (1953). Endosymbiose der Tiere mit Pflanzlichen Mikroorganismen. vol. 12 Birkhäuser: Basel/Stuttgart.
Burke GR, Moran NA . (2011). Massive genomic decay in Serratia symbiotica, a recently evolved symbiont of aphids. Genome Biol Evol 3: 195–208.
Carver T, Thomson N, Bleasby A, Berriman M, Parkhill J . (2009). DNAPlotter: circular and linear interactive genome visualization. Bioinformatics 25: 119–120.
Cole ST, Eiglmeier K, Parkhill J, James KD, Thomson NR, Wheeler PR et al. (2001). Massive gene decay in the leprosy bacillus. Nature 409: 1007–1011.
Consortium TU . (2010). The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) in 2010. Nucl Acids Res 38: D142–D148.
Daims H, Stoecker K, Wagner M . (2005). Fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of prokaryotes. In: Osborn A, Smith C (eds) Advanced Methods in Molecular Microbial Ecology. Bios-Garland: Abingdon, UK, pp 213–239.
Degnan PH, Lazarus AB, Wernegreen JJ . (2005). Genome sequence of Blochmannia pennsylvanicus indicates parallel evolutionary trends among bacterial mutualists of insects. Genome Res 15: 1023–1033.
Degnan PH, Yu Y, Sisneros N, Wing RA, Moran NA . (2009). Hamiltonella defensa, genome evolution of protective bacterial endosymbiont from pathogenic ancestors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 9063–9068.
Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC, Salzberg SL . (2007). Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 23: 673–679.
Eichhorn O . (1967). On methods of differentiating the species of the harmful white woolly aphids (genus Dreyfusia Cb.=Adelges An.) on fir, and the consequences for forest protection. Tech Bull CIBC 8: 53–82.
Eichhorn O . (1973). Folgerungen aus dem Auftreten der Gallen von Dreyfusia nordmannianae Eckst. (= D. nüsslini CB) in Mitteleuropa auf ihren Generationszyklus. Z Angew Entomol 74: 196–199.
Foottit RG, Maw HEL, Havill NP, Ahern RG, Montgomery ME . (2009). DNA barcodes to identify species and explore diversity in the Adelgidae (Insecta: Hemiptera: Aphidoidea). Mol Ecol Resour 9: 188–195.
Frishman D, Albermann K, Hani J, Heumann K, Metanomski A, Zollner A et al. (2001). Functional and structural genomics using PEDANT. Bioinformatics 17: 44–57.
Gardner PP, Daub J, Tate JG, Nawrocki EP, Kolbe DL, Lindgreen S et al. (2009). Rfam: updates to the RNA families database. Nucl Acids Res 37: D136–D140.
Gosalbes MJ, Lamelas A, Moya A, Latorre A . (2008). The striking case of tryptophan provision in the cedar aphid Cinara cedri. J Bacteriol 190: 6026–6029.
Guindon S, Gascuel O . (2003). A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52: 696–704.
Havill NP, Foottit RG . (2007). Biology and evolution of Adelgidae. Annu Rev Entomol 52: 325–349.
Havill NP, Foottit RG, von Dohlen CD . (2007). Evolution of host specialization in the Adelgidae (Insecta: Hemiptera) inferred from molecular phylogenetics. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44: 357–370.
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F . (2001). MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17: 754–755.
Ishikawa H . (1982). Host-symbiont interactions in the protein synthesis in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Insect Biochem 12: 613–622.
Kaiwa N, Hosokawa T, Kikuchi Y, Nikoh N, Meng XY, Kimura N et al. (2010). Primary gut symbiont and secondary Sodalis-allied symbiont in the scutellerid stinkbug Cantao ocellatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 76: 3486–3494 AEM.00421-00410.
Kanehisa M, Goto S . (2000). KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucl Acids Res 28: 27–30.
Karp PD, Ouzounis CA, Moore-Kochlacs C, Goldovsky L, Kaipa P, Ahrén D et al. (2005). Expansion of the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases to 160 genomes. Nucl Acids Res 33: 6083–6089.
