Abstract
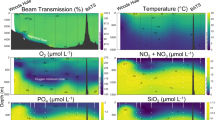
The monthly, seasonal and interannual variability of microbial eukaryote assemblages were examined at 5 m, the deep chlorophyll maximum, 150 m and 500 m at the San Pedro Ocean Time-series station (eastern North Pacific). The depths spanned transitions in temperature, light, nutrients and oxygen, and included a persistently hypoxic environment at 500 m. Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism was used for the analysis of 237 samples that were collected between September 2000 and December 2010. Spatiotemporal variability patterns of microeukaryote assemblages indicated the presence of distinct shallow and deep communities at the SPOT station, presumably reflecting taxa that were specifically adapted for the conditions in those environments. Community similarity values between assemblages collected 1 month apart at each depth ranged between ∼20% and ∼84% (averages were ∼50–59%). The assemblage at 5 m was temporally more dynamic than deeper assemblages and also displayed substantial interannual variability during the first ∼3 years of the study. Evidence of seasonality was detected for the microbial eukaryote assemblage at 5 m between January 2008 and December 2010 and at 150 m between September 2000 and December 2003. Seasonality was not detected for assemblages at the deep chlorophyll a maximum, which varied in depth seasonally, or at 500 m. Microbial eukaryote assemblages exhibited cyclical patterns in at least 1 year at each depth, implying an annual resetting of communities. Substantial interannual variability was detected for assemblages at all depths and represented the largest source of temporal variability in this temperate coastal ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aguilera A, Zettler E, Gomez F, Amaral-Zettler L, Rodriguez N, Amils R . (2007). Distribution and seasonal variability in the benthic eukaryotic community of Rio Tinto (SW, Spain), an acidic, high metal extreme environment. Syst Appl Microbiol 30: 531–546.
Balzano S, Marie D, Gourvil P, Vaulot D . (2012). Composition of the summer photosynthetic pico and nanoplankton communities in the Beaufort Sea assessed by T-RFLP and sequences of the 18S rRNA gene from flow cytometry sorted samples. ISME J 6: 1480–1498.
Beman JM, Sachdeva R, Fuhrman JA . (2010). Population ecology of nitrifying Archaea and Bacteria in the Southern California Bight. Environ Microbiol 12: 1282–1292.
Berelson WM . (1991). The flushing of 2 deep-sea basins, Southern California borderland. Limnol Oceanogr 36: 1150–1166.
Caron DA, Countway PD, Jones AC, Kim DY, Schnetzer A . (2012). Marine protistan diversity. Annu Rev Mar Sci 4: 467–493.
Chapin FS III, Zavaleta ES, Eviner VT, Naylor RL, Vitousek PM, Reynolds HL et al (2000). Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 405: 232–242.
Chow CET, Kim DY, Sachdeva R, Caron DA, Fuhrman JA Top-down controls on bacterial community structure: microbial network analysis of bacterial, viral and protistan communities ISME J (accepted).
Clarke KR . (1993). Nonparametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18: 117–143.
Clarke KR, Gorley RN . (2006). PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. In: PRIMER-E. Plymouth.
Countway PD, Caron DA . (2006). Abundance and distribution of Ostreococcus sp. in the San Pedro Channel, California, as revealed by quantitative PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 2496–2506.
Countway PD, Gast RJ, Dennett MR, Savai P, Rose JM, Caron DA . (2007). Distinct protistan assemblages characerize the euphotic zone and deep sea (2500 m) of the western North Atlantic (Sargasso Sea and Gulf Stream). Environ Microbiol 9: 1219–1232.
Countway PD, Gast RJ, Savai P, Caron DA . (2005). Protistan diversity estimates based on 18S rDNA from seawater incubations in the western North Atlantic. J Eukaryot Microbiol 52: 95–106.
Countway PD, Vigil PD, Schnetzer A, Moorthi SD, Caron DA . (2010). Seasonal analysis of protistan community structure and diversity at the USC Microbial Observatory (San Pedro Channel, North Pacific Ocean). Limnol Oceanogr 55: 2381–2396.
