Abstract
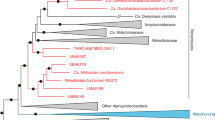
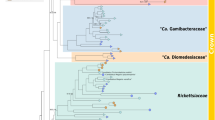
The bacterial family Rickettsiaceae includes a group of well-known etiological agents of many human and vertebrate diseases, including epidemic typhus-causing pathogen Rickettsia prowazekii. Owing to their medical relevance, rickettsiae have attracted a great deal of attention and their host-pathogen interactions have been thoroughly investigated. All known members display obligate intracellular lifestyles, and the best-studied genera, Rickettsia and Orientia, include species that are hosted by terrestrial arthropods. Their obligate intracellular lifestyle and host adaptation is reflected in the small size of their genomes, a general feature shared with all other families of the Rickettsiales. Yet, despite that the Rickettsiaceae and other Rickettsiales families have been extensively studied for decades, many details of the origin and evolution of their obligate host-association remain elusive. Here we report the discovery and single-cell sequencing of ‘Candidatus Arcanobacter lacustris’, a rare environmental alphaproteobacterium that was sampled from Damariscotta Lake that represents a deeply rooting sister lineage of the Rickettsiaceae. Intriguingly, phylogenomic and comparative analysis of the partial ‘Candidatus Arcanobacter lacustris’ genome revealed the presence chemotaxis genes and vertically inherited flagellar genes, a novelty in sequenced Rickettsiaceae, as well as several host-associated features. This finding suggests that the ancestor of the Rickettsiaceae might have had a facultative intracellular lifestyle. Our study underlines the efficacy of single-cell genomics for studying microbial diversity and evolution in general, and for rare microbial cells in particular.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ . (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410.
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25: 3389–3402.
Andersson SGE, Zomorodipour A, Andersson JO, Sicheritz-Pontén T, Alsmark UCM, Podowski RM et al. (1998). The genome sequence of Rickettsia prowazekii and the origin of mitochondria. Nature 396: 133–140.
Andrews S . (2012). FastQC A Quality Control tool for High Throughput Sequence Data http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
Audia JP, Winkler HH . (2006). Study of the five Rickettsia prowazekii proteins annotated as ATP/ADP translocases (Tlc): only Tlc1 transports ATP/ADP, while Tlc4 and Tlc5 transport other ribonucleotides. J Bacteriol 188: 6261–6268.
Bi D, Liu L, Tai C, Deng Z, Rajakumar K, Ou H-Y . (2013). SecReT4: a web-based bacterial type IV secretion system resource. Nucleic Acids Res 41: D660–D665.
Boscaro V, Schrallhammer M, Benken KA, Krenek S, Szokoli F, Berendonk TU et al. (2013). Rediscovering the genus Lyticum, multiflagellated symbionts of the order Rickettsiales. Sci Rep 3: 3305.
Brayton KA, Kappmeyer LS, Herndon DR, Dark MJ, Tibbals DL, Palmer GH et al. (2005). Complete genome sequencing of Anaplasma marginale reveals that the surface is skewed to two superfamilies of outer membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 844–849.
Brindefalk B, Ettema TJG, Viklund J, Thollesson M, Andersson SGE . (2011). A phylometagenomic exploration of oceanic alphaproteobacteria reveals mitochondrial relatives unrelated to the SAR11 clade. PLoS One 6: e24457.
Capella-Gutiérrez S, Silla-Martínez JM, Gabaldón T . (2009). trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25: 1972–1973.
Chen H, Boutros PC . (2011). VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinformatics 12: 35.
Cho N-H, Kim H-R, Lee J-H, Kim S-Y, Kim J, Cha S et al. (2007). The Orientia tsutsugamushi genome reveals massive proliferation of conjugative type IV secretion system and host–cell interaction genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 7981–7986.
Collins NE, Liebenberg J, Villiers EP, de Brayton KA, Louw E, Pretorius A et al. (2005). The genome of the heartwater agent Ehrlichia ruminantium contains multiple tandem repeats of actively variable copy number. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 838–843.
Darby AC, Cho N-H, Fuxelius H-H, Westberg J, Andersson SGE . (2007). Intracellular pathogens go extreme: genome evolution in the Rickettsiales. Trends Genet 23: 511–520.
Driscoll T, Gillespie JJ, Nordberg EK, Azad AF, Sobral BW . (2013). Bacterial DNA sifted from the trichoplax adhaerens (animalia: placozoa) genome project reveals a putative rickettsial endosymbiont. Genome Biol Evol 5: 621–645.
Dunning Hotopp JC, Lin M, Madupu R, Crabtree J, Angiuoli SV, Eisen J et al. (2006). Comparative genomics of emerging human ehrlichiosis agents. PLoS Genet 2: e21.
Eddy SR . (1998). Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 14: 755–763.
