Abstract
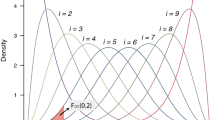
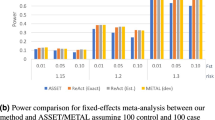
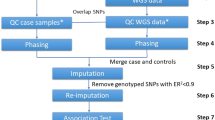
Meta-analysis is a useful tool to increase the statistical power to detect gene–disease associations by combining results from the original and subsequent replication studies. Recently, consortium-based meta-analyses of several genome-wide association (GWA) data sets have discovered new susceptibility genes of common diseases. We reviewed the process and the methods of meta-analysis of genetic association studies. To conduct and report a transparent meta-analysis, the search strategy, the inclusion or exclusion criteria of studies and the statistical procedures should be fully described. Assessing consistency or heterogeneity of the associations across studies is an important aim of meta-analysis. Random effects model (REM) meta-analysis can incorporate between-study heterogeneity. We illustrated properties of test for and measures of between-study heterogeneity and the effect of between-study heterogeneity on conclusions of meta-analyses through simulations. Our simulation shows that the power of REM meta-analysis of GWA data sets (total case–control sample size: 5000–20 000) to detect a small genetic effect (odds ratio (OR)=1.4 under dominant model) decreases as between-study heterogeneity increases and then the mean of OR of the simulated meta-analyses passing the genome-wide significance threshold would be upwardly biased (winner's curse phenomenon). Addressing observed between-study heterogeneity may be challenging but give a new insight into the gene–disease association.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lander, E. S. The new genomics: global views of biology. Science 274, 536–539 (1996).
Risch, N. & Merikangas, K. The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 273, 1516–1517 (1996).
The International HapMap Consortium. The International HapMap Project. Nature 426, 789–796 (2003).
International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 431, 931–945 (2004).
Lander, E. S., Linton, L. M., Birren, B., Nusbaum, C., Zody, M. C., Baldwin, J. et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921 (2001).
Venter, J. C., Adams, M. D., Myers, E. W., Li, P. W., Mural, R. J., Sutton, G. G. et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 291, 1304–1351 (2001).
Manolio, T. A., Brooks, L. D. & Collins, F. S. A HapMap harvest of insights into the genetics of common disease. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 1590–1605 (2008).
Hirschhorn, J. N., Lohmueller, K., Byrne, E. & Hirschhorn, K. A comprehensive review of genetic association studies. Genet. Med. 4, 45–61 (2002).
Lohmueller, K. E., Pearce, C. L., Pike, M., Lander, E. S. & Hirschhorn, J. N. Meta-analysis of genetic association studies supports a contribution of common variants to susceptibility to common disease. Nat. Genet. 33, 177–182 (2003).
Ioannidis, J. P., Ntzani, E. E., Trikalinos, T. A. & Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D. G. Replication validity of genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 29, 306–309 (2001).
Cardon, L. R. & Bell, J. I. Association study designs for complex diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 91–99 (2001).
Freely associating. Nat. Genet. 22, 1–2 (1999).
Colhoun, H. M., McKeigue, P. M. & Davey Smith, G. Problems of reporting genetic associations with complex outcomes. Lancet 361, 865–872 (2003).
Ioannidis, J. P. Non-replication and inconsistency in the genome-wide association setting. Hum. Hered. 64, 203–213 (2007).
Khoury, M. J., Little, J., Gwinn, M. & Ioannidis, J. P. On the synthesis and interpretation of consistent but weak gene–disease associations in the era of genome-wide association studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 36, 439–445 (2007).
NCI-NHGRI Working Group on Replication in Association Studies Chanock, S. J. Manolio, T., Boehnke, M., Boerwinkle, E., Hunter, D. J. et al. Replicating genotype–phenotype associations. Nature 447, 655–660 (2007).
Elbaz, A., Nelson, L. M., Payami, H., Ioannidis, J. P., Fiske, B. K., Annesi, G. et al. Lack of replication of thirteen single-nucleotide polymorphisms implicated in Parkinson's disease: a large-scale international study. Lancet Neurol. 5, 917–923 (2006).
Munafo, M. R. & Flint, J. Meta-analysis of genetic association studies. Trends Genet. 20, 439–444 (2004).
Lau, J., Ioannidis, J. P. & Schmid, C. H. Summing up evidence: one answer is not always enough. Lancet 351, 123–127 (1998).
Ioannidis, J. P., Patsopoulos, N. A. & Evangelou, E. Heterogeneity in meta-analyses of genome-wide association investigations. PLoS ONE 2, e841 (2007).
Sagoo, G. S., Little, J. & Higgins, J. P. Systematic reviews of genetic association studies. Human Genome Epidemiology Network. PLoS Med. 6, e28 (2009).
Egger, M. & Smith, G. D. Bias in location and selection of studies. BMJ 316, 61–66 (1998).
