Abstract
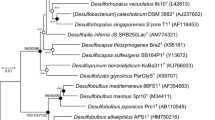
Marine and estuary sediments contain a variety of uncultured archaea whose metabolic and ecological roles are unknown. De novo assembly and binning of high-throughput metagenomic sequences from the sulfate–methane transition zone in estuary sediments resulted in the reconstruction of three partial to near-complete (2.4–3.9 Mb) genomes belonging to a previously unrecognized archaeal group. Phylogenetic analyses of ribosomal RNA genes and ribosomal proteins revealed that this group is distinct from any previously characterized archaea. For this group, found in the White Oak River estuary, and previously registered in sedimentary samples, we propose the name ‘Thorarchaeota’. The Thorarchaeota appear to be capable of acetate production from the degradation of proteins. Interestingly, they also have elemental sulfur and thiosulfate reduction genes suggesting they have an important role in intermediate sulfur cycling. The reconstruction of these genomes from a deeply branched, widespread group expands our understanding of sediment biogeochemistry and the evolutionary history of Archaea.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Amaral-Zettler LA, Rocca JD, Lamontagne MG, Dennett MR, Gast RJ . (2008). Changes in microbial community structure in the wake of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Environ Sci Technol 42: 9072–9078.
Baker BJ, Comolli LR, Dick GJ, Hauser LJ, Hyatt D, Dill BD et al. (2010). Enigmatic, ultrasmall, uncultivated Archaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 8806–8811.
Baker BJ, Dick GJ . (2013). Omic approaches in microbial ecology: charting the unknown. Microbe 8: 353–359.
Baker BJ, Lazar CS, Teske AP, Dick GJ . (2015). Genomic resolution of linkages in carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycling among widespread estuary sediment bacteria. Microbiome 3: 14.
Bauer JE, Cai W-J, Raymond PA, Bianchi TS, Hopkinson CS, Regnier PAG . (2013). The changing carbon cycle of the coastal ocean. Nature 504: 61–70.
Biddle JF, Lipp JS, Lever MA, Lloyd KG, Sørensen KB, Anderson R et al. (2006). Heterotrophic Archaea dominate sedimentary subsurface ecosystems off Peru. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 3846–3851.
Brasen C, Esser D, Rauch B, Siebers B . (2014). Carbohydrate metabolism in archaea: current insights into unusual enzymes and pathways and their regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 78: 89–175.
Brenner DJ . (1983). Opposition to the proposal to replace the family name Enterobacteriaceae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33: 892–895.
Brysch K, Schneider C, Fuchs G, Widdel F . (1987). Lithoautotrophic growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria, and description of Desulfobacterium autotrophicum gen. nov., sp. nov. Arch Microbiol 148: 264–274.
Cabello P, Roldan MD, Moreno-Vivián C . (2004). Nitrate reduction and the nitrogen cycle in archaea. Microbiology 150: 3527–3546.
Cai W-J . (2011). Estuarine and coastal ocean carbon paradox: CO2 sinks or sites of terrestrial carbon incineration? Annu Rev Mar Sci 3: 123–145.
Canfield DE, Raiswell R . (1999). The evolution of the sulfur cycle. American J Sci 299: 697–723.
Castelle CJ, Hug LA, Wrighton KC, Thomas BC, Williams KH, Dongying W et al. (2013). Extraordinary phylogenetic diversity and metabolic versatility in aquifer sediment. Nat Commun 4: 2120.
Castelle CJ, Wrighton KC, Thomas BC, Hug LA, Brown CT, Wilkins MJ et al. (2015). Genomic expansion of domain Archaea highlights roles for organisms from new phyla in anaerobic carbon cycling. Current Biol 25: 690–701.
Criscuolo A, Gribaldo S . (2010). BMGE (Block Mapping and Gathering with Entropy): a new software for selection of phylogenetic informative regions from multiple sequence alignments. BMC Evolutionary Biol 10: 210.
Darling AE, Jospin G, Lowe E, Matsen FA, Bik HM, Eisen JA . (2014). Phylosift phylogenetic analysis of genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ 2: e243.
Dick GJ, Andersson AF, Baker BJ, Simmons SL, Thomas BC, Yelton AP et al. (2009). Community-wide analysis of genome sequence signatures. Gen Biol 10: R85.
Durbin AM, Teske A . (2011). Microbial diversity and stratification of South Pacific abyssal marine sediments. Environ Microbiol 12: 3219–3234.
Edgar R . (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32: 1792–1791.
Glasemacher J, Bock AK, Schmid R, Schönheit P . (1997). Purification and properties of acetyl-coa synthetase (adp-forming), an archaeal enzyme of acetate formation and ATP synthesis, from the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus. Eur J Biochem 244: 561–567.
Guy L, Ettema TJ . (2011). The archaeal ‘TACK’ superphylum and the origins of eukaryotes. Trends Microbiol 19: 580–587.
