Abstract
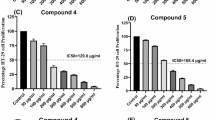
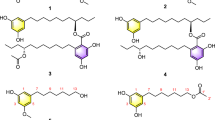
With the aim of identifying more novel natural epothilone derivatives produced by the epothilones A and B producing strain Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2, a large-scale fermentation (5000 l) of the strain was carried out. As a result, five new epothilone variants (1–5) were isolated from the fermentation broth. Their structures were established as 3-α-D-arabinofuranosides of epothilones A (1), B (2), D (3), C9 (4) and 8-demethyl epothilone A (5) by extensive NMR analysis and chemical methods. Bioassay results showed that compounds 1 and 2 had a weaker cytotoxic activity than did epothilone B.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Höfle, G., Bedorf, N., Gerth, K. & Reichenbach, H. (GBF). Epothilones, process for preparing the same and their use as medicaments and as plant protecting agents. D.E. 4,138,042, May 27 (1993).
Gerth, K., Bedorf, N., Höfle, G., Irschik, H. & Reichenbach, H. Epothilons A and B: antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (Myxobacteria). production, physico-chemical and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 49, 560–563 (1996).
Höfle, G. et al. Epothilone A and B-novel 16-membered macrolides with cytotoxic activity: isolation, crystal structures, and conformation in solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 35, 1567–1569 (1996).
Hardt, I. H. et al. New natural epothilones from Sorangium cellulosum, strains So ce90/B2 and So ce90/D13: isolation, structure elucidation, and SAR studies. J. Nat. Prod. 64, 847–856 (2001).
Arslanian, R. L. et al. A new cytotoxic epothilone from modified polyketide synthases heterologously expressed in Myxococcus xanthus. J. Nat. Prod. 65, 1061–1064 (2002).
Starks, C. M., Zhou, Y., Liu, F. & Licari, P. J. Isolation and characterization of new epothilone analogues from recombinant Myxococcus xanthus fermentations. J. Nat. Prod. 66, 1313–1317 (2003).
Nicolaou, K. C., Roschangar, F. & Vourloumis, D. Chemical biology of epothilones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 37, 2014–2045 (1998).
Dong, S. D. et al. Rapid access to epothilone analogs via semisynthetic degradation and reconstruction of epothilone D. Tetrahedron Lett. 45, 1945–1947 (2004).
Lee, J. J. & Swain, S. M. The epothilones: translating from the laboratory to the clinic. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 1618–1624 (2008).
Gong, G. L. et al. Mutation and a high-throughput screening method for improving the production of epothilones of Sorangium. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 34, 615–623 (2007).
Tanaka, T., Nakashima, T., Ueda, T., Tomii, K. & Kouno, I. Facile discrimination of aldose enantiomers by reversed-phase HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 55, 899–901 (2007).
Gorin, P. A. J. & Mazurek, M. Further studies on the assignment of signals in 13C magnetic resonance spectra of aldoses and derived methyl glycosides. Can. J. Chem. 53, 1212–1223 (1975).
Wang, J. D. et al. HS071, A new furan-type cytotoxic metabolite from Streptomyces sp. HS-HY-071. J. Antibiot. 61, 623–626 (2008).
Nicolaou, K. C. et al. Designed epothilones: solid phase synthesis on microtubes, tubulin assembly properties and cytotoxic action against taxol-resistant tumor cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 36, 2097–2103 (1997).
Nicolaou, K. C. et al. Probing the ring size of epothilones: total synthesis of [14]-, [15]-, [17]-, and [18]-epothilones A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 37, 81–84 (1998).
Meng, D. et al. Remote effects in macrolide formation through ring-forming olefin metathesis: an application to the synthesis of fully active epothilone congeners. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 2733–2734 (1997).
Erdélyi, M. et al. Conformational preferences of natural and C3-modified epothilones in aqueous solution. J. Med. Chem. 51, 1469–1473 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The Journal of Antibiotics website (http://www.nature.com/ja)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, H., Ying, L. et al. Five new epothilone metabolites from Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2. J Antibiot 62, 483–487 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2009.55
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2009.55
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Micromonospora zhangzhouensis sp. nov., a Novel Actinobacterium Isolated from Mangrove Soil, Exerts a Cytotoxic Activity in vitro
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Two new glutarimide antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. HS-NF-780
The Journal of Antibiotics (2019)
-
Two new lankacidin-related metabolites from Streptomyces sp. HS-NF-1178
The Journal of Antibiotics (2018)
-
Two new spliceostatin analogs from the strain Pseudomonas sp. HS-NF-1408
The Journal of Antibiotics (2018)
-
A new anthracycline-type metabolite from Streptomyces sp. NEAU-L3
The Journal of Antibiotics (2017)