Abstract
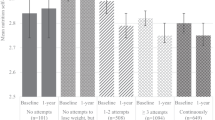
Common variants of fat mass and obesity-associated gene (FTO, fat mass- and obesity-associated gene) have been shown to be associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes in population of European and non-European ethnicity. However, studies in Indian population have provided inconsistent results. Here, we examined association of eight FTO variants (rs1421085, rs8050136, rs9939609, rs9930506, rs1861867, rs9926180, rs2540769 and rs708277) with obesity and type 2 diabetes in 5364 North Indians (2474 type 2 diabetes patients and 2890 non-diabetic controls) in two stages. None of the variants including previously reported intron 1 variants (rs1421085, rs8050136, rs9939609 and rs9930506) showed body mass index (BMI)-dependent/independent association with type 2 diabetes. However, rs1421085, rs8050136 and rs9939609 were associated with obesity status and measures of obesity (BMI, waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio) in stage 2 and combined study population. Meta-analysis of the two study population results also revealed that rs1421085, rs8050136 and rs9939609 were significantly associated with BMI both under the random- and fixed-effect models (P (random/fixed)=0.02/0.0001, 0.004/0.0006 and 0.01/0.01, respectively). In conclusion, common variants of FTO were associated with obesity, but not with type 2 diabetes in North Indian population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Wild, S., Roglic, G., Green, A., Sicree, R. & King, H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabet. Care 27, 1047–1053 (2004).
Misra, A. & Khurana, L. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in developing countries. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, S9–S30 (2008).
Frayling, T. M., Timpson, N. J., Weedon, M. N., Zeggini, E., Freathy, R. M., Lindgren, C. M. et al. A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science 316, 889–894 (2007).
Scott, L. J., Mohlke, K. L., Bonnycastle, L. L., Willer, C. J., Li, Y., Duren, W. L. et al. Genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science 316, 1341–1345 (2007).
Loos, R. J. & Bouchard, C. FTO: the first gene contributing to common forms of human obesity. Obes. Rev. 9, 246–250 (2008).
Scuteri, A., Sanna, S., Chen, W. M., Uda, M., Albai, G., Strait, J. et al. Genome-wide association scan shows genetic variants in the FTO gene are associated with obesity-related traits. PLoS Genet. 3, e115 (2007).
Legry, V., Cottel, D., Ferrières, J., Arveiler, D., Andrieux, N., Bingham, A. et al. Effect of an FTO polymorphism on fat mass, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the French MONICA Study. Metabolism 58, 971–975 (2009).
Adeyemo, A., Chen, G., Zhou, J., Shriner, D., Doumatey, A., Huang, H. et al. FTO genetic variation and association with obesity in West Africans and African Americans. Diabetes 59, 1549–1554 (2010).
Tönjes, A., Zeggini, E., Kovacs, P., Böttcher, Y., Schleinitz, D., Dietrich, K. et al. Association of FTO variants with BMI and fat mass in the self-contained population of Sorbs in Germany. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18, 104–110 (2010).
Zhang, G., Karns, R., Narancic, N. S., Sun, G., Cheng, H., Missoni, S. et al. Common SNPs in FTO gene are associated with obesity related anthropometric traits in an island population from the eastern Adriatic coast of Croatia. PLoS One 28, e10375 (2010).
Hotta, K., Nakata, Y., Matsuo, T., Kamohara, S., Kotani, K., Komatsu, R. et al. Variations in the FTO gene are associated with severe obesity in the Japanese. J. Hum. Genet. 53, 546–553 (2008).
Horikoshi, M., Hara, K., Ito, C., Shojima, N., Nagai, R., Ueki, K. et al. Variations in the HHEX gene are associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetologia 50, 2461–2466 (2007).
Omori, S., Tanaka, Y., Takahashi, A., Hirose, H., Kashiwagi, A., Kaku, K. et al. Association of CDKAL1, IGF2BP2, CDKN2A/B, HHEX, SLC30A8, and KCNJ11 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. Diabetes 57, 791–795 (2008).
Chang, Y. C., Liu, P. H., Lee, W. J., Chang, T. J., Jiang, Y. D., Li, H. Y. et al. Common variation in the fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene confers risk of obesity and modulates BMI in the Chinese population. Diabetes 57, 2245–2252 (2008).
Li, H., Wu, Y., Loos, R. J., Hu, F. B., Liu, Y., Wang, J. et al. Variants in the fat mass- and obesity-associated (FTO) gene are not associated with obesity in a Chinese Han population. Diabetes 57, 264–268 (2008).
Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Song, Y., Zhou, D., Zhang, D., Zhao, T. et al. Meta-analysis added power to identify variants in FTO associated with type 2 diabetes and obesity in the Asian population. Obesity 18, 1619–1624 (2010).
