Abstract
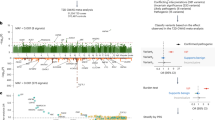
Recent genome-wide association studies have identified several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on chromosome 6p21.1 and 6p22.3 as type 2 diabetes (T2D) susceptibility loci in the European and Japanese populations. However, these SNPs have not been well evaluated in Chinese population. Here, we performed a case–control study with 2925 T2D cases and 3281 controls in a Chinese population. We used TaqMan OpenArray and Sequenom MassARRAY to genotype the four SNPs (rs4712523, rs7756992, rs4712524 and rs6931514) in CDKAL1 (cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1-like 1) at 6p22.3 and one SNP (rs9472138) near vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) at 6p21.1. All the five SNPs were significantly associated with T2D risk with overall effects (odds ratio, OR) from 1.19 to 1.29 in the additive genetic model (rs6931514: OR=1.29, 95% confidence intervals (95% CI)=1.19–1.39, P=5.6 × 10−10; rs7756992: OR=1.23, 95% CI=1.15–1.32, P=1.2 × 10−8; rs4712523: OR=1.25, 95% CI=1.15–1.35, P=3.8 × 10−8; rs4712524: OR=1.24, 95% CI=1.15–1.35, P=6.8 × 10−8; rs9472138: OR=1.19, 95% CI=1.05–1.34, P=006). Conditional analysis identified two independent signals (rs6931514 at 6p22.3 and rs9472138 at 6p21.1) that were significantly associated with T2D. Compared with the wild homozygote of rs6931514 and rs9472138, subjects with variant alleles of the two SNPs had increased risk for T2D susceptibility in a dose-response manner (Ptrend=7.4 × 10−12). Our findings indicated that genetic variants of CDKAL1 and VEGFA on chromosome 6 may contribute to T2D risk in Chinese population, especially for rs9472138 at 6p21.1 identified for the first time to significantly increase the T2D risk in Chinese individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Narayan, K. M., Boyle, J. P., Geiss, L. S., Saaddine, J. B. & Thompson, T. J. Impact of recent increase in incidence on future diabetes burden: US, 2005-2050. Diabetes Care 29, 2114–2116 (2006).
Chan, J. C., Malik, V., Jia, W., Kadowaki, T., Yajnik, C. S., Yoon, K. H. et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 301, 2129–2140 (2009).
Yang, W., Lu, J., Weng, J., Jia, W., Ji, L., Xiao, J. et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 362, 1090–1101 (2010).
Stumvoll, M., Goldstein, B. J. & van Haeften, T. W. Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 365, 1333–1346 (2005).
Moore, A. F. & Florez, J. C. Genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes and implications for antidiabetic therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 59, 95–111 (2008).
Imamura, M. & Maeda, S. Genetics of type 2 diabetes: the GWAS era and future perspectives [Review]. Endocr. J. 58, 723–739 (2011).
Zeggini, E., Weedon, M. N., Lindgren, C. M., Frayling, T. M., Elliott, K. S., Lango, H. et al. Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 316, 1336–1341 (2007).
Steinthorsdottir, V., Thorleifsson, G., Reynisdottir, I., Benediktsson, R., Jonsdottir, T., Walters, G. B. et al. A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 39, 770–775 (2007).
Scott, L. J., Mohlke, K. L., Bonnycastle, L. L., Willer, C. J., Li, Y., Duren, W. L. et al. A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science 316, 1341–1345 (2007).
Consortium T.W.T.C.C. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447, 661–678 (2007).
Zeggini, E., Scott, L. J., Saxena, R., Voight, B. F., Marchini, J. L., Hu, T. et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 40, 638–645 (2008).
Unoki, H., Takahashi, A., Kawaguchi, T., Hara, K., Horikoshi, M., Andersen, G. et al. SNPs in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations. Nat. Genet. 40, 1098–1102 (2008).
Takeuchi, F., Serizawa, M., Yamamoto, K., Fujisawa, T., Nakashima, E., Ohnaka, K. et al. Confirmation of multiple risk loci and genetic impacts by a genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 58, 1690–1699 (2009).
Voight, B. F., Scott, L. J., Steinthorsdottir, V., Morris, A. P., Dina, C., Welch, R. P. et al. Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat. Genet. 42, 579–589 (2010).
Ching, Y. P., Pang, A. S., Lam, W. H., Qi, R. Z. & Wang, J. H. Identification of a neuronal Cdk5 activator-binding protein as Cdk5 inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 15237–15240 (2002).
Wei, F. Y., Nagashima, K., Ohshima, T., Saheki, Y., Lu, Y. F., Matsushita, M. et al. Cdk5-dependent regulation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Nat. Med. 11, 1104–1108 (2005).
Olsson, A. K., Dimberg, A., Kreuger, J. & Claesson-Welsh, L. VEGF receptor signalling- in control of vascular function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 359–371 (2006).
Takahashi, H. & Shibuya, M. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor system and its role under physiological and pathological conditions. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 109, 227–241 (2005).
Ng, M. C., Park, K. S., Oh, B., Tam, C. H., Cho, Y. M., Shin, H. D. et al. Implication of genetic variants near TCF7L2, SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, IGF2BP2, and FTO in type 2 diabetes and obesity in 6,719 Asians. Diabetes 57, 2226–2233 (2008).
Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Song, Y., Zhou, D., Zhang, D., Zhao, T. et al. Meta-analysis added power to identify variants in FTO associated with type 2 diabetes and obesity in the Asian population. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18, 1619–1624 (2010).
Liu, C., Ma, X., Ma, Y. T., Liu, F., Yang, Y. N., Huang, D. et al. Prevalence on overweight and obesity in Han, Uygur and Hazakh in adults from Xinjiang. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 31, 1139–1143 (2010).
Hu, Z., Wu, C., Shi, Y., Guo, H., Zhao, X., Yin, Z. et al. A genome-wide association study identifies two new lung cancer susceptibility loci at 13q12.12 and 22q12.2 in Han Chinese. Nat. Genet. 43, 792–796 (2011).
Hu, C., Zhang, R., Wang, C., Wang, J., Ma, X., Lu, J. et al. PPARG, KCNJ11, CDKAL1, CDKN2A-CDKN2B, IDE-KIF11-HHEX, IGF2BP2 and SLC30A8 are associated with type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. PLoS. One. 4, e7643 (2009).
Wu, Y., Li, H., Loos, R. J., Yu, Z., Ye, X., Chen, L. et al. Common variants in CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, IGF2BP2, SLC30A8, and HHEX/IDE genes are associated with type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in a Chinese Han population. Diabetes 57, 2834–2842 (2008).
Liu, Y., Yu, L., Zhang, D., Chen, Z., Zhou, D. Z., Zhao, T. et al. Positive association between variations in CDKAL1 and type 2 diabetes in Han Chinese individuals. Diabetologia 51, 2134–2137 (2008).
Lin, Y., Li, P., Cai, L., Zhang, B., Tang, X., Zhang, X. et al. Association study of genetic variants in eight genes/loci with type 2 diabetes in a Han Chinese population. BMC Med. Genet. 11, 97 (2010).
Wen, J., Ronn, T., Olsson, A., Yang, Z., Lu, B., Du, Y. et al. Investigation of type 2 diabetes risk alleles support CDKN2A/B, CDKAL1, and TCF7L2 as susceptibility genes in a Han Chinese cohort. PLoS. One. 5, e9153 (2010).
Han, X., Luo, Y., Ren, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, F., Sun, X. et al. Implication of genetic variants near SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, IGF2BP2, FTO, TCF2, KCNQ1, and WFS1 in type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. BMC Med. Genet. 11, 81 (2010).
Ubeda, M., Rukstalis, J. M. & Habener, J. F. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity protects pancreatic beta cells from glucotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 28858–28864 (2006).
Wei, F. Y., Suzuki, T., Watanabe, S., Kimura, S., Kaitsuka, T., Fujimura, A. et al. Deficit of tRNA(Lys) modification by Cdkal1 causes the development of type 2 diabetes in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 121, 3598–3608 (2011).
Wei, F. Y. & Tomizawa, K. Functional loss of Cdkal1, a novel tRNA modification enzyme, causes the development of type 2 diabetes [Review]. Endocr. J. 58, 819–825 (2011).
Staiger, H., Machicao, F., Kantartzis, K., Schafer, S. A., Kirchhoff, K., Guthoff, M. et al. Novel meta-analysis-derived type 2 diabetes risk loci do not determine prediabetic phenotypes. PLoS. One. 3, e3019 (2008).
Sharma, N. K., Langberg, K. A., Mondal, A. K., Elbein, S. C. & Das, S. K. Type 2 diabetes (T2D) associated polymorphisms regulate expression of adjacent transcripts in transformed lymphocytes, adipose, and muscle from Caucasian and African-American subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, E394–403 (2011).
Langberg, K. A., Ma, L., Sharma, N. K., Hanis, C. L., Elbein, S. C., Hasstedt, S. J. et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in JAZF1 and BCL11A gene are nominally associated with type 2 diabetes in African-American families from the GENNID study. J. Hum. Genet. 57, 57–61 (2011).
Omori, S., Tanaka, Y., Horikoshi, M., Takahashi, A., Hara, K., Hirose, H. et al. Replication study for the association of new meta-analysis-derived risk loci with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in 6,244 Japanese individuals. Diabetologia 52, 1554–1560 (2009).
Cho, Y. S., Chen, C. H., Hu, C., Long, J., Hee Ong, R. T., Sim, X. et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies eight new loci for type 2 diabetes in east Asians. Nat. Genet. 44, 67–72 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation Grant 81072379, Ministry of Health Research Program Grant WKJ2010-2-032, Wuxi Science & Technology Research Program Grant CSE01016 and the Priority Academic Program for the Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Public Health and Preventive Medicine).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, F., Qian, Y., Li, H. et al. Genetic variants on chromosome 6p21.1 and 6p22.3 are associated with type 2 diabetes risk: a case–control study in Han Chinese. J Hum Genet 57, 320–325 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.25
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.25
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic variant in fat mass and obesity-associated gene associated with type 2 diabetes risk in Han Chinese
BMC Genetics (2013)
-
The sodium channel gene family is specifically expressed in hen uterus and associated with eggshell quality traits
BMC Genetics (2013)
-
CDKAL1 gene rs7756992 A/G polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of 62,567 subjects
Scientific Reports (2013)