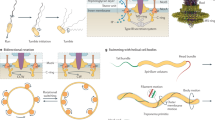
Abstract
Swimming motility is considered a beneficial trait among bacterial species as it enables movement across fluid environments and augments invasion of tissues within the host. However, non-swimming bacteria also flourish in fluid habitats, but how they effectively spread and colonize distant ecological niches remains unclear. We show that non-motile staphylococci can gain motility by hitchhiking on swimming bacteria, leading to extended and directed motion with increased velocity. This phoretic interaction was observed between Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis and P. aeruginosa, as well as S. aureus and Escherichia coli, suggesting hitchhiking as a general translocation mechanism for non-motile staphylococcal species. By leveraging the motility of swimming bacteria, it was observed that staphylococci can colonize new niches that are less available in the absence of swimming carriers. This work highlights the importance of considering interactions between species within polymicrobial communities, in which bacteria can utilize each other as resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adler J . (1966). Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science 153: 708–716.
Berg HC . (1975). Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng 4: 119–136.
Burmølle M, Ren D, Bjarnsholt T, Sørensen SJ . (2014). Interactions in multispecies biofilms: do they actually matter? Trends Microbiol 22: 84–91.
Ceri H, Olson ME, Stremick C, Read RR, Morck D, Buret A . (1999). The Calgary Biofilm Device: new technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biofilms. J Clin Microbiol 37: 1771–1776.
Consortium THMP. (2012). Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 486: 207–214.
Dennis PG, Seymour J, Kumbun K, Tyson GW . (2013). Diverse populations of lake water bacteria exhibit chemotaxis towards inorganic nutrients. ISME J 7: 1661–1664.
Fernandez AS, Hashsham SA, Dollhopf SL, Raskin L, Glagoleva O, Dazzo FB et al. (2000). Flexible community structure correlates with stable community function in methanogenic bioreactor communities perturbed by glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 66: 4058–4067.
Finkelshtein A, Roth D, Jacob EB, Ingham CJ . (2015). Bacterial swarms recruit cargo bacteria to pave the way in toxic environments. mBio 6: e00074–15.
Freney J, Kloos WE, Hajek V, Webster JA, Bes M, Brun Y et al. (1999). Recommended minimal standards for description of new staphylococcal species. Subcommittee on the taxonomy of staphylococci and streptococci of the International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49: 489–502.
Hagai E, Dvora R, Havkin-Blank T, Zelinger E, Porat Z, Schulz S et al. (2014). Surface-motility induction, attraction and hitchhiking between bacterial species promote dispersal on solid surfaces. ISME J 8: 1147–1151.
Hosni T, Moretti C, Devescovi G, Suarez-Moreno ZR, Fatmi MB, Guarnaccia C et al. (2011). Sharing of quorum-sensing signals and role of interspecies communities in a bacterial plant disease. ISME J 5: 1857–1870.
Kaito C, Sekimizu K . (2007). Colony spreading in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 189: 2553–2557.
Kloos WE, Bannerman TL . (1994). Update on clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Rev 7: 117–140.
Lauga E, Powers TR . (2009). The hydrodynamics of swimming microorganisms. Rep Prog Phys 72: 96601.
Matthäus F, Jagodic M, Dobnikar J . (2009). E. coli superdiffusion and chemotaxis-search strategy, precision, and motility. Biophys J 97: 946–957.
Pollitt EJG, Crusz SA, Diggle SP . (2015). Staphylococcus aureus forms spreading dendrites that have characteristics of active motility. Sci Rep 5: 17698.
Sibley CD, Parkins MD, Rabin HR, Duan K, Norgaard JC, Surette MG . (2008). A polymicrobial perspective of pulmonary infections exposes an enigmatic pathogen in cystic fibrosis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 15070–15075.
Stocker R, Seymour JR, Samadani A, Hunt DE, Polz MF . (2008). Rapid chemotactic response enables marine bacteria to exploit ephemeral microscale nutrient patches. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 4209–4214.
Acknowledgements
We thank Gerardo Cárcamo-Oyarce, Erica Shapiro Frenkel and Jacob Witten for helpful feedback on the manuscript. TS was supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship under Grant 1122374. NB was supported by NIH-NIEHS Training Grant in Toxicology T32 ES7020-37. AB was supported by Hugh Hampton Young Memorial Fellowship and NIH-NIAID F30 Fellowship 1F30AI110053. TC was supported by The Marie Curie International Outgoing Fellowship (BIOMUC). PSD acknowledged support from Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART). This work is funded in part by the MRSEC Program of the National Science Foundation under award number DMR-0819762, the CAREER program of the National Science Foundation under award number PHY-1454673, NIH-NIBIB Grant R01EB017755 and P30ES002109 NIH-NIEHS Core Center. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samad, T., Billings, N., Birjiniuk, A. et al. Swimming bacteria promote dispersal of non-motile staphylococcal species. ISME J 11, 1933–1937 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.23
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.23
This article is cited by
-
Comprehensive review of bacterial death mechanism on nanopillared nanostructured surfaces
Biophysical Reviews (2025)
-
An innovative process chain for the production of antibiofouling polymer parts using ultrafast laser texturing
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (2024)
-
Role of bacterial motility in differential resistance mechanisms of silver nanoparticles and silver ions
Nature Nanotechnology (2021)
-
Microbial hitchhiking: how Streptomyces spores are transported by motile soil bacteria
The ISME Journal (2021)