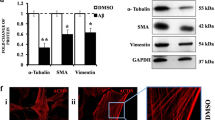
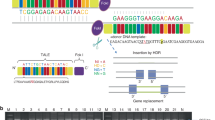
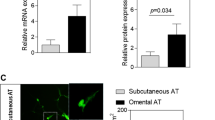
Abstract
Mutations in ROR2, encoding the receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2, cause two distinct skeletal diseases: autosomal dominant brachydactyly type B1 (BDB1) and autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome. In a large Chinese family with a limb phenotype, consisting of atypical BDB1 and cutaneous syndactyly of varying degrees, we performed a two-point linkage analysis using microsatellite markers on 2q33–q37 and 9q22.31, and found a significant linkage to the ROR2 locus. We identified a novel single-base deletion in ROR2, c.2243delC (p.W749fsX24), and confirmed its segregation with the limb phenotype in the family. This deletion is predicted to produce a truncated ROR2 protein with an additional C-terminal polypeptide of 24 amino-acid residues. To the best of our knowledge, the deletion represents the second ROR2 mutation associated with a BDB1-syndactyly phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Afzal, A. R. & Jeffery, S. One gene, two phenotypes: ROR2 mutations in autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome and autosomal dominant brachydactyly type B. Hum. Mutat. 22, 1–11 (2003).
Oldridge, M., Fortuna, A. M., Maringa, M., Propping, P., Mansour, S., Pollitt, C. et al. Dominant mutations in ROR2, encoding an orphan receptor tyrosine kinase, cause brachydactyly type B. Nat. Genet. 24, 275–278 (2000).
Schwabe, G. C., Tinschert, S., Buschow, C., Meinecke, P., Wolff, G., Gillessen-Kaesbach, G. et al. Distinct mutations in the receptor tyrosine kinase gene ROR2 cause brachydactyly type B. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67, 822–831 (2000).
Afzal, A. R., Rajab, A., Fenske, C. D., Oldridge, M., Elanko, N., Ternes-Pereira, E. et al. Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat. Genet. 25, 419–422 (2000).
van Bokhoven, H., Celli, J., Kayserili, H., van Beusekom, E., Balci, S., Brussel, W. et al. Mutation of the gene encoding the ROR2 tyrosine kinase causes autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome. Nat. Genet. 25, 423–426 (2000).
Bacchelli, C., Wilson, L., Cook, J., Winter, R. & Goodman, F. ROR2 is mutated in hereditary brachydactyly with nail dysplasia, but not in Sorsby syndrome. Clin. Genet. 64, 263–265 (2003).
Yang, W., Tan, F. Q., Sun, M., Zeng, X., Liu, J., Liu, G. Y. et al. Identification of a recurrent mutation in the ROR2 gene in a Chinese family with brachydactyly type B. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 21, 61–63 (2004).
Hamamy, H., Saleh, N., Oldridge, M., Al-Hadidy, A. & Ajlouni, K. Brachydactyly type B1: report of a family with de novo ROR2 mutation. Clin. Genet. 70, 538–540 (2006).
Zhao, X., Sun, M., Zhao, J., Leyva, J. A., Zhu, H., Yang, W. et al. Mutations in HOXD13 underlie syndactyly type V and a novel brachydactyly-syndactyly syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 361–371 (2007).
Bosse, K., Betz, R. C., Lee, Y. A., Wienker, T. F., Reis, A., Kleen, H. et al. Localization of a gene for syndactyly type 1 to chromosome 2q34–q36. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67, 492–497 (2000).
Ghadami, M., Majidzadeh-A, K., Haerian, B. S., Damavandi, E., Yamada, K., Pasallar, P. et al. Confirmation of genetic homogeneity of syndactyly type 1 in an Iranian family. Am. J. Med. Genet. 104, 147–151 (2001).
Ben-Shachar, S., Khajavi, M., Withers, M., Shaw, C., van Bokhoven, H., Brunner, H. et al. Dominant versus recessive traits conveyed by allelic mutations—to what extent is nonsense-mediated decay involved? Clin. Genet. 75, 394–400 (2009).
Lehmann, K., Seemann, P., Silan, F, Goecke, T. O., Irgang, S., Kjaer, K. W. et al. A new subtype of brachydactyly type B caused by point mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein antagonist NOGGIN. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 388–396 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the family members for their participation in this study. This work was mainly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30730097 and 30721063) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2005DKA21302) (to XZ). XZ is a Chang Jiang Scholar of Genetic Medicine supported by the Ministry of Education of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/jhg)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, D., Luo, Y., Yang, W. et al. A novel single-base deletion in ROR2 causes atypical brachydactyly type B1 with cutaneous syndactyly in a large Chinese family. J Hum Genet 54, 422–425 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.48
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.48
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel variant in the ROR2 gene underlying brachydactyly type B: a case report
BMC Pediatrics (2022)