Abstract
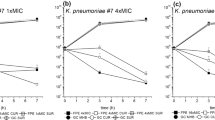
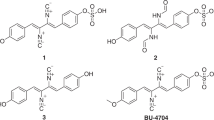
Furbenicillin is a broad-spectrum semisynthetic penicillin with strong antibacterial activity against Gram-negative bacteria. In this study, three impurities in furbenicillin, including an unknown epimer, were determined. On the basis of a complete analysis of the spectrum (MS, 1H,13C, 2D NMR and CD) and the results of chemical methods, the unknown epimer impurity was identified as 10-epi-furbenicillin (impurity 1). Isolation and structure elucidation of impurity 1 was also reported here for the first time.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Jiang, Y., Zhang, Z. F. & Wang, H. Isomeric impurity research and quality control of β-lactam antibiotics. Chin. J. Antibiot. 35, 561–566 (2010).
Busson, R. & Vanderhaeghe, H. Preparation and isomerization of 5-epibenzylpenicillins. J. Org. Chem. 41, 2561–2565 (1976).
Wiitala, K. W., Cramer, C. J. & Hoye, T. R. Comparison of various density functional methods for distinguishing stereoisomers based on computed 1H or 13C NMR chemical shifts using diastereomeric penam β-lactams as a test set. Magn. Reson. Chem. 45, 819–829 (2007).
Bird, A. E., Steele, B. R., Boles, M. O. & Gane, P. A. C. Nuclear magnetic resonance and circular dichroism of penicillins derived from disubstituted acetic acids. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 563–569 (1982).
Hutt, A. G. & O'Grady, J. Drug chirality: a consideration of the significance of the stereochemistry of antimicrobial agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 37, 7–32 (1996).
Nayler, J. H. Advances in penicillin research. Adv. Drug Res. 7, 1–105 (1973).
Nomura, H. et al. Studies on diastereomers of sulbenicillin by nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Takeda Res. Lab. 31, 442–452 (1972).
Bodey, G. P. & Stewart, D. In vitro studies of semisynthetic alpha(substituted-ureido)penicillins. Appl. Microbiol. 21, 710–717 (1971).
Jiatai, L., Zhongmin, S., Tieying, L., Lingjia, M. & Mei, F. Furbenicillin and its antibacterial activity. Chin. Med. J. 92, 185–192 (1979).
Ma, Y. Z., Liu, Y. X., Zhou, Y. P., Mei, W. J. & She, Z. G. Improved synthesis of furbenicillin sodium. Chin. J. Med. Chem. 16, 51–53 (2006).
Li, J. T. & Williams, J. D. Comparative activity of furbenicillin and carbenicillin-like compounds. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 9, 171–181 (1982).
Zhang, J., Jiang, J. & Gao, Y. Determination of Furbenicillin Sodium related substances and in vitro antibacterial activity comparison. Chin. Pharm. 19, 34–35 (2010).
Zhang, J., Jiang, J. & Gao, Y. HPLC-Electrospray Ionization-Mass spectrum analysis of Furbenicillin sodium and its related substances. Chin. Pharm. 18, 16–17 (2009).
Elks, J. (ed.). Recent Advances in the Chemistry of β-Lactam Antibiotics. Special Publication No. 28, 304–313 (The Chemical Society: London, UK, (1976).
Gan, M. et al. Polyketides with New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase 1 inhibitory activity from Penicillium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 76, 1535–1540 (2013).
Bhushan, R. & Brückner, H. Marfey’s reagent for chiral amino acid analysis: a review. Amino Acids 27, 231–247 (2004).
Robinson-Fuentes, V. A., Jefferies, T. M. & Branch, S. K. Degradation pathways of ampicillin in alkaline solutions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 49, 843–851 (1997).
Aboul Khier, A., Blaschke, G. & El Sadek, M. Determination of some penicillin derivatives using high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Lett. 17, 1659–1666 (1984).
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically; approved standard—8th edition. Report No.:12M07-A7 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Youth development research foundation of NIFDC (2013NA2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The Journal of Antibiotics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Chang, Y., Feng, YC. et al. Isolation, identification and characterization of related substances in furbenicillin. J Antibiot 68, 133–136 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.145
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.145