Yajnik, C. S., Janipalli, C. S., Bhaskar, S., Kulkarni, S. R., Freathy, R. M., Prakash, S. et al. FTO gene variants are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes in South Asian Indians. Diabetologia 52, 247–252 (2009).
Sanghera, D. K., Ortega, L., Han, S., Singh, J., Ralhan, S. K., Wander, G. S. et al. Impact of nine common type 2 diabetes risk polymorphisms in Asian Indian Sikhs: PPARG2 (Pro12Ala), IGF2BP2, TCF7L2 and FTO variants confer a significant risk. BMC Med. Genet. 9, 59 (2008).
Ramya, K., Radha, V., Ghosh, S., Majumder, P. P. & Mohan, V. Genetic variations in the FTO gene are associated with type 2 diabetes and obesity in south Indians (CURES-79). Diabetes Technol. Ther. 13, 33–42 (2011).
Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 26, S5–S20 (2003).
Tabassum, R., Chavali, S., Dwivedi, O. P., Tandon, N. & Bharadwaj, D. Genetic variants of FOXA2: risk of type 2 diabetes and effect on metabolic traits in North Indians. J. Hum. Genet. 53, 957–965 (2008).
Mahajan, A., Tabassum, R., Chavali, S., Dwivedi, O. P., Bharadwaj, M., Tandon, N. et al. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels and type 2 diabetes in urban North Indians. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 2123–2127 (2009).
Matthews, R. D., Hosker, J. P., Rudenski, A. S., Naylor, B. A., Treacher, D. F. & Turner, R. C. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28, 412–419 (1985).
Mahajan, A., Tabassum, R., Chavali, S., Dwivedi, O. P., Chauhan, G., Tandon, N. et al. Obesity-dependent association of TNF-LTA locus with type 2 diabetes in North Indians. J. Mol. Med. 88, 515–522 (2010).
Purcell, S., Neale, B., Todd-Brown, K., Thomas, L., Ferreira, M. A., Bender, D. et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 559–575 (2007).
Barrett, J. C., Fry, B., Maller, J. & Daly, M. J. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21, 263–265 (2005).
WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 363, 157–163 (2004).
Misra, A., Wasir, J. S. & Pandey, R. M. An evaluation of candidate definitions of the metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians. Diabet. Care 28, 398–403 (2005).
Willett, W. C., Dietz, W. H. & Colditz, G. A. Guidelines for healthy weight. N. Engl. J. Med. 341, 427–434 (1999).
Chauhan, G., Spurgeon, C. J., Tabassum, R., Bhaskar, S., Kulkarni, S. R., Mahajan, A. et al. Impact of common variants of PPARG, KCNJ11, TCF7L2, SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKN2A, IGF2BP2 and CDKAL1 on the risk of type 2 diabetes in 5164 Indians. Diabetes 59, 2068–2074 (2010).
Misra, A. & Khurana, L. Obesity-related non-communicable diseases: South Asians vs White Caucasians. Int. J. Obes. 35, 167–187 (2011).
Sonestedt, E., Roos, C., Gullberg, B., Ericson, U., Wirfält, E. & Orho-Melander, M. Fat and carbohydrate intake modify the association between genetic variation in the FTO genotype and obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 90, 1418–1425 (2009).
Vimaleswaran, K. S., Li, S., Zhao, J. H., Luan, J., Bingham, S. A., Khaw, K. T. et al. Physical activity attenuates the body mass index–increasing influence of genetic variation in the FTO gene. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 90, 425–428 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants who volunteered for the study. We also thank Mr AK Sharma for his help in sample collection. This study was supported by ‘Diabetes mellitus-New drug discovery R&D, molecular mechanisms and genetic and epidemiological factors’ (NWP0032-11) funded by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India. We thank Dr Mitali Mukerji (IGIB) and Dr Anurag Agrawal (IGIB) for critical evaluation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chauhan, G., Tabassum, R., Mahajan, A. et al. Common variants of FTO and the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes in Indians. J Hum Genet 56, 720–726 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.87
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.87
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dietary approach to stop hypertension and healthy eating index 2015, modify the association between FTO polymorphisms and obesity phenotypes
BMC Research Notes (2023)
-
Position statement on nutrition therapy for overweight and obesity: nutrition department of the Brazilian association for the study of obesity and metabolic syndrome (ABESO—2022)
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2023)
-
The genetic susceptibility profile of type 2 diabetes and reflection of its possible role related to reproductive dysfunctions in the southern Indian population of Hyderabad
BMC Medical Genomics (2021)
-
The influence of polymorphisms of fat mass and obesity (FTO, rs9939609) and vitamin D receptor (VDR, BsmI, TaqI, ApaI, FokI) genes on weight loss by diet and exercise interventions in non-diabetic overweight/obese Asian Indians in North India
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2020)
-
Assessment of the FTO gene polymorphisms (rs1421085, rs17817449 and rs9939609) in exercise-trained men and women: the effects of a 4-week hypocaloric diet
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition (2019)