Katoh K, Kuma K, Toh H, Miyata T . (2005). MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucl Acids Res 33: 511–518.
Klasson L, Andersson SGE . (2004). Evolution of minimal-gene-sets in host-dependent bacteria. Trends Microbiol 12: 37–43.
Lamelas A, Perez-Brocal V, Gomez-Valero L, Gosalbes MJ, Moya A, Latorre A . (2008). Evolution of the secondary symbiont ‘Candidatus Serratia symbiotica’ in aphid species of the subfamily Lachninae. Appl Environ Microbiol 74: 4236–4240.
Lowe T, Eddy S . (1997). tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucl Acids Res 25: 955–964.
Loy A, Maixner F, Wagner M, Horn M . (2007). probeBase: an online resource for rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes: new features 2007. Nucl Acids Res 35: D800–D804.
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar et al. (2004). ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucl Acids Res 32: 1363–1371.
McCutcheon JP, McDonald BR, Moran NA . (2009). Convergent evolution of metabolic roles in bacterial co-symbionts of insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 15394–15399.
McCutcheon JP, Moran NA . (2007). Parallel genomic evolution and metabolic interdependence in an ancient symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 19392–19397.
Mira A, Ochman H, Moran NA . (2001). Deletional bias and the evolution of bacterial genomes. Trends Genet 17: 589–596.
Montllor CB, Maxmen A, Purcell AH . (2002). Facultative bacterial endosymbionts benefit pea aphids Acyrthosiphon pisum under heat stress. Ecol Entomol 27: 189–195.
Moran NA . (2002). Microbial minimalism: genome reduction in bacterial pathogens. Cell 108: 583–586.
Moran NA, McCutcheon JP, Nakabachi A . (2008). Genomics and evolution of heritable bacterial symbionts. Annu Rev Genet 42: 165–190.
Moran NA, Munson MA, Baumann P, Ishikawa H . (1993). A molecular clock in endosymbiotic bacteria is calibrated using the insect hosts. Proc R Soc B 253: 167–171.
Moran NA, Plague GR, Sandstrom JP, Wilcox JL . (2003). A genomic perspective on nutrient provisioning by bacterial symbionts of insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100 (Suppl 2): 14543–14548.
Moran NA, Russell JA, Koga R, Fukatsu T . (2005). Evolutionary relationships of three new species of Enterobacteriaceae living as symbionts of aphids and other insects. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 3302–3310.
Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E . (1995). Taxonomic note: implementation of the provisional status Candidatus for incompletely described procaryotes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45: 186–187.
Nakabachi A, Yamashita A, Toh H, Ishikawa H, Dunbar HE, Moran NA et al. (2006). The 160-kilobase genome of the bacterial endosymbiont Carsonella. Science 314: 267–26.
Oliver KM, Russell JA, Moran NA, Hunter MS . (2003). Facultative bacterial symbionts in aphids confer resistance to parasitic wasps. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 1803–1807.
Profft J . (1936). Beiträge zur Symbiose der Aphiden und Psylliden. Z Morphol Oekol Tiere 32: 289–326.
Ramsey JS, MacDonald SJ, Jander G, Nakabachi A, Thomas GH, Douglas AE . (2010). Genomic evidence for complementary purine metabolism in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, and its symbiotic bacterium Buchnera aphidicola. Insect Mol Biol 19: 241–248.
Richardson KC, Jarett L, Finke EH . (1960). Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35: 313–323.
Rio RV, Lefevre C, Heddi A, Aksoy S . (2003). Comparative genomics of insect-symbiotic bacteria: influence of host environment on microbial genome composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 6825–6832.
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP . (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19: 1572–1574.
Scarborough CL, Ferrari J, Godfray HC . (2005). Aphid protected from pathogen by endosymbiont. Science 310: 1781.
Schmidt HA, Strimmer K, Vingron M, von Haeseler A . (2002). TREE-PUZZLE: maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 18: 502–504.
