Abstract
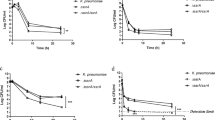
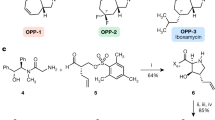
Novel azithromycin (AZM) derivatives with the C-4″ bisamide side chains were synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro antibacterial activities. The 4″-O-(benzamido)alkyl carbamates showed excellent activity against the erythromycin-susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae and exhibited greatly improved activity against erythromycin-resistant S. pneumoniae. Among them, compounds 5g and 6g, which had the same electron-withdrawing group, 3,5-dinitrophenyl, on the termination of their C-4″ bisamide side chains, demonstrated the most potent activity against erythromycin-resistant S. pneumoniae expressing the erm gene, the mef gene and the erm and mef genes, showing 128-fold, 33-fold and 32-fold improved activity in comparison with the parent AZM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Chu, D. T., Plattner, J. J. & Katz, L. New directions in antibacterial research. J. Med. Chem. 39, 3853–3874 (1996).
Morimoto, S., Takahashi, Y., Watanabe, Y. & Omura, S. Chemical modification of erythromycins. I. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 6-O-methylerythromycins A. J. Antibiot. 37, 187–189 (1984).
Djokic, S., Kobrehel, G. & Lazarevski, G. Erythromycin series. XII. Antibacterial in vitro evaluation of 10-dihydro-10-deoxo-11-azaerythromycin A: synthesis and structure-activity relationship of its acyl derivatives. J. Antibiot. 40, 1006–1015 (1987).
File, T. M. Telithromycin new product overview. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 115, S1–S13 (2005).
Denis, A. et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of HMR 3647 a new ketolide highly potent against erythromycin-resistant and susceptible pathogens. Bioorg.Med. Chem. Lett. 9, 3075–3080 (1999).
Bryskier, A. Novelties in the field of anti-infectives in 1997. Clin. Infect. Dis. 27, 865–883 (1998).
Champney, W. S. & Tober, C. L. Preferential inhibition of protein synthesis by ketolide antibiotics in Haemophilus influenzae cells. Curr. Microbiol. 46, 103–108 (2003).
Henninger, T. C. Recent progress in the field of macrolide antibiotics. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 13, 787–805 (2003).
Wu, Y. J. & Su, W. G. Recent developments on ketolides and macrolides. Curr. Med. Chem. 8, 1727–1758 (2001).
Fernandes, P. B., Baker, W.R., Freiberg, L. A., Hardy, D.J. & McDonald, E. J. New macrolides active against Streptococcus pyogenes with inducible or constitutive type of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33, 78–81 (1989).
Takashima, H. Structural consideration of macrolide antibiotics in relation to the ribosomal interaction and drug design. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 3, 991–999 (2003).
Ma, S., Ma, R., Liu, Z., Ma, C. & Shen, X. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel 15-membered macrolide derivatives: 4”-carbamate, 11,12-cyclic carbonate-4”-carbamate and 11,4”-di-O-arylcarbamoyl analogs of azithromycin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 4010–4020 (2009).
Ma, C. et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel 11,12-cyclic carbonate azithromycin 4″-O-carbamate derivatives. J Antibiot. 63, 3–8 (2010).
Schlünzen, F. et al. Structural basis for the antibiotic activity of ketolides and azalides. Structure. 11, 329–338 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (20872081 and 21072114), Major R&D Program of New Drugs–National S&T Key Special Subject of China (2009ZX09103-115), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (ZR2010HM092) and the Project-sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The Journal of Antibiotics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, W., An, L., Ma, C. et al. Novel azithromycin derivatives with the C-4″ bisamide side chains: synthesis and biological evaluation against gram-positive bacteria. J Antibiot (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2012.3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2012.3