Demir-Hilton E, Sudek S, Cuvelier ML, Gentemann CL, Zehr JP, Worden AZ . (2011). Global distribution patterns of distinct clades of the photosynthetic picoeukaryote Ostreococcus. ISME J 5: 1095–1107.
Dong CM, Idica EY, McWilliams JC . (2009). Circulation and multiple-scale variability in the Southern California Bight. Prog Oceanogr 82: 168–190.
Dong CM, McWilliams JC . (2007). A numerical study of island wakes in the Southern California Bight. Cont Shelf Res 27: 1233–1248.
Dore JE, Letelier RM, Church MJ, Lukas R, Karl DM . (2008). Summer phytoplankton blooms in the oligotrophic North Pacific Subtropical Gyre: historical perspective and recent observations. Prog Oceanogr 76: 2–38.
Edgcomb V, Orsi W, Bunge J, Jeon S, Christen R, Leslin C et al (2011). Protistan microbial observatory in the Cariaco Basin, Caribbean. I. Pyrosequencing vs Sanger insights into species richness. ISME J 5: 1344–1356.
Edgcomb VP, Kysela DT, Teske A, Gomez AD, Sogin ML . (2002). Benthic eukaryotic diversity in the Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vent environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 7658–7662.
Egert M, Friedrich MW . (2003). Formation of pseudo-terminal restriction fragments, a PCR-related bias affecting terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of microbial community structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 2555–2562.
Fitzpatrick E, Caron DA, Schnetzer A . (2010). Development and environmental application of a genus-specific quantitative PCR approach for Pseudo-nitzschia species. Mar Biol 157: 1161–1169.
Fuhrman JA, Steele JA . (2008). Community structure of marine bacterioplankton: patterns, networks, and relationships to function. Aquat Microb Ecol 53: 69–81.
Gilg IC, Amaral-Zettler LA, Countway PD, Moorthi S, Schnetzer A, Caron DA . (2010). Phylogenetic affiliations of Mesopelagic Acantharia and Acantharian-like environmental 18S rRNA genes off the Southern California Coast. Protist 161: 197–211.
Gordon LI, Jennings JJC, Ross AA, Krest JM . (1993). A Suggested Protocol for Continuous Flow Automated Analysis of Seawater Nutrients (Phosphate, Nitrate, Nitrite And Silicic Acid) in the WOCE Hydrographic Program and the Joint Global Ocean Fluxes Study, WHP Operations And Methods. WOCE Hydrographic Program Office, College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University: Corvallis, Oregon p 52.
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M . (2007) Methods of Seawater Anlaysis 3 edn. Wiley-VCH GmbH: Weinheim Germany.
Groisillier A, Massana R, Valentin K, Vaulotl D, Guilloul L . (2006). Genetic diversity and habitats of two enigmatic marine alveolate lineages. Aquat Microb Ecol 42: 277–291.
Hamersley MR, Turk KA, Leinweber A, Gruber N, Zehr JP, Gunderson T et al (2011). Nitrogen fixation within the water column associated with two hypoxic basins in the Southern California Bight. Aquat Microb Ecol 63: 193.
Hayward TL . (2000). El Nino 1997-98 in the coastal waters of Southern California: a timeline of events. Cal Coop Ocean Fish 41: 98–116.
Hickey BM . (1991). Variability in 2 deep coastal basins (Santa Monica and San Pedro) off Southern California. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 96: 16689–16708.
Hickey BM, Dobbins EL, Allen SE . (2003). Local and remote forcing of currents and temperature in the central Southern California Bight. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 108 doi:101029/2000JC000313.
Hinder SL, Hays GC, Edwards M, Roberts EC, Walne AW, Gravenor MB . (2012). Changes in marine dinoflagellate and diatom abundance under climate change. Nat Clim Change 2: 271–275.
Hooker SB, McClain CR . (2000). The calibration and validation of SeaWiFS data. Prog Oceanogr 45: 427–465.
Kaplan CW, Kitts CL . (2004). Bacterial succession in a petroleum land treatment unit. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 1777–1786.
Kim DY, Countway PD, Gast RJ, Caron DA . (2011). Rapid shifts in the structure and composition of a protistan assemblage during bottle incubations affect estimates of total protistan species richness. Microb Ecol 62: 383–398.