Shields KS, Hirth RT . (2005). Bacterial Endosymbionts of Adelges Tsugae Annand: Potential Targets for Biocontrol?. USDA For. Serv: Morgantown; http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.65.638&rep=rep1&type=pdf#page=371.
Shigenobu S, Watanabe H, Hattori M, Sakaki Y, Ishikawa H . (2000). Genome sequence of the endocellular bacterial symbiont of aphids Buchnera sp. APS Nat 407: 81–86.
Spurr AR . (1969). A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26: 31–43.
Steffan AW . (1968). Evolution und Systematik der Adelgidae (Homoptera: Aphidina): Eine Verwandtschaftsanalyse auf vorwiegend ethologischer, zytologischer und karyologischer Grundlage. Zoologica 115: 1–139.
Steffan AW . (1972). Unterordnung Aphidina, Blattläuse. Parey: Hamburg.
Tatusov RL, Natale DA, Garkavtsev IV, Tatusova TA, Shankavaram UT, Rao BS et al. (2001). The COG database: new developments in phylogenetic classification of proteins from complete genomes. Nucl Acids Res 29: 22–28.
Thomas G, Zucker J, Macdonald S, Sorokin A, Goryanin I, Douglas A . (2009). A fragile metabolic network adapted for cooperation in the symbiotic bacterium Buchnera aphidicola. BMC Syst Biol 3: 24.
Toh H, Weiss BL, Perkin SAH, Yamashita A, Oshima K, Hattori M et al. (2006). Massive genome erosion and functional adaptations provide insights into the symbiotic lifestyle of Sodalis glossinidius in the tsetse host. Genome Res 16: 149–156.
Tsuchida T, Koga R, Fukatsu T . (2004). Host plant specialization governed by facultative symbiont. Science 303: 1989.
Vorburger C, Gehrer L, Rodriguez P . (2010). A strain of the bacterial symbiont Regiella insecticola protects aphids against parasitoids. Biol Lett 6: 109–111.
Walter MC, Rattei T, Arnold R, Güldener U, Münsterkötter M, Nenova K et al. (2009). PEDANT covers all complete RefSeq genomes. Nucl Acids Res 37: D408–D411.
Wheeler DL, Barrett T, Benson DA, Bryant SH, Canese K, Chetvernin V et al. (2008). Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucl Acids Res 36: D13–D21.
Williams KP, Gillespie JJ, Sobral BWS, Nordberg EK, Snyder EE, Shallom JM et al. (2010). Phylogeny of Gammaproteobacteria. J Bacteriol 192: 2305–2314 JB.01480-01409.
Wu D, Daugherty SC, Aken SE, Pai GH, Watkins KL, Khouri H et al. (2006). Metabolic complementarity and genomics of the dual bacterial symbiosis of sharpshooters. PLoS Biol 4: e188.
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM . (1996). DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 316–322.
Zientz E, Dandekar T, Gross R . (2004). Metabolic interdependence of obligate intracellular bacteria and their insect hosts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68: 745–770.
Zurovcova M, Havelka J, Stary P, Vechtova P, Chundelova D, Jarosova A et al. (2010). ‘DNA barcoding’ is of limited value for identifying adelgids (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) but supports traditional morphological taxonomy. Eur J Entomol 107: 147–156.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Marc Mußmann for advice during fosmid library preparation, and Frank Maixner and Patrick Tischler for help with sampling and annotation, respectively. This work was partially funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) grants Y277-B03 and P22533-B17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toenshoff, E., Penz, T., Narzt, T. et al. Bacteriocyte-associated gammaproteobacterial symbionts of the Adelges nordmannianae/piceae complex (Hemiptera: Adelgidae). ISME J 6, 384–396 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.102
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Symbioses shape feeding niches and diversification across insects
Nature Ecology & Evolution (2023)
-
Transitional genomes and nutritional role reversals identified for dual symbionts of adelgids (Aphidoidea: Adelgidae)
The ISME Journal (2022)