Abstract
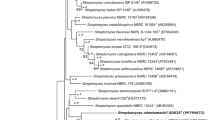
A novel actinobacterium MBRL 251T, isolated from a sample collected from a limestone quarry at Hundung, Manipur, India, was characterized using a polyphasic approach. The 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequence of strain MBRL 251T showed closest similarities with Streptomyces xanthochromogenes NRRL B-5410T (99.6%) and Streptomyces michiganensis NBRC 12797T (99.6%). The DNA relatedness between MBRL 251T and S. xanthochromogenes NBRC 12828T, and S. michiganensis NBRC 12797T was 46.6% and 40.7%, respectively. Strain MBRL 251T contained LL-diaminopimelic acid as the diagnostic diamino acid, with glucose and xylose as the main cell wall sugars, whereas small amounts of galactose, mannose, rhamnose and ribose were also detected in the whole-cell wall hydrolysates. The major fatty acids identified were anteiso-C15:0 (35.1%), iso-C16:0 (21.1%) and anteiso-C17:1 (13.2%). The predominant menaquinones detected were MK-9(H6) and MK-9(H8), whereas the polar lipids were diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylinositolmannosides. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 72.3%. The phenotypic and genotypic data showed that strain MBRL 251T merits the recognition as a representative of a novel species of the genus Streptomyces. It is proposed that the isolate should be classified in the genus Streptomyces as a novel species, Streptomyces hundungensis sp. nov. The type strain is MBRL 251T (=JCM 17577T=KCTC 29124T).
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Berdy, J. Bioactive microbial metabolites: a personal view. J. Antibiot. 58, 1–26 (2005).
Brautaset, T. et al. Biosynthesis of the polyene antifungal antibiotic nystatin in Streptomyces noursei ATCC 11455: analysis of the gene cluster and deduction of the biosynthetic pathway. Chem. Biol. 7, 395–403 (2000).
Caffrey, P., Lynch, S., Flood, E., Finnan, S. & Oliynk, M. Amphotericin biosynthesis in Streptomyces nodosus: deductions from analysis of polyketide synthase and late genes. Chem. Biol. 8, 713–723 (2001).
Yuan, W. M. & Crawford, D. L. Characterization of Streptomyces lydicus WYEC108 as a potential biocontrol agent against fungal root and seed rots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 3119–3128 (1995).
Hamdali, H., Halidi, M., Virolle, M. J. & Qahdouch, Y. Rock phosphate-solubilizing actinomycetes: screening for plant growth-promoting activities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 2565–2575 (2008).
Khamna, S., Yokota, A. & Lumyong, S. Actinomycetes isolated from medicinal plant rhizospheric soils: diversity and screening of antifungal compounds, indole-3-acetic acid and siderophore production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25, 649–655 (2009).
Khamna, S., Yokota, A., Peberdy, J. F. & Lumyong, S. Indole-3-acetic acid production by Streptomyces sp. isolated from some Thai medicinal plant rhizosphere soils. EurAsia J. Biosci. 4, 23–32 (2010).
Lechevalier, M. P. & Lechevalier, H. A. Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 20, 435–443 (1970).
Anderson, A. S. & Wellington, E. M. H. The taxonomy of Streptomyces and related genera. Int, J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51, 797–814 (2001).
Kuster, E. & Williams, S. T. Selection of media for isolation of Streptomyces. Nature 202, 928–929 (1964).
Shirling, E. B. & Gottlieb, D. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 16, 313–340 (1966).
Kelly, K. L. Inter-Society Color Council—National Bureau of Standards Color-Name Charts Illustrated with Centroid Colors (US Government Printing Office, Washington, 1964).
Gordon, R. E., Barnett, D. A., Handerhan, J. E. & Pang, C. H. N. Nocardia coeliaca, Nocardia autotrophica, and the nocardin strain. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 24, 54–63 (1974).
Collins, C. H., Lyne, P. M., Grange, J. M. & Falkinham, J. O. Microbiological Methods 8th edn (Arnold, London, 2004).
Lanyi, B. Classical and rapid identification methods for medically important bacteria. Methods Microbiol. 19, 1–67 (1987).
Goodfellow, M. Genus rhodococcus Zopf 1891, 28AL in Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology (eds Sneath P. H. A., Mair N. S., Sharpe M. E., Holt. J. G.) vol. 2, pp 1472–1481 (Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1986).
