Abstract
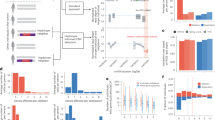
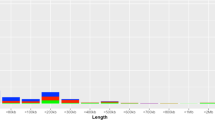
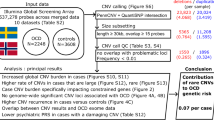
The abundance of copy number variants (CNVs) and regions of homozygosity (ROHs) have been well documented in previous studies. In addition, their roles in complex diseases and traits have since been increasingly appreciated. However, only a limited amount of CNV and ROH data is currently available for the Swedish population. We conducted a population-based study to detect and characterize CNVs and ROHs in 87 randomly selected healthy Swedish individuals using the Affymetrix SNP Array 6.0. More than 600 CNV loci were detected in the population using two different CNV-detection algorithms (PennCNV and Birdsuite). A total of 196 loci were consistently identified by both algorithms, suggesting their reliability. Numerous disease-associated and pharmacogenetics-related genes were found to be overlapping with common CNV loci such as CFHR1/R3, LCE3B/3C, UGT2B17 and GSTT1. Correlation analysis between copy number polymorphisms (CNPs) and genome-wide association studies-identified single-nucleotide polymorphisms also indicates the potential roles of several CNPs as causal variants for diseases and traits such as body mass index, Crohn's disease and multiple sclerosis. In addition, we also identified a total of 14 815 ROHs ⩾500 kb or 2814 ROHs ⩾1M in the Swedish individuals with an average of 170 and 32 regions detected per individual respectively. Approximately 141 Mb or 4.92% of the genome is homozygous in each individual of the Swedish population. This is the first population-based study to investigate the population characteristics of CNVs and ROHs in the Swedish population. This study found many CNV loci that warrant further investigation, and also highlighted the abundance and importance of investigating ROHs for their associations with complex diseases and traits.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
McCarroll, S. A., Kuruvilla, F. G., Korn, J. M., Cawley, S., Nemesh, J., Wysoker, A. et al. Integrated detection and population-genetic analysis of SNPs and copy number variation. Nat. Genet. 40, 1166–1174 (2008).
Conrad, D. F., Pinto, D., Redon, R., Feuk, L., Gokcumen, O., Zhang, Y. et al. Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature 464, 704–712 (2010).
Park, H., Kim, J. I., Ju, Y. S., Gokcumen, O., Mills, R. E., Kim, S. et al. Discovery of common Asian copy number variants using integrated high-resolution array CGH and massively parallel DNA sequencing. Nat. Genet. 42, 400–405 (2010).
Yim, S. H., Kim, T. M., Hu, H. J., Kim, J. H., Kim, B. J., Lee, J. Y. et al. Copy number variations in East-Asian population and their evolutionary and functional implications. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 1001–1008 (2010).
Ku, C. S., Pawitan, Y., Sim, X., Ong, R. T., Seielstad, M., Lee, E. J. et al. Genomic copy number variations in three Southeast Asian populations. Hum. Mutat. 31, 851–857 (2010).
Redon, R., Ishikawa, S., Fitch, K. R., Feuk, L., Perry, G. H., Andrews, T. D. et al. Global variation in copy number in the human genome. Nature 444, 444–454 (2006).
Pinto, D., Marshall, C., Feuk, L. & Scherer, S. W. Copy-number variation in control population cohorts. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, R168–R173 (2007).
Zogopoulos, G., Ha, K. C., Naqib, F., Moore, S., Kim, H., Montpetit, A. et al. Germ-line DNA copy number variation frequencies in a large North American population. Hum. Genet. 122, 345–353 (2007).
de Smith, A. J., Tsalenko, A., Sampas, N., Scheffer, A., Yamada, N. A., Tsang, P. et al. Array CGH analysis of copy number variation identifies 1284 new genes variant in healthy white males: implications for association studies of complex diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, 2783–2794 (2007).
Díaz de Ståhl, T., Sandgren, J., Piotrowski, A., Nord, H., Andersson, R., Menzel, U. et al. Profiling of copy number variations (CNVs) in healthy individuals from three ethnic groups using a human genome 32 K BAC-clone-based array. Hum. Mutat. 29, 398–408 (2008).