Kim DY, Countway PD, Yamashito W, Caron DA . (2012). A combined sequence-based and fragment-based characterization of microbial eukaryote assemblages provides taxonomic context for the Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (T-RFLP) method. J Microbiol Meth 91: 527–536.
Kim HJ, Miller AJ, McGowan J, Carter ML . (2009). Coastal phytoplankton blooms in the Southern California Bight. Prog Oceanogr 82: 137–147.
Lepere C, Boucher D, Jardillier L, Domaizon I, Debroas D . (2006). Succession and regulation factors of small eukaryote community. composition in a lacustrine ecosystem (Lake pavin). Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 2971–2981.
Levitus S . (1982) Climatological Atlas of the World Ocean NOAA Professional Paper 13 U.S. Gov. Printing Office, Rockville, MD, pp 190.
Liu WT, Marsh TL, Cheng H, Forney LJ . (1997). Characterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 4516–4522.
Massana R, Balague V, Guillou L, Pedros-Alio C . (2004). Picoeukaryotic diversity in an oligotrophic coastal site studied by molecular and culturing approaches. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 50: 231–243.
Massana R, Pedros-Alio C . (2008). Unveiling new microbial eukaryotes in the surface ocean. Curr Opin Microbiol 11: 213–218.
McGradySteed J, Harris PM, Morin PJ . (1997). Biodiversity regulates ecosystem predictability. Nature 390: 162–165.
Medlin LK, Elwood HJ, Stickel S, Sogin ML . (1988). The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Genetica 71: 491–499.
Medlin LK, Metfies K, Mehl H, Wiltshire K, Valentin K . (2006). Picoeukaryotic plankton diversity at the Helgoland time series site as assessed by three molecular methods. Microb Ecol 52: 53–71.
Moorthi SD, Countway PD, Stauffer BA, Caron DA . (2006). Use of quantitative real-time PCR to investigate the dynamics of the red tide dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum. Microb Ecol 52: 136–150.
Moreira D, Lopez-Garcia P . (2002). The molecular ecology of microbial eukaryotes unveils a hidden world. Trends Microbiol 10: 31–38.
Naeem S, Li SB . (1997). Biodiversity enhances ecosystem reliability. Nature 390: 507–509.
Nolte V, Pandey RV, Jost S, Medinger R, Ottenwalder B, Boenigk J et al (2010). Contrasting seasonal niche separation between rare and abundant taxa conceals the extent of protist diversity. Mol Ecol 19: 2908–2915.
Not F, Gausling R, Azam F, Heidelberg JF, Worden AZ . (2007). Vertical distribution of picoeukaryotic diversity in the Sargasso Sea. Environ Microbiol 9: 1233–1252.
Orsi W, Edgcomb V, Jeon S, Leslin C, Bunge J, Taylor GT et al (2011). Protistan microbial observatory in the Cariaco Basin, Caribbean. II. Habitat specialization. ISME J 5: 1357–1373.
Osborn AM, Moore ERB, Timmis KN . (2000). An evaluation of terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis for the study of microbial community structure and dynamics. Environ Microbiol 2: 39–50.
Piwosz K, Pernthaler J . (2010). Seasonal population dynamics and trophic role of planktonic nanoflagellates in coastal surface waters of the Southern Baltic Sea. Environ Microbiol 12: 364–377.
Potvin M, Lovejoy C . (2009). PCR-based diversity estimates of artificial and environmental 18S rRNA gene libraries. J Eukaryot Microbiol 56: 174–181.
Romari K, Vaulot D . (2004). Composition and temporal variability of picoeukaryote communities at a coastal site of the English Channel from 18S rDNA sequences. Limnol Oceanogr 49: 784–798.
Rossi P, Gillet F, Rohrbach E, Diaby N, Holliger C . (2009). Statistical assessment of variability of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis applied to complex microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75: 7268–7270.
Schnetzer A, Moorthi SD, Countway PD, Gast RJ, Gilg IC, Caron DA . (2011). Depth matters: microbial eukaryote diversity and community structure in the eastern North Pacific revealed through environmental gene libraries. Deep Sea Res I 58: 16–26.