Heinzinger NK, Fujimoto SY, Clark MA, Moreno MS, Barrett EL . (1995). Sequence analysis of the phs operon in Salmonella typhimurium and the contribution of thiosulfate reduction to anaerobic energy metabolism. J Bacteriol 177: 2813–2820.
Hinsley AP, Berks BC . (2002). Specificity of respiratory pathways involved in the reduction of sulfur compounds by Salmonella enterica. Microbiology 148: 3631–3638.
Hug LA, Castelle CJ, Wrighton KC, Thomas BC, Sharon I, Frischkorn KR et al. (2013). Community genomic analyses constrain the distribution of metabolic traits across the Chloroflexi phylum and indicate roles in sediment carbon cycling. Microbiome 1: 22.
Jørgensen BB . (1982). Mineralization of organic matter in the sea bed – the role of sulphate reduction. Nature 296: 643–645.
Jørgensen BB . (1990). A thiosulfate shunt in the sulfur cycle of marine sediments. Science 249: 152–154.
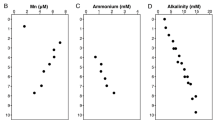
Kelley CA, Martens CS, Chanton JP . (1990). Variations in sedimentary carbon remineralization rates in the White Oak River Estuary, North Carolina. Limnol Oceanogr 35: 372–383.
Kelley CA, Martens CS, Ussler W III . (1995). Methane dynamics across a tidally flooded riverbank margin. Limnol Oceanogr 40: 1112–1129.
Kostka JE, Roychoudhury A, Van Cappellen P . (2002). Rates and controls of anaerobic respiration across spatial and temporal gradients in saltmarch sediments. Biogeochemistry 60: 49–76.
Kubo K, Lloyd KG, Biddle JF, Teske A, Amann R, Knittel K . (2012). Archaea of the Miscellaneous Crenarchaeotal Group are abundant, diverse and widespread in marine sediments. ISME J 6: 1949–1965.
Lazar CS, Biddle JF, Meador TB, Blair N, Hinrichs KU, Teske AP . (2014). Environmental controls on intragroup diversity of the uncultured benthic archaea of the miscellaneous Crenarchaeotal group lineage naturally enriched in anoxic sediments of the White Oak River estuary (North Carolina, USA). Environ Microbiol 17: 2228–2238.
Lever MA . (2012). Acetogenesis in the energy-starved deep biosphere – a paradox? Front Microbiol 2: 284.
Lloyd KG, Alperin MJ, Teske A . (2011). Environmental evidence for net methane production and oxidation in putative ANaerobic MEthanotrophic (ANME) archaea. Environ Microbiol 13: 2548–2564.
Lloyd KG, Schreiber L, Petersen DG, Kjeldsen KU, Lever MA, Steen AD et al. (2013). Predominant archaea in marine sediments degrade detrital proteins. Nature 496: 215–218.
Lombard V, Golaconda Ramulu H, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B . (2014). The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res 42: 490–495.
Lucas S, Copeland A, Lapidus A, Glavina del Rio T, Dalin E, Tice H et al. (2008). Complete sequence of Pelodictyon phaeoclathratiforme BU-1. EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar et al. (2004). ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32: 1363–1371.
Ma K, Schicho RN, Kelly RM, Adams MWW . (1993). Hydrogenase of the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus is an elemental sulfur reductase or sulfhydrogenase: evidence for a sulfur-reducing hydrogenase ancestor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 5341–5344.
Markowitz VM, Chen IM, Palaniappan K, Chu K, Szeto E, Grechkin Y et al. (2012). IMG, the integrated microbial genomes database and comparative analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res 40: D115–D122.
Martens CS, Goldhaber MB . (1978). Early diagenesis in transitional sedimentary environments of the White Oak River Estuary, North Carolina. Limnol Oceanogr 23: 428–441.
Meng J, Xu J, Qin D, He Y, Xiao X, Wang F . (2014). Genetic and functional properties of uncultivated MCG archaea assessed by metagenome and gene expression analyses. ISME J 8: 650–659.
Miller CS, Baker BJ, Thomas BC, Singer S, Banfield JF . (2011). EMIRGE: reconstruction of full-length ribosomal genes from microbial community short read sequencing data. Gen Biol 12: R44.
Moyer CL, Birrien JL, Aoike K, Sunamura M, Urabe T, Mottl MJ et al. (2013). The first microbiological contamination assessment by deep-sea drilling and coring by the D/V Chikyu at the Iheya North hydrothermal field in the Mid-Okinawa Trough (IODP Expedition 331). Front Microbiol 4: 327.
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ . (2015). IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32: 268–274.
Oremland RS, Polcin S . (1982). Methanogenesis and sulfate reduction: competitive and noncompetitive substrates in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 44: 1270–1276.