Estivill, X. & Armengol, L. Copy number variants and common disorders: filling the gaps and exploring complexity in genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 3, 1787–1799 (2007).
Gibson, J., Morton, N. E. & Collins, A. Extended tracts of homozygosity in outbred human populations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 789–795 (2006).
Li, L. H., Ho, S. F., Chen, C. H., Wei, C. Y., Wong, W. C., Li, L. Y. et al. Long contiguous stretches of homozygosity in the human genome. Hum. Mutat. 27, 1115–1121 (2006).
McQuillan, R., Leutenegger, A. L., Abdel-Rahman, R., Abdel-Rahman, R., Franklin, C. S., Pericic, M. et al. Runs of homozygosity in European populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 83, 359–372 (2008).
Nothnagel, M., Lu, T. T., Kayser, M. & Krawczak, M. Genomic and geographic distribution of SNP-defined runs of homozygosity in Europeans. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 2927–2935 (2010).
Lencz, T., Lambert, C., DeRosse, P., Burdick, K. E., Morgan, T. V., Kane, J. M. et al. Runs of homozygosity reveal highly penetrant recessive loci in schizophrenia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 19942–19947 (2007).
Nalls, M. A., Guerreiro, R. J., Simon-Sanchez, J., Bras, J. T., Traynor, B. J., Gibbs, J. R. et al. Extended tracts of homozygosity identify novel candidate genes associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurogenetics 10, 183–190 (2009).
Yang, T. L., Guo, Y., Zhang, L. S., Tian, Q., Yan, H., Papasian, C. J. et al. Runs of homozygosity identify a recessive locus 12q21.31 for human adult height. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 3777–3782 (2010).
O’Dushlaine, C. T., Morris, D., Moskvina, V., Kirov, G., Consortium, I. S., Gill, M. et al. Population structure and genome-wide patterns of variation in Ireland and Britain. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18, 1248–1254 (2010).
International HapMap 3 Consortium. Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature 467, 52–58 (2010).
Wang, K., Li, M., Hadley, D., Liu, R., Glessner, J., Grant, S. F. et al. PennCNV: an integrated hidden Markov model designed for high-resolution copy number variation detection in whole-genome SNP genotyping data. Genome Res. 17, 1665–1674 (2007).
Korn, J. M., Kuruvilla, F. G., McCarroll, S. A., Wysoker, A., Nemesh, J., Cawley, S. et al. Integrated genotype calling and association analysis of SNPs, common copy number polymorphisms and rare CNVs. Nat. Genet. 40, 1253–1260 (2008).
Mei, T. S., Salim, A., Calza, S., Seng, K. C., Seng, C. K. & Pawitan, Y. Identification of recurrent regions of copy-number variants across multiple individuals. BMC Bioinformatics 11, 147 (2010).
Iafrate, A. J., Feuk, L., Rivera, M. N., Listewnik, M. L., Donahoe, P. K., Qi, Y. et al. Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 36, 949–951 (2004).
Aqeilan, R. I., Kuroki, T., Pekarsky, Y., Albagha, O., Trapasso, F., Baffa, Re et al. Loss of WWOX expression in gastric carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 3053–3058 (2004).
Kuroki, T., Yendamuri, S., Trapasso, F., Matsuyama, A., Aqeilan, R. I., Alder, H. et al. The tumor suppressor gene WWOX at FRA16D is involved in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 2459–2465 (2004).
Prickett, T. D., Agrawal, N. S., Wei, X., Yates, K. E., Lin, J. C., Wunderlich, J. R. et al. Analysis of the tyrosine kinome in melanoma reveals recurrent mutations in ERBB4. Nat. Genet. 41, 1127–1132 (2009).
Ferreira, M. A., O’Donovan, M. C., Meng, Y. A., Jones, I. R., Ruderfer, D. M., Jones, L. et al. Collaborative genome-wide association analysis supports a role for ANK3 and CACNA1C in bipolar disorder. Nat. Genet. 40, 1056–1058 (2008).
