Abstract
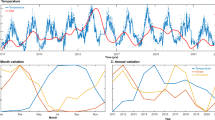
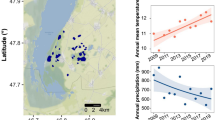
Marine microbes exhibit seasonal cycles in community composition, yet the key drivers of these patterns and microbial population fidelity to specific environmental conditions remain to be determined. To begin addressing these questions, we characterized microbial dynamics weekly for 3 years at a temperate, coastal site with dramatic environmental seasonality. This high-resolution time series reveals that changes in microbial community composition are not continuous; over the duration of the time series, the community instead resolves into distinct summer and winter profiles with rapid spring and fall transitions between these states. Here, we show that these community shifts involve switching between closely related strains that exhibit either summer or winter preferences. Moreover, taxa repeat this process annually in both this and another temperate coastal time series, suggesting that this phenomenon may be widespread in marine ecosystems. To address potential biogeochemical impacts of these community changes, PICRUSt-based metagenomes predict seasonality in transporters, photosynthetic proteins, peptidases and carbohydrate metabolic pathways in spite of closely related summer- and winter-associated taxa. Thus, even small temperature shifts, such as those predicted by climate change models, could affect both the structure and function of marine ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Alonso-Sáez L, Díaz-Pérez L, Morán XAG . (2015). The hidden seasonality of the rare biosphere in coastal marine bacterioplankton. Environ Microbiol 17: 3766–3780.
Baltar F, Palovaara J, Vila-Costa M, Salazar G, Calvo E, Pelejero C et al. (2015). Response of rare, common and abundant bacterioplankton to anthropogenic perturbations in a Mediterranean coastal site. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91: fiv058.
Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB . (2004). Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 85: 1771–1789.
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK et al. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7: 335–336.
Caporaso JG, Paszkiewicz K, Field D, Knight R, Gilbert JA . (2011). The Western English Channel contains a persistent microbial seed bank. ISME J 6: 1089–1093.
Chow C-ET, Sachdeva R, Cram JA, Steele JA, Needham DM, Patel A et al. (2013). Temporal variability and coherence of euphotic zone bacterial communities over a decade in the Southern California Bight. ISME J 7: 2259–2273.
Doney SC, Ruckelshaus M, Duffy JE, Barry JP, Chan F, English CA et al. (2012). Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Mar Sci 4: 11–37.
Dutkiewicz S, Scott JR, Follows M . (2013). Winners and losers: ecological and biogeochemical changes in a warming ocean. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 27: 463–477.
Edgar RC . (2010). Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26: 2460–2461.
Edgar RC . (2013). UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10: 996–998.
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R . (2011). UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27: 2194–2200.
El-Swais H, Dunn KA, Bielawski JP, Li WK, Walsh DA . (2015). Seasonal assemblages and short-lived blooms in coastal north-west Atlantic Ocean bacterioplankton. Environ Microbiol 17: 3642–3661.
Eren AM, Maignien L, Sul WJ, Murphy LG, Grim SL, Morrison HG et al. (2013). Oligotyping: differentiating between closely related microbial taxa using 16S rRNA gene data. Methods Ecol Evol 4: 1111–1119.
Eren AM, Morrison HG, Lescault PJ, Reveillaud J, Vineis JH, Sogin ML . (2015). Minimum entropy decomposition: unsupervised oligotyping for sensitive partitioning of high-throughput marker gene sequences. ISME J 9: 968–979.
Fuhrman JA, Hewson I, Schwalbach MS, Steele JA, Brown MV, Naeem S . (2006). Annually reoccurring bacterial communities are predictable from ocean conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 13104–13109.
Fuhrman JA, Steele JA, Hewson I, Schwalbach MS, Brown MV, Green JL et al. (2008). A latitudinal diversity gradient in planktonic marine bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 7774–7778.