Fitzpatrick DA, Creevey CJ, McInerney JO . (2006). Genome phylogenies indicate a meaningful α-proteobacterial phylogeny and support a grouping of the mitochondria with the Rickettsiales. Mol Biol Evol 23: 74–85.
Georgiades K, Madoui M-A, Le P, Robert C, Raoult D . (2011). Phylogenomic analysis of odyssella thessalonicensis fortifies the common origin of Rickettsiales, Pelagibacter ubique and Reclimonas americana mitochondrion. PLoS One 6: e24857.
Grote J, Thrash JC, Huggett MJ, Landry ZC, Carini P, Giovannoni SJ et al (2012) Streamlining and core genome conservation among highly divergent members of the SAR11 clade. Mbio 3: e00252–e002512.
Hackstadt T . (1996). The biology of Rickettsiae. Infect Agents Dis 5: 127–143.
Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML . (2010). Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ Microbiol 12: 1889–1898.
Huson DH, Mitra S, Ruscheweyh H-J, Weber N, Schuster SC . (2011). Integrative analysis of environmental sequences using MEGAN4. Genome Res 21: 1552–1560.
Hyatt D, Chen G-L, LoCascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ . (2010). Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics 11: 119.
Jehl M-A, Arnold R, Rattei T . (2011). Effective—a database of predicted secreted bacterial proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 39: D591–D595.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M . (2014). Data, information, knowledge and principle: back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res 42: D199–D205.
Katoh K, Standley DM . (2013). MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol Biol Evol 30: 772–780.
Kodama Y, Shumway M, Leinonen R, International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration.. (2012). The sequence read archive: explosive growth of sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 40: D54–D56.
Krause DC, Winkler HH, Wood DO . (1985). Cloning and expression of the Rickettsia prowazekii ADP/ATP translocator in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 3015–3019.
Kurtz S, Phillippy A, Delcher AL, Smoot M, Shumway M, Antonescu C et al. (2004). Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol 5: R12.
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW . (2007). RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35: 3100–3108.
Lagkouvardos I, Weinmaier T, Lauro FM, Cavicchioli R, Rattei T, Horn M . (2014). Integrating metagenomic and amplicon databases to resolve the phylogenetic and ecological diversity of the Chlamydiae. ISME J 8: 115–125.
Lartillot N, Rodrigue N, Stubbs D, Richer J . (2013). PhyloBayes MPI: phylogenetic reconstruction with infinite mixtures of profiles in a parallel environment. Syst Biol 62: 611–615.
Lasken RS, Stockwell TB . (2007). Mechanism of chimera formation during the Multiple Displacement Amplification reaction. BMC Biotechnol 7: 19.
Le SQ, Gascuel O . (2008). An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol Biol Evol 25: 1307–1320.
Linka N, Hurka H, Lang BF, Burger G, Winkler HH, Stamme C et al. (2003). Phylogenetic relationships of non-mitochondrial nucleotide transport proteins in bacteria and eukaryotes. Gene 306: 27–35.
Liu H, Bao W, Lin M, Niu H, Rikihisa Y . (2012). Ehrlichia type IV secretion effector ECH0825 is translocated to mitochondria and curbs ROS and apoptosis by upregulating host MnSOD. Cell Microbiol 14: 1037–1050.
Liu R, Ochman H . (2007). Stepwise formation of the bacterial flagellar system. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104: 7116–7121.
Lockwood S, Voth DE, Brayton KA, Beare PA, Brown WC, Heinzen RA et al. (2011). Identification of anaplasma marginale type iv secretion system effector proteins. PLoS One 6: e27724.
Mariconti M, Epis S, Sacchi L, Biggiogera M, Sassera D, Genchi M et al. (2012). A study on the presence of flagella in the order Rickettsiales: the case of ‘Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii’. Microbiology 158: 1677–1683.
Martinez-Garcia M, Swan BK, Poulton NJ, Gomez ML, Masland D, Sieracki ME et al. (2012). High-throughput single-cell sequencing identifies photoheterotrophs and chemoautotrophs in freshwater bacterioplankton. ISME J 6: 113–123.
Merhej V, Raoult D . (2011). Rickettsial evolution in the light of comparative genomics. Biol Rev 86: 379–405.
Montagna M, Sassera D, Epis S, Bazzocchi C, Vannini C, Lo N et al. (2013). ‘Candidatus Midichloriaceae’ fam. nov. (Rickettsiales), an ecologically widespread clade of intracellular Alphaproteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 79: 3241–3248.
Nurk S, Bankevich A, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Korobeynikov A, Lapidus A et al. (2013). Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J Comput Biol 20: 714–737.
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P et al. (2012). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41: D590–D596.