Lin, B. K., Clyne, M., Walsh, M., Gomez, O., Yu, W., Gwinn, M. et al. Tracking the epidemiology of human genes in the literature: the HuGE Published Literature database. Am. J. Epidemiol. 164, 1–4 (2006).
Tang, J. L. Selection bias in meta-analyses of gene–disease associations. PLoS Med. 2, e409 (2005).
Kavvoura, F. K. & Ioannidis, J. P. Methods for meta-analysis in genetic association studies: a review of their potential and pitfalls. Hum. Genet. 123, 1–14 (2008).
Attia, J., Thakkinstian, A. & D'Este, C. Meta-analyses of molecular association studies: methodologic lessons for genetic epidemiology. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 56, 297–303 (2003).
Begg, C. B. & Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50, 1088–1101 (1994).
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315, 629–634 (1997).
Lau, J., Antman, E. M., Jimenez-Silva, J., Kupelnick, B., Mosteller, F. & Chalmers, T. C. Cumulative meta-analysis of therapeutic trials for myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 327, 248–254 (1992).
Ioannidis, J. P., Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D. G. & Lau, J. Recursive cumulative meta-analysis: a diagnostic for the evolution of total randomized evidence from group and individual patient data. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 52, 281–291 (1999).
Ioannidis, J. & Lau, J. Evolution of treatment effects over time: empirical insight from recursive cumulative metaanalyses. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 831–836 (2001).
McCarthy, M. I., Abecasis, G. R., Cardon, L. R., Goldstein, D. B., Little, J., Ioannidis, J. P. et al. Genome-wide association studies for complex traits: consensus, uncertainty and challenges. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 356–369 (2008).
Seminara, D., Khoury, M. J., O'Brien, T. R., Manolio, T., Gwinn, M. L., Little, J. et al. The emergence of networks in human genome epidemiology: challenges and opportunities. Epidemiology 18, 1–8 (2007).
Ioannidis, J. P., Bernstein, J., Boffetta, P., Danesh, J., Dolan, S., Hartge, P. et al. A network of investigator networks in human genome epidemiology. Am. J. Epidemiol. 162, 302–304 (2005).
Zeggini, E. & Ioannidis, J. P. Meta-analysis in genome-wide association studies. Pharmacogenomics 10, 191–201 (2009).
Zeggini, E., Scott, L. J., Saxena, R., Voight, B. F., Marchini, J. L., Hu, T. et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 40, 638–645 (2008).
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14 000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 447, 661–678 (2007).
Evangelou, E., Maraganore, D. M. & Ioannidis, J. P. Meta-analysis in genome-wide association datasets: strategies and application in Parkinson disease. PLoS ONE 2, e196 (2007).
Barrett, J. C., Hansoul, S., Nicolae, D. L., Cho, J. H., Duerr, R. H., Rioux, J. D. et al. Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn's disease. Nat. Genet. 40, 955–962 (2008).
Browning, S. R. Missing data imputation and haplotype phase inference for genome-wide association studies. Hum. Genet. 124, 439–450 (2008).
Hosking, L., Lumsden, S., Lewis, K., Yeo, A., McCarthy, L., Bansal, A. et al. Detection of genotyping errors by Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium testing. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 12, 395–399 (2004).
Cox, D. G. & Kraft, P. Quantification of the power of Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium testing to detect genotyping error. Hum. Hered. 61, 10–14 (2006).
Wittke-Thompson, J. K., Pluzhnikov, A. & Cox, N. J. Rational inferences about departures from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76, 967–986 (2005).
Minelli, C., Thompson, J. R., Abrams, K. R., Thakkinstian, A. & Attia, J. How should we use information about HWE in the meta-analyses of genetic association studies? Int. J. Epidemiol. 37, 136–146 (2008).
Zintzaras, E. & Lau, J. Synthesis of genetic association studies for pertinent gene–disease associations requires appropriate methodological and statistical approaches. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 61, 634–645 (2008).
Thakkinstian, A., McElduff, P., D'Este, C., Duffy, D. & Attia, J. A method for meta-analysis of molecular association studies. Stat. Med. 24, 1291–1306 (2005).
Salanti, G., Sanderson, S. & Higgins, J. P. Obstacles and opportunities in meta-analysis of genetic association studies. Genet. Med. 7, 13–20 (2005).
Lindley, D. Statistical inference concerning Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. Bayesian Stat. 3, 307–326 (1988).
Weir, B. S. in Genetic Data Analysis II: Methods for Discrete Population Genetic Data (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, 1996).
Hernandez, J. L. & Weir, B. S. A disequilibrium coefficient approach to Hardy–Weinberg testing. Biometrics 45, 53–70 (1989).
Minelli, C., Thompson, J. R., Abrams, K. R., Thakkinstian, A. & Attia, J. The choice of a genetic model in the meta-analysis of molecular association studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 34, 1319–1328 (2005).
Mantel, N. & Haenszel, W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 22, 719–748 (1959).