García FC, Alonso-Sáez L, Morán XAG, López-Urrutia Á . (2015). Seasonality in molecular and cytometric diversity of marine bacterioplankton: the re-shuffling of bacterial taxa by vertical mixing. Environ Microbiol 17: 4133–4142.
Gifford SM, Sharma S, Moran MA . (2014). Linking activity and function to ecosystem dynamics in a coastal bacterioplankton community. Front Microbiol 5: 185.
Gilbert JA, Steele JA, Caporaso JG, Steinbrück L, Reeder J, Temperton B et al. (2012). Defining seasonal marine microbial community dynamics. ISME J 6: 298–308.
Guindon S, Dufayard J-F, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O . (2010). New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59: 307–321.
Hunt DE, David LA, Gevers D, Preheim SP, Alm EJ, Polz MF . (2008). Resource partitioning and sympatric differentiation among closely related bacterioplankton. Science 320: 1081–1085.
Hunt DE, Lin Y, Church MJ, Karl DM, Izzo LK, Tringe S et al. (2013). Relationship between abundance and specific activity of bacterioplankton in open ocean surface waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 79: 177–184.
Hunt DE, Ward CS . (2015). A network-based approach to disturbance transmission through microbial interactions. Front Microbiol 6: 1182.
Johnson ZI, Wheeler BJ, Blinebry SK, Carlson CM, Ward CS, Hunt DE . (2013). Dramatic variability of the carbonate system at a temperate coastal ocean site (Beaufort, North Carolina, USA) is regulated by physical and biogeochemical processes on multiple timescales. PLoS ONE 8: e85117.
Johnson ZI, Zinser ER, Coe A, McNulty NP, Woodward EMS, Chisholm SW . (2006). Niche partitioning among Prochlorococcus ecotypes along ocean-scale environmental gradients. Science 311: 1737–1740.
Kashtan N, Roggensack SE, Rodrigue S, Thompson JW, Biller SJ, Coe A et al. (2014). Single-cell genomics reveals hundreds of coexisting subpopulations in wild Prochlorococcus. Science 344: 416–420.
Kozich JJ, Westcott SL, Baxter NT, Highlander SK, Schloss PD . (2013). Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl Environ Microbiol 79: 5112–5120.
Kumar L, Futschik ME . (2007). Mfuzz: a software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation 2: 5–7.
Ladau J, Sharpton TJ, Finucane MM, Jospin G, Kembel SW, O'Dwyer J et al. (2013). Global marine bacterial diversity peaks at high latitudes in winter. ISME J 7: 1669–1677.
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA et al. (2013). Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31: 814–821.
Larkin AA, Blinebry SK, Howes C, Lin Y, Loftus SE, Schmaus CA et al. (2016). Niche partitioning and biogeography of high light adapted Prochlorococcus across taxonomic ranks in the North Pacific. ISME J 10: 1555–1567.
Lindh MV, Sjöstedt J, Andersson AF, Baltar F, Hugerth LW, Lundin D et al. (2015). Disentangling seasonal bacterioplankton population dynamics by high-frequency sampling. Environ Microbiol 17: 2459–2476.
Louca S, Parfrey LW, Doebeli M . (2016). Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 353: 1272–1277.
Martiny JB, Jones SE, Lennon JT, Martiny AC . (2015). Microbiomes in light of traits: a phylogenetic perspective. Science 350: aac9323.
Massana R, Murray AE, Preston CM, DeLong EF . (1997). Vertical distribution and phylogenetic characterization of marine planktonic Archaea in the Santa Barbara Channel. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 50–56.
Needham DM, Chow C-ET, Cram JA, Sachdeva R, Parada A, Fuhrman JA . (2013). Short-term observations of marine bacterial and viral communities: patterns, connections and resilience. ISME J 7: 1274–1285.
Needham DM, Fuhrman JA . (2016). Pronounced daily succession of phytoplankton, archaea and bacteria following a spring bloom. Nat Microbiol 1: 16005.