Oren A . (2012). There must be an acetogen somewhere. Front Microbiol 3: 22.
Park C-I, Choib SY, Kimb WS, Ohb MJ, Kimb EH, Kimb HY et al. (2012). Characterization of the unusual non-thiosulfate-reducing Edwardsiella tarda isolated from eel (Anguilla japonica farms. Aquaculture 356–357: 415–419.
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW . (2015). CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Gen Res 25: 1043–1055.
Peng Y, Leung HCM, Yiu SM, Chin FYL . (2012). IDBA-UD: a de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 28: 1420–1428.
Pires AC, Cleary DF, Almeida A, Cunha A, Dealtry S, Mendonca-Hagler LC et al. (2012). Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and barcoded pyrosequencing reveal unprecedented archaeal diversity in mangrove sediment and rhizosphere samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 78: 5520–5528.
Raes J, Korbel JO, Lercher MJ, von Mering C, Bork P . (2007). Prediction of effective genome size in metagenomic samples. Genome Biol 8: R10.
Ragsdale SW, Pierce E . (2008). Acetogenesis and the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway of CO2 fixation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784: 1873–1898.
Rinke C, Schwientek P, Sczyrba A, Ivanova NN, Anderson IJ, Cheng JF et al. (2013). Insights into the phylogeny and coding potential of microbial dark matter. Nature 499: 431–437.
Sakazaki R . (1984). Genus IV. Citrobacter Werkman and Gillen 1932, 173AL. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, vol. 2. The Williams & Wilkins Co: Baltimore, pp 458–461.
Sapra R, Bagramyan K, Adams M . (2003). A simple energy-conserving system: proton reduction coupled to proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 7545–7550.
Seyler LM, McGuinness LM, Kerkhof LJ . (2014). Crenarchaeal heterotrophy in salt marsh sediments. ISME J 8: 1534–1543.
Sorek R, Zhu Y, Creevey CJ, Francino MP, Bork P, Rubin EM . (2007). Genome-wide experimental determination of barriers to horizontal gene transfer. Science 318: 1449–1452.
Spang A, Saw JH, Jorgensen SL, Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka K, Martijn J, Lind AE et al. (2015). Complex archaea that bridge the gap between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Nature 521: 173–179.
Stamatakis A . (2014). RAxML Version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30: 1312–1313.
Stoffels L, Krehenbrink M, Berks BC, Unden G . (2012). Thiosulfate reduction in Salmonella enterica Is driven by the proton motive force. J Bacteriol 194: 475–485.
Wrighton KC, Castelle CJ, Wilkins MJ, Hug LA, Sharon I, Thomas BC et al. (2014). Metabolic interdependencies between phylogenetically novel fermenters and respiratory organisms in an unconfined aquifer. ISME J 7: 1452–1463.
Wrighton KC, Thomas BC, Sharon I, Miller CS, Castelle CJ, VerBerkmoes NC et al. (2012). Fermentation, hydrogen, and sulfur metabolism in multiple uncultivated bacterial phyla. Science 337: 1661–1665.
Yanagawa K, Morono Y, Beer DD, Haeckel M, Sunamura M, Futagami T et al. (2013a). Metabolically active microbial communities in marine sediment under high-CO2 and low-pH extremes. ISME J 7: 555–567.
Yanagawa K, Nunoura T, McAllister SM, Hirai M, Breuker A, Brandt L et al. (2013b). The first microbiological contamination assessment by deep-sea drilling and coring by the D/V Chikyu at the Iheya North hydrothermal field in the Mid-Okinawa Trough (IODP Expedition 331). Front Microbiol 4: 327.
Acknowledgements
The sequencing at JGI was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231 to BJB. Cassandre Lazar as well as sampling in the White Oak River estuary have been supported by the European Research Council ‘DARCLIFE’ grant 247153 to K-U Hinrichs. AT was in part supported by the Center for Dark Energy Biosphere Investigations (C-DEBI). We thank Dr Thijs JG Ettema for the naming of Thorarchaeota.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seitz, K., Lazar, C., Hinrichs, KU. et al. Genomic reconstruction of a novel, deeply branched sediment archaeal phylum with pathways for acetogenesis and sulfur reduction. ISME J 10, 1696–1705 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.233
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.233
This article is cited by
-
Inference and reconstruction of the heimdallarchaeial ancestry of eukaryotes
Nature (2023)
-
Microbial diversity in extreme environments
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2022)
-
Three families of Asgard archaeal viruses identified in metagenome-assembled genomes
Nature Microbiology (2022)
-
A standardized archaeal taxonomy for the Genome Taxonomy Database
Nature Microbiology (2021)
-
Design of targeted primers based on 16S rRNA sequences in meta-transcriptomic datasets and identification of a novel taxonomic group in the Asgard archaea
BMC Microbiology (2020)