Abstract
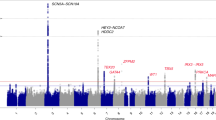
Myocardial infarction (MI) occurs as the result of complex interactions of multiple genetic and environmental factors. By conducting a genome wide association study in a Japanese population using 210 785 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers, we identified a novel susceptible locus for MI on chromosome 5p15.3. An SNP (rs11748327) in this locus showed significant association in several independent cohorts (combined P=5.3 × 10−13, odds ratio=0.80, comparison of allele frequency). Association study using tag SNPs in the same linkage disequilibrium block revealed that two additional SNPs (rs490556 and rs521660) conferred risk of MI. These findings indicate that the SNPs on chromosome 5p15.3 are novel protective genetic factors against MI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Libby, P & Theroux, P Pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. Circulation 111, 3481–3488 (2005).
Haga, H, Yamada, R, Ohnishi, Y, Nakamura, Y & Tanaka, T Gene-based SNP discovery as part of the Japanese Millennium Genome project; identification of 190 562 genetic variations in the human genome. J. Hum. Genet. 47, 605–610 (2002).
Ohnishi, Y, Tanaka, T, Ozaki, K, Yamada, R, Suzuki, H & Nakamura, Y A high-throughput SNP typing system for genome-wide association studies. J. Hum. Genet. 46, 471–477 (2001).
Ozaki, K, Ohnishi, Y, Iida, A, Sekine, A, Yamada, R, Tsunoda, T et al. Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-α gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 32, 650–654 (2002).
Ishii, N, Ozaki, K, Sato, H, Mizuno, H, Saito, S, Takahashi, A et al. Identification of a novel non-coding RNA, MIAT, that confers risk of myocardial infarction. J. Hum. Genet. 51, 1087–1099 (2006).
Ebana, Y, Ozaki, K, Inoue, K, Sato, H, Iida, A, Lwin, H et al. A functional SNP in ITIH3 is associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. J. Hum. Genet. 52, 220–229 (2007).
Ozaki, K, Inoue, K, Sato, H, Iida, A, Ohnishi, Y, Sekine, A et al. Functional variation in LGALS2 confers risk of myocardial infarction and regulates lymphotoxin-a secretion in vitro. Nature 429, 72–75 (2004).
Ozaki, K, Sato, H, Iida, A, Mizuno, H, Nakamura, T, Miyamoto, Y et al. A functional SNP in PSMA6 confers risk of myocardial infarction in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 38, 921–925 (2006).
Ozaki, K, Sato, H, Inoue, K, Tsunoda, T, Sakata, Y, Mizuno, H et al. SNPs in BRAP associated with risk of myocardial infarction in Asian populations. Nat. Genet. 41, 329–333 (2009).
Helgadottir, A, Thorleifsson, G, Manolescu, A, Gretarsdottir, S, Blondal, T, Jonasdottir, A et al. A common variant on chromosome 9p21 affects the risk of myocardial infarction. Science 316, 1491–1493 (2007).
McPherson, R, Pertsemlidis, A, Kavaslar, N, Stewart, A, Roberts, R, Cox, D R et al. A common allele on chromosome 9 associated with coronary heart disease. Science 316, 1488–1491 (2007).
Samani, N J, Erdmann, J, Hall, A S, Hengstenberg, C, Mangino, M, Mayer, B, et al. WTCCC and the Cardiogenics Consortium Genome-wide association analysis of coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 443–453 (2007).
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14 000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 447, 661–678 (2007).
Erdmann, J, Großhennig, A, Braund, P S, König, I R, Hengstenberg, C, Hall, A S, et al. Italian Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Working Group; Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; Cardiogenics Consortium New susceptibility locus for coronary artery disease on chromosome 3q22.3. Nat. Genet. 41, 280–282 (2009).
Gudbjartsson, D F, Bjornsdottir, U S, Halapi, E, Helgadottir, A, Sulem, P, Jonsdottir, G M et al. Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 41, 342–347 (2009).
Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium. Genome-wide association of early-onset myocardial infarction with single nucleotide polymorphisms and copy number variants. Nat. Genet. 41, 334–341 (2009).
Trégouët, D A, König, I R, Erdmann, J, Munteanu, A, Braund, P S, Hall, A S, et al. Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; Cardiogenics Consortium Genome-wide haplotype association study identifies the SLC22A3-LPAL2-LPA gene cluster as a risk locus for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 41, 283–285 (2009).
Unoki, H, Takahashi, A, Kawaguchi, T, Hara, K, Horikoshi, M, Andersen, G et al. SNPs in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations. Nat. Genet. 40, 1098–1102 (2008).
Barrett, J C, Fry, B, Maller, J & Daly, M J Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21, 263–265 (2005).
Tregouet, D A & Garelle, V A new JAVA interface implementation of THESIAS: testing haplotype effects in association studies. Bioinformatics 23, 1038–1039 (2007).
Price, A L, Patterson, N J, Plenge, R M, Weinblatt, M E, Shadick, N A & Reich, D Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 38, 904–909 (2006).
The International HapMap Consortium. A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437, 1299–1320 (2005).
Rinn, J L, Kertesz, M, Wang, J K, Squazzo, S L, Xu, X, Brugmann, S A et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 129, 1311–1323 (2007).
Brennecke, J, Stark, A, Russell, R B & Cohen, S M Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PloS Biol. 3, e85 (2005).
Duan, R, Pak, C & Jin, P Single nucleotide polymorphism associated with mature miR-125a alters the processing of pri-miRNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, 1124 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank Maki Takahashi, Mayumi Yoshii, Saori Kawakami, Rumiko Oishi, Makiko Matsuda, Taeko Nakajima and Michiko Nakamura for their assistance. We also thank all the members of OACIS, the Rotary Club of Osaka-Midosuji District 2660 Rotary International and BioBank Japan for their contribution to the completion of our study. This work was conducted as a part of the BioBank Japan Project that was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Sciences and Technology of the Japanese government. This work was also supported in part by grants from the Takeda science foundation, the Uehara science foundation, the Naito foundation, the Mitsubishi foundation, the Tokyo Biochemical Research foundation and NHRI-Ex96-9607PI (Taiwan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki, A., Ozaki, K., Sato, H. et al. SNPs on chromosome 5p15.3 associated with myocardial infarction in Japanese population. J Hum Genet 56, 47–51 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2010.141
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2010.141
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genome-Wide Linkage Analysis of Large Multiple Multigenerational Families Identifies Novel Genetic Loci for Coronary Artery Disease
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Genetic risk factors for myocardial infarction more clearly manifest for early age of first onset
Molecular Biology Reports (2017)
-
Genome-wide association study identifies a missense variant at APOA5 for coronary artery disease in Multi-Ethnic Cohorts from Southeast Asia
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Molecular genetics of coronary artery disease
Journal of Human Genetics (2016)
-
Experimental Biology for the Identification of Causal Pathways in Atherosclerosis
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy (2016)