Yusuf, S., Peto, R., Lewis, J., Collins, R. & Sleight, P. Beta blockade during and after myocardial infarction: an overview of the randomized trials. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 27, 335–371 (1985).
Cochran, W. G. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 10, 101–129 (1954).
Hardy, R. J. & Thompson, S. G. Detecting and describing heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 17, 841–856 (1998).
Petitti, D. B. Approaches to heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 20, 3625–3633 (2001).
DerSimonian, R. & Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 7, 177–188 (1986).
Higgins, J. P. & Thompson, S. G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21, 1539–1558 (2002).
Mittlbock, M. & Heinzl, H. A simulation study comparing properties of heterogeneity measures in meta-analyses. Stat. Med. 25, 4321–4333 (2006).
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J. & Altman, D. G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327, 557–560 (2003).
Ioannidis, J. P., Patsopoulos, N. A. & Evangelou, E. Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses. BMJ 335, 914–916 (2007).
Cardon, L. R. & Palmer, L. J. Population stratification and spurious allelic association. Lancet 361, 598–604 (2003).
Wacholder, S., Rothman, N. & Caporaso, N. Population stratification in epidemiologic studies of common genetic variants and cancer: quantification of bias. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 92, 1151–1158 (2000).
Wacholder, S., Rothman, N. & Caporaso, N. Counterpoint: bias from population stratification is not a major threat to the validity of conclusions from epidemiological studies of common polymorphisms and cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 11, 513–520 (2002).
Marchini, J., Cardon, L. R., Phillips, M. S. & Donnelly, P. The effects of human population structure on large genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 36, 512–517 (2004).
Thomas, D. C. & Witte, J. S. Point: population stratification: a problem for case–control studies of candidate-gene associations? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 11, 505–512 (2002).
Ioannidis, J. P., Ntzani, E. E. & Trikalinos, T. A. ‘Racial’ differences in genetic effects for complex diseases. Nat. Genet. 36, 1312–1318 (2004).
Garner, C. Upward bias in odds ratio estimates from genome-wide association studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 31, 288–295 (2007).
Zollner, S. & Pritchard, J. K. Overcoming the winner's curse: estimating penetrance parameters from case–control data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 605–615 (2007).
Ghosh, A., Zou, F. & Wright, F. A. Estimating odds ratios in genome scans: an approximate conditional likelihood approach. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 1064–1074 (2008).
Ioannidis, J. P. Why most discovered true associations are inflated. Epidemiology 19, 640–648 (2008).
Kraft, P. Curses—winner's and otherwise—in genetic epidemiology. Epidemiology 19, 649–651 (2008); discussion 657–658.
Yu, K., Chatterjee, N., Wheeler, W., Li, Q., Wang, S., Rothman, N. et al. Flexible design for following up positive findings. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 540–551 (2007).
Ioannidis, J. P., Thomas, G. & Daly, M. J. Validating, augmenting and refining genome-wide association signals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 318–329 (2009).
Zondervan, K. T. & Cardon, L. R. The complex interplay among factors that influence allelic association. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 89–100 (2004).
Moonesinghe, R., Khoury, M. J., Liu, T. & Ioannidis, J. P. Required sample size and nonreplicability thresholds for heterogeneous genetic associations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 617–622 (2008).
Scott, L. J., Mohlke, K. L., Bonnycastle, L. L., Willer, C. J., Li, Y., Duren, W. L. et al. A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science 316, 1341–1345 (2007).
Hedges, L. V. & Pigott, T. D. The power of statistical tests in meta-analysis. Psychol. Methods 6, 203–217 (2001).
Helgason, A., Palsson, S., Thorleifsson, G., Grant, S. F., Emilsson, V., Gunnarsdottir, S. et al. Refining the impact of TCF7L2 gene variants on type 2 diabetes and adaptive evolution. Nat. Genet. 39, 218–225 (2007).
Garcia-Closas, M., Hall, P., Nevanlinna, H., Pooley, K., Morrison, J., Richesson, D. A. et al. Heterogeneity of breast cancer associations with five susceptibility loci by clinical and pathological characteristics. PLoS Genet. 4, e1000054 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/jhg)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakaoka, H., Inoue, I. Meta-analysis of genetic association studies: methodologies, between-study heterogeneity and winner's curse. J Hum Genet 54, 615–623 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.95
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.95
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Reproducibility of cerebellar involvement as quantified by consensus structural MRI biomarkers in advanced essential tremor
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
“Association of MTHFR and MS/MTR gene polymorphisms with congenital heart defects in North Indian population (Jammu and Kashmir): a case–control study encompassing meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis”
BMC Pediatrics (2022)
-
Risk of type 2 diabetes and KCNJ11 gene polymorphisms: a nested case–control study and meta-analysis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The role of FTO variant rs1421085 in the relationship with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2022)
-
The association between polymorphisms near TMEM18 and the risk of obesity: a meta-analysis
BMC Medical Genomics (2021)