Nemergut DR, Schmidt SK, Fukami T, O'Neill SP, Bilinski TM, Stanish LF et al. (2013). Patterns and processes of microbial community assembly. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77: 342–356.
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara R et al. (2013). Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.
Salter I, Galand PE, Fagervold SK, Lebaron P, Obernosterer I, Oliver MJ et al. (2015). Seasonal dynamics of active SAR11 ecotypes in the oligotrophic Northwest Mediterranean Sea. ISME J 9: 347–360.
Shade A, Chiu CY, McMahon KD . (2010). Differential bacterial dynamics promote emergent community robustness to lake mixing: an epilimnion to hypolimnion transplant experiment. Environ Microbiol 12: 455–466.
Sharma AK, Becker JW, Ottesen EA, Bryant JA, Duhamel S, Karl DM et al. (2014). Distinct dissolved organic matter sources induce rapid transcriptional responses in coexisting populations of Prochlorococcus Pelagibacter and the OM60 clade. Environ Microbiol 16: 2815–2830.
Steele JA, Countway PD, Xia L, Vigil PD, Beman JM, Kim DY et al. (2011). Marine bacterial, archaeal and protistan association networks reveal ecological linkages. ISME J 5: 1414–1425.
Stoddard SF, Smith BJ, Hein R, Roller BR, Schmidt TM . (2014). rrnDB: improved tools for interpreting rRNA gene abundance in bacteria and archaea and a new foundation for future development. Nucleic Acids Res 43: D593–D598.
Sunagawa S, Coelho LP, Chaffron S, Kultima JR, Labadie K, Salazar G et al. (2015). Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 348: 1261359.
Teeling H, Fuchs BM, Bennke CM, Krüger K, Chafee M, Kappelmann L et al. (2016). Recurring patterns in bacterioplankton dynamics during coastal spring algae blooms. eLife 5: e11888.
ter Braak CJ, Verdonschot PF . (1995). Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquatic Sci 57: 255–289.
Thomas MK, Kremer CT, Klausmeier CA, Litchman E . (2012). A global pattern of thermal adaptation in marine phytoplankton. Science 338: 1085–1088.
Yawata Y, Cordero OX, Menolascina F, Hehemann J-H, Polz MF, Stocker R . (2014). Competition–dispersal tradeoff ecologically differentiates recently speciated marine bacterioplankton populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111: 5622–5627.
Yung C-M, Vereen MK, Herbert A, Davis KM, Yang J, Kantorowska A et al. (2015). Thermally adaptive tradeoffs in closely-related marine bacterial strains. Environ Microbiol 17: 2421–2429.
Yung C-M, Ward CS, Davis KM, Johnson ZI, Hunt DE . (2016). Insensitivity of diverse and temporally variable particle-associated microbial communities to bulk seawater environmental parameters. Appl Environ Microbiol 82: 3431–3437.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the entire PICO team for help with environmental sampling. This work was supported by grants from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation (GBMF3768 to DEH) and the National Science Foundation (OCE1322950 to DEH; OCE1416665 to DEH and ZIJ; and a GRFP award to CSW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, C., Yung, CM., Davis, K. et al. Annual community patterns are driven by seasonal switching between closely related marine bacteria. ISME J 11, 1412–1422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.4
This article is cited by
-
Correlating the Water Quality Parameters on Algal Diversity through Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Identifying the Bioindicator of Water Pollution in the Freshwater Ecosystems of Dakshina, Karnataka
Water, Air, & Soil Pollution (2026)
-
Multi-domain temporal patterns reveal stable community membership but dynamic interactions in the coastal microbiome
Environmental Microbiome (2025)
-
Identifying the drivers of microbial community changes and interactions in polluted coastal sediments
Environmental Microbiome (2025)
-
On the growth and form of bacterial colonies
Nature Reviews Physics (2025)
-
Climate-driven succession in marine microbiome biodiversity and biogeochemical function
Nature Communications (2025)