Schutte UME, Abdo Z, Bent SJ, Shyu C, Williams CJ, Pierson JD et al (2008). Advances in the use of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis of 16S rRNA genes to characterize microbial communities. Appl Microbiol Biot 80: 365–380.
Sherr BF, Sherr EB, Caron DA, Vaulot D, Worden AZ . (2007). Oceanic protists. Oceanography 20: 130–134.
Steele JA, Countway PD, Xia L, Vigil PD, Beman JM, Kim DY et al (2011). Marine bacterial, archaeal and protistan association networks reveal ecological linkages. ISME J 5: 1414–1425.
Steinberg DK, Carlson CA, Bates NR, Johnson RJ, Michaels AF, Knap AH . (2001). Overview of the US JGOFS Bermuda Atlantic Time-series Study (BATS): a decade-scale look at ocean biology and biogeochemistry. Deep Sea Res II 48: 1405–1447.
Stoeck T, Epstein S . (2003). Novel eukaryotic lineages inferred from small-subunit rRNA analyses of oxygen-depleted marine environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 2657–2663.
Thunell RC, Pilskaln CH, Tappa E, Sautter LR . (1994). Temporal variability in sediment fluxes in the San-Pedro Basin, Southern California Bight. Cont Shelf Res 14: 333–352.
Vaulot D, Eikrem W, Viprey M, Moreau H . (2008). The diversity of small eukaryotic phytoplankton (<=3 mu m) in marine ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32: 795–820.
Venrick EL . (1998). Spring in the California current: the distribution of phytoplankton species, April 1993 and April 1995. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 167: 73–88.
Venrick EL . (2002). Floral patterns in the California current system off southern California: 1990–1996. J Mar Res 60: 171–189.
Vigil P, Countway PD, Rose J, Lonsdale DJ, Gobler CJ, Caron DA . (2009). Rapid shifts in dominant taxa among microbial eukaryotes in estuarine ecosystems. Aquat Microb Ecol 54: 83–100.
Weber F, Del Campo J, Wylezich C, Massana R, Jurgens K . (2012). Unveiling trophic functions of uncultured protist taxa by incubation experiments in the brackish Baltic Sea. PLoS One 7: e41970.
Weekers PHH, Gast RJ, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ . (1994). Sequence variations in small-subunit ribosomal-RNAs of Hartmannella vermiformis and their phylogenetic implications. Mol Biol Evol 11: 684–690.
Worden AZ . (2006). Picoeukaryote diversity in coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean. Aquat Microb Ecol 43: 165–175.
Wu XQ, Menzel WP, Wade GS . (1999). Estimation of sea surface temperatures using GOES-8/9 radiance measurements. B Am Meteorol Soc 80: 1127–1138.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Wrigley Institute for Environmental Studies for providing ship time and the environmental data used in this study. Troy Gunderson was instrumental in sampling, CTD operations and processing of environmental samples. We also thank the captain and crew of the R/V Seawatch and R/V Yellowfin for their help on cruises. Jed Fuhrman and members of his lab provided helpful comments and discussions. Victoria Campbell, Jacob Cram, Alyssa Gellene, Ian Hewson, Alle Lie, David Needham, Alma Parada, Anand Patel and Joshua Steele helped with sample collection and processing of samples. This work was funded by NSF Grants MCB-0703159, MCB-0084231 and OCE-1136818.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Countway, P., Jones, A. et al. Monthly to interannual variability of microbial eukaryote assemblages at four depths in the eastern North Pacific. ISME J 8, 515–530 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.173
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.173
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Integrated Biogeography and Assembly Mechanisms of Microeukaryotic Communities in Coastal Waters Near Shellfish Cultivation
Microbial Ecology (2023)
-
Long-term seasonal and interannual variability of marine aerobic anoxygenic photoheterotrophic bacteria
The ISME Journal (2019)
-
Rhythmicity of coastal marine picoeukaryotes, bacteria and archaea despite irregular environmental perturbations
The ISME Journal (2019)
-
Short-term dynamics and interactions of marine protist communities during the spring–summer transition
The ISME Journal (2018)
-
Marked seasonality and high spatial variability of protist communities in shallow freshwater systems
The ISME Journal (2015)