Rinke C, Schwientek P, Sczyrba A, Ivanova NN, Anderson IJ, Cheng J-F et al (2013) Insights into the phylogeny and coding potential of microbial dark matter. Nature,. (2013) 499: 431–437.
Rodríguez-Ezpeleta N, Embley TM . (2012). The SAR11 group of alpha-proteobacteria is not related to the origin of mitochondria. PLoS One 7: e30520.
Sassera D, Lo N, Epis S, D’Auria G, Montagna M, Comandatore F et al. (2011). Phylogenomic evidence for the presence of a flagellum and cbb3 oxidase in the free-living mitochondrial ancestor. Mol Biol Evol 28: 3285–3296.
Schmitz-Esser S, Haferkamp I, Knab S, Penz T, Ast M, Kohl C et al. (2008). Lawsonia intracellularis contains a gene encoding a functional Rickettsia-Like ATP/ADP translocase for host exploitation. J Bacteriol 190: 5746–5752.
Schmitz-Esser S, Linka N, Collingro A, Beier CL, Neuhaus HE, Wagner M et al. (2004). ATP/ADP translocases: a common feature of obligate intracellular amoebal symbionts related to Chlamydiae and Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol 186: 683–691.
Schrallhammer M, Ferrantini F, Vannini C, Galati S, Schweikert M, Görtz H-D et al. (2013). ‘Candidatus megaira polyxenophila’ gen. nov., sp. nov.: considerations on evolutionary history, host range and shift of early divergent Rickettsiae. PLoS One 8: e72581.
Seemann T . (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30: 2068–2069.
Stamatakis A . (2006). RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22: 2688–2690.
Swan BK, Martinez-Garcia M, Preston CM, Sczyrba A, Woyke T, Lamy D et al. (2011). Potential for chemolithoautotrophy among ubiquitous bacteria lineages in the Dark Ocean. Science 333: 1296–1300.
Vahling CM, Duan Y, Lin H . (2010). Characterization of an ATP Translocase Identified in the Destructive Plant Pathogen ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’. J Bacteriol 192: 834–840.
Vannini C, Boscaro V, Ferrantini F, Benken KA, Mironov TI, Schweikert M et al. (2014). Flagellar movement in two bacteria of the family Rickettsiaceae: a re-evaluation of motility in an evolutionary perspective. PLoS One 9: e87718.
Viklund J, Ettema TJG, Andersson SGE . (2012). Independent Genome Reduction and Phylogenetic Reclassification of the Oceanic SAR11 Clade. Mol Biol Evol 29: 599–615.
Wang Z, Wu M . (2015). An integrated phylogenomic approach toward pinpointing the origin of mitochondria. Sci Rep 5: 7949.
Williams KP, Sobral BW, Dickerman AW . (2007). A robust species tree for the Alphaproteobacteria. J Bacteriol 189: 4578–4586.
Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka K, Viklund J, Zhao W, Ast J, Sczyrba A, Woyke T et al. (2013). Single-cell genomics reveal low recombination frequencies in freshwater bacteria of the SAR11 clade. Genome Biol 14: R130.
Acknowledgements
All sequencing was performed by the SNP and SEQ Technology Platform, Science for Life Laboratory at Uppsala University, a national infrastructure supported by the Swedish Research Council (VR-RFI) and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation. We thank the Uppsala Multidisciplinary Center for Advanced Computational Science (UPPMAX) at Uppsala University for providing computational resources. We thank Ilias Lagkouvardos for help in the analysis of the environmental distribution of A. lacustris and Davide Sassera for providing the flagella data set. This work was supported by grants to TJGE and SGEA of the Swedish Research Council (621-2009-4813; 621-2011-4669) and to TJGE and MH of the European Research Council (ERC Starting grant 310039-PUZZLE_CELL and 281633-EvoChlamy). FS is a recipient of the DOC fellowship of the Austrian Academy of Sciences at the Division of Microbial Ecology, University of Vienna, Austria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martijn, J., Schulz, F., Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka, K. et al. Single-cell genomics of a rare environmental alphaproteobacterium provides unique insights into Rickettsiaceae evolution. ISME J 9, 2373–2385 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.46
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.46
This article is cited by
-
Deianiraea, an extracellular bacterium associated with the ciliate Paramecium, suggests an alternative scenario for the evolution of Rickettsiales
The ISME Journal (2019)
-
Diversity and environmental distribution of the cosmopolitan endosymbiont “Candidatus Megaira”
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The Hidden World of Rickettsiales Symbionts: “Candidatus Spectririckettsia obscura,” a Novel Bacterium Found in Brazilian and Indian Paramecium caudatum
Microbial Ecology (2019)
-
A gene transfer event suggests a long-term partnership between eustigmatophyte algae and a novel lineage of endosymbiotic bacteria
The ISME Journal (2018)
-
Deep mitochondrial origin outside the sampled alphaproteobacteria
Nature (2018)