Staneck, J. L. & Robert, G. D. Simplified approached to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl. Microbiol. 28, 226–231 (1974).
Tang, S. K. et al. Zhihengliuella alba sp. nov., and emended description of the genus Zhihengliuella. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 2025–2031 (2009).
Minnikin, D. E. et al. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2, 233–241 (1984).
Collins, M. D., Pirouz, T., Goodfellow, M. & Minnikin, D. E. Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 100, 221–230 (1977).
Tamaoka, J., Katayama-Fujimura, Y. & Kuraishi, H. Analysis of bacterial menaquinone mixtures by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 54, 31–36 (1983).
Sasser, M. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newsl. 20, 16 (1990).
Li, W. J. et al. Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China), and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 1424–1428 (2007).
Kim, O. S. et al. Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA Gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 716–721 (2012).
Larkin, M. A. et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948 (2007).
Tamura, K. et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsinomy methods. Mol. Bio. Evol. 28, 2731–2739 (2011).
Kimura, M. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1983).
Saitou, N. & Nei, M. The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Bio. Evol. 4, 406–425 (1987).
Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791 (1985).
Kluge, A. G. & Farris, F. S. Quantitative phyletics and the evolution of anurans. Syst. Zool. 18, 1–32 (1969).
Mesbah, M., Premachandran, U. & Whitman, W. B. Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 159–167 (1989).
DeLey, J., Caltoir, H. & Reeynaerts, A. The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rate. Eur. J. Biochem. 12, 133–142 (1970).
You, J. L. et al. Isolation and characterization of actinomycetes antagonistic to pathogenic Vibrio spp. from nearshore marine sediments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 21, 679–682 (2004).
Bano, N. & Musarrat, J. Characterization of a new Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain NJ-15 as a potential biocontrol agent. Curr. Microbiol. 46, 324–328 (2003).
Cappuccino, J. C. & Sherman, N. in Microbiology: A Laboratory Manual. pp 125–179 (New York, 1992).
Mehta, S. & Nautiyal, C. S. An efficient method for qualitative screening of Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 43, 51–56 (2001).
Bouchek-Mechiche, K., Gardan, L., Normand, P. & Jouan, B. DNA relatedness among strains of Streptomyces pathogenic to potato in France: description of three new species, S. europaeiscabiei sp. nov. and S. stelliscabiei sp. nov. associated with common scab, and S. reticuliscabiei sp. nov. associated with netted scab. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 91–99 (2000).
Dastager, S. G. et al. Streptomyces gulbargensis sp. nov., isolated from soil in Karnataka, India. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 91, 99–104 (2007).
Goodfellow, M., Kumar, Y., Labeda, D. P. & Sembiring, L. The Streptomyces violaceusniger clade: a home for streptomycetes with rugose ornamented spores. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 92, 173–199 (2007).
Nimaichand, S. et al. Streptomyces manipurensis sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from a limestone deposit site in Manipur, India. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 102, 133–139 (2012).
Wayne, L. G. et al. International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematic. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464 (1987).
Labeda, D. P. et al. Phylogenetic study of the species within the family. Streptomycetaceae. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 101, 73–104 (2012).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Professor Tomohiko Tamura (NBRC) for providing the reference type strains. SN wishes to thank the University Grants Commission (UGC), Government of India, for offering him the Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship. KT wishes to thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India for offering him the CSIR-SRF. LL wishes to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31200008). Y-GZ wishes to thank the West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences. W-J Li was also supported by ‘Hundred Talents Program’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The Journal of Antibiotics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nimaichand, S., Tamrihao, K., Yang, LL. et al. Streptomyces hundungensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete with antifungal activity and plant growth promoting traits. J Antibiot 66, 205–209 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2012.119
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2012.119
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of Streptomyces species in controlling plant diseases: a comprehensive review
Australasian Plant Pathology (2024)
-
Streptomyces desertarenae sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from a desert sample
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2019)
-
Biodiversity and ecology of flower-associated actinomycetes in different flowering stages of Protea repens
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2018)
-
Effect of fairy ring bacteria on the growth of Tricholoma matsutake in vitro culture
Mycorrhiza (2018)
-
Streptomyces seymenliensis sp. nov., isolated from soil
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2015)