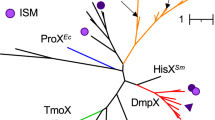
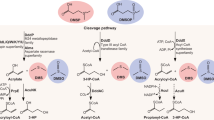
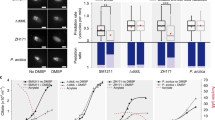
Abstract
Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3 is a model Roseobacter marine bacterium, particularly regarding its catabolism of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), an abundant anti-stress molecule made by marine phytoplankton. We found a novel gene, dddW, which encodes a DMSP lyase that cleaves DMSP into acrylate plus the environmentally important volatile dimethyl sulfide (DMS). Mutations in dddW reduced, but did not abolish DMS production. Transcription of dddW was greatly enhanced by pre-growth of cells with DMSP, via a LysR-type regulator. Close DddW homologs occur in only one other Roseobacter species, and there are no close homologs and only a few related sequences in metagenomes of marine bacteria. In addition to DddW, R. pomeroyi DSS-3 had been shown to have two other, different, DMSP lyases, DddP and DddQ, plus an enzyme that demethylates DMSP, emphasizing the importance of this substrate for this model bacterium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Charlson RJ, Lovelock JE, Andreae MO, Warren SG . (1987). Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulphur, cloud albedo and climate. Nature 326: 655–661.
Curson ARJ, Sullivan MJ, Todd JD, Johnston AWB . (2011). DddY, a periplasmic dimethylsulfoniopropionate lyase found in taxonomically diverse species of proteobacteria. ISME J; e-pub ahead of print 20 January 2011.
Curson ARJ, Rogers R, Todd JD, Brearley CA, Johnston AWB . (2008). Molecular genetic analysis of a dimethylsulfoniopropionate lyase that liberates the climate-changing gas dimethylsulfide in several marine alpha-proteobacteria and Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Environ Microbiol 10: 757–767.
Dunwell JM, Purvis A, Khuri S . (2004). Cupins: the most functionally diverse protein superfamily? Phytochemistry 65: 7–17.
González JM, Kiene RP, Moran MA . (1999). Transformation of sulfur compounds by an abundant lineage of marine bacteria in the α-subclass of the class Proteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 65: 3810–3819.
Howard EC, Henriksen JR, Buchan A, Reisch CR, Bürgmann H, Welsh R et al. (2006). Bacterial taxa that limit sulfur flux from the ocean. Science 314: 649–652.
Kettle AJ, Andreae MO, Amouroux D, Andreae TW, Bates TS, Berresheim H et al. (1999). A global database of sea surface dimethylsulfide (DMS) measurements and a procedure to predict sea surface DMS as a function of latitude, longitude, and month. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 13: 399–444.
Kirkwood M, Le Brun NE, Todd JD, Johnston AWB . (2010). The dddP gene of Roseovarius nubinhibens encodes a novel lyase that cleaves dimethylsulfoniopropionate into acrylate plus dimethyl sulfide. Microbiol 156: 1900–1906.
Maddocks SE, Oyston PCF . (2008). Structure and function of the LysR-type transcriptional regulator (LTTR) family proteins. Microbiol 154: 3609–3623.
Newton RJ, Griffin LE, Bowles KM, Meile C, Gifford S, Givens CE et al. (2010). Genome characteristics of a generalist marine bacterial lineage. ISME J 4: 784–798.
Rinta-Kanto JM, Bürgmann H, Gifford SM, Sun S, Sharma S, Del Valle DA et al. (2011). Analysis of sulfur-related transcription by Roseobacter communities using a taxon-specific functional gene microarray. Environ Microbiol 13: 453–467.
Rusch DB, Halpern AL, Sutton G, Heidelberg KB, Williamson S, Yooseph S et al. (2007). The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Expedition: northwest Atlantic through eastern tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol 5: e77.
Seymour JR, Simó R, Ahmed T, Stocker R . (2010). Chemoattraction to dimethylsulfoniopropionate throughout the marine microbial food web. Science 329: 342–345.
Todd JD, Curson ARJ, Kirkwood M, Sullivan MJ, Green RT, Johnston AWB . (2011). DddQ, a novel, cupin-containing, dimethylsulfoniopropionate lyase in marine roseobacters and in uncultured marine bacteria. Environ Microbiol 13: 427–438.
Todd JD, Curson ARJ, Dupont CL, Nicholson P, Johnston AWB . (2009). The dddP gene, encoding a novel enzyme that converts dimethylsulfoniopropionate into dimethyl sulfide, is widespread in ocean metagenomes and marine bacteria and also occurs in some Ascomycete fungi. Environ Microbiol 11: 1376–1385.
Todd JD, Rogers R, Li YG, Wexler M, Bond PL, Sun L et al. (2007). Structural and regulatory genes required to make the gas dimethyl sulfide in bacteria. Science 315: 666–669.
Young JPW, Crossman LC, Johnston AWB, Thomson NR, Ghazoui ZF, Hull KH et al. (2006). The genome of Rhizobium leguminosarum has recognizable core and accessory components. Genome Biol 7: R34.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the BBSRC and the NERC of the United Kingdom. We are grateful to Pamela Wells for technical support and to Andrew Curson and Rob Green for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todd, J., Kirkwood, M., Newton-Payne, S. et al. DddW, a third DMSP lyase in a model Roseobacter marine bacterium, Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3. ISME J 6, 223–226 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.79
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.79
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ubiquitous occurrence of a dimethylsulfoniopropionate ABC transporter in abundant marine bacteria
The ISME Journal (2023)
-
The biogeochemistry of marine dimethylsulfide
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (2023)
-
Oceanospirillales containing the DMSP lyase DddD are key utilisers of carbon from DMSP in coastal seawater
Microbiome (2022)
-
Biogeographical and seasonal dynamics of the marine Roseobacter community and ecological links to DMSP-producing phytoplankton
ISME Communications (2022)
-
Transcriptome analysis of Antarctic Rhodococcus sp. NJ-530 in the response to dimethylsulfoniopropionate
Polar Biology (2022)