Ouahchi, K., Lindeman, N. & Lee, C. Copy number variants and pharmacogenomics. Pharmacogenomics 7, 25–29 (2006).
Fanciulli, M., Norsworthy, P. J., Petretto, E., Dong, R., Harper, L., Kamesh, L. et al. FCGR3B copy number variation is associated with susceptibility to systemic, but not organ-specific, autoimmunity. Nat. Genet. 39, 721–723 (2007).
Miki, D., Kubo, M., Takahashi, A., Yoon, K. A., Kim, J., Lee, G. K. et al. Variation in TP63 is associated with lung adenocarcinoma susceptibility in Japanese and Korean populations. Nat. Genet. 42, 893–896 (2010).
Spencer, K. L., Hauser, M. A., Olson, L. M., Schmidt, S., Scott, W. K., Gallins, P. et al. Deletion of CFHR3 and CFHR1 genes in age-related macular degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 17, 971–977 (2008).
Karypidis, A. H., Olsson, M., Andersson, S. O., Rane, A. & Ekström, L. Deletion polymorphism of the UGT2B17 gene is associated with increased risk for prostate cancer and correlated to gene expression in the prostate. Pharmacogenomics J. 8, 147–151 (2008).
McCarroll, S. A., Bradner, J. E., Turpeinen, H., Volin, L., Martin, P. J., Chilewski, S. D. et al. Donor-recipient mismatch for common gene deletion polymorphisms in graft-versus-host disease. Nat. Genet. 41, 1341–1344 (2009).
Docampo, E., Rabionet, R., Riveira-Muñoz, E., Escaramís, G., Julià, A., Marsal, S. et al. Deletion of the late cornified envelope genes, LCE3C and LCE3B, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 1246–1251 (2010).
de Cid, R., Riveira-Munoz, E., Zeeuwen, P. L., Robarge, J., Liao, W., Dannhauser, E. N. et al. Deletion of the late cornified envelope LCE3B and LCE3C genes as a susceptibility factor for psoriasis. Nat. Genet. 41, 211–215 (2009).
Wang, J., Wang, W., Li, R., Li, Y., Tian, G., Goodman, L. et al. The diploid genome sequence of an Asian individual. Nature 456, 60–65 (2008).
Wheeler, D. A., Srinivasan, M., Egholm, M., Shen, Y., Chen, L., McGuire, A. et al. The complete genome of an individual by massively parallel DNA sequencing. Nature 452, 872–876 (2008).
Korbel, J. O., Urban, A. E., Affourtit, J. P., Godwin, B., Grubert, F., Simons, J. F. et al. Paired-end mapping reveals extensive structural variation in the human genome. Science 318, 420–426 (2007).
Willer, C. J., Speliotes, E. K., Loos, R. J., Li, S., Lindgren, C. M., Heid, I. M. et al. Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation. Nat. Genet. 41, 25–34 (2009).
McCarroll, S. A., Huett, A., Kuballa, P., Chilewski, S. D., Landry, A., Goyette, P. et al. Deletion polymorphism upstream of IRGM associated with altered IRGM expression and Crohn's disease. Nat. Genet. 40, 1107–1112 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, the Life Science Institute and the Office of Deputy President (Research and Technology), National University of Singapore. We also acknowledge the support of the Genome Institute of Singapore, and Agency for Science, Technology and Research, Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teo, SM., Ku, CS., Naidoo, N. et al. A population-based study of copy number variants and regions of homozygosity in healthy Swedish individuals. J Hum Genet 56, 524–533 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.52
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.52
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A map of copy number variations in the Tunisian population: a valuable tool for medical genomics in North Africa
npj Genomic Medicine (2021)
-
Weighted likelihood inference of genomic autozygosity patterns in dense genotype data
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
An association-adjusted consensus deleterious scheme to classify homozygous Mis-sense mutations for personal genome interpretation
BioData Mining (2013)
-
The genome-wide landscape of copy number variations in the MUSGEN study provides evidence for a founder effect in the isolated Finnish population
European Journal of Human Genetics (2013)