Abstract
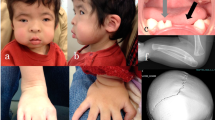
Oculofaciocardiodental syndrome (OFCD) is an X-linked dominant disorder associated with male lethality, presenting with congenital cataract, dysmorphic face, dental abnormalities and septal heart defects. Mutations in BCOR (encoding BCL-6-interacting corepressor) cause OFCD. Here, we report on a Korean family with common features of OFCD including bilateral 2nd–3rd toe syndactyly and septal heart defects in three affected females (mother and two daughters). Through the mutation screening and copy number analysis using genomic microarray, we identified a novel heterozygous mutation, c.888delG, in the BCOR gene and two interstitial microduplications at Xp22.2–22.13 and Xp21.3 in all the three affected females. The BCOR mutation may lead to a premature stop codon (p.N297IfsX80). The duplication at Xp22.2–22.13 involved the NHS gene causative for Nance–Horan syndrome, which is an X-linked disorder showing similar clinical features with OFCD in affected males, and in carrier females with milder presentation. Considering the presence of bilateral 2nd–3rd toe syndactyly and septal heart defects, which is unique to OFCD, the mutation in BCOR is likely to be the major determinant for the phenotypes in this family.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Wilkie, A. O., Taylor, D., Scambler, P. J. & Baraitser, M. Congenital cataract, microphthalmia and septal heart defect in two generations: a new syndrome? Clin. Dysmorphol. 2, 114–119 (1993).
Aalfs, C. M., Oosterwijk, J. C., van Schooneveld, M. J., Begeman, C. J., Wabeke, K. B. & Hennekam, R. C. Cataracts, radiculomegaly, septal heart defects and hearing loss in two unrelated adult females with normal intelligence and similar facial appearance: confirmation of a syndrome? Clin. Dysmorphol. 5, 93–103 (1996).
Ng, D., Thakker, N., Corcoran, C. M., Donnai, D., Perveen, R., Schneider, A. et al. Oculofaciocardiodental and Lenz microphthalmia syndromes result from distinct classes of mutations in BCOR. Nat. Genet. 36, 411–416 (2004).
Huynh, K. D., Fischle, W., Verdin, E. & Bardwell, V. J. BCoR, a novel corepressor involved in BCL-6 repression. Genes Dev. 14, 1810–1823 (2000).
Wamstad, J. A. & Bardwell, V. J. Characterization of Bcor expression in mouse development. Gene Expr. Patterns 7, 550–557 (2007).
Hilton, E., Johnston, J., Whalen, S., Okamoto, N., Hatsukawa, Y., Nishio, J. et al. BCOR analysis in patients with OFCD and Lenz microphthalmia syndromes, mental retardation with ocular anomalies, and cardiac laterality defects. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 17, 1325–1335 (2009).
Nance, W. E., Warburg, M., Bixler, D. & Helveston, E. M. Congenital X-linked cataract, dental anomalies and brachymetacarpalia. Birth Defects Orig. Artic. Ser. 10, 285–291 (1974).
Coccia, M., Brooks, S. P., Webb, T. R., Christodoulou, K., Wozniak, I. O., Murday, V. et al. X-linked cataract and Nance-Horan syndrome are allelic disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 2643–2655 (2009).
Lewis, R. A., Nussbaum, R. L. & Stambolian, D. Mapping X-linked ophthalmic diseases. IV. Provisional assignment of the locus for X-linked congenital cataracts and microcornea (the Nance-Horan syndrome) to Xp22.2-p22.3. Ophthalmology. 97, 110–120; discussion 120–111 (1990).
Stambolian, D., Lewis, R. A., Buetow, K., Bond, A. & Nussbaum, R. Nance-Horan syndrome: localization within the region Xp21.1-Xp22.3 by linkage analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 47, 13–19 (1990).
Burdon, K. P., McKay, J. D., Sale, M. M., Russell-Eggitt, I. M., Mackey, D. A., Wirth, M. G. et al. Mutations in a novel gene, NHS, cause the pleiotropic effects of Nance-Horan syndrome, including severe congenital cataract, dental anomalies, and mental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 1120–1130 (2003).
Miyamoto, T., Yu, Y. S., Sato, H., Hayashi, H., Sakugawa, N., Ishikawa, M. et al. Mutational analysis of the human MBX gene in four Korean families demonstrating microphthalmia with congenital cataract. Turk J. Pediatr. 49, 334–336 (2007).
Allen, R. C., Zoghbi, H. Y., Moseley, A. B., Rosenblatt, H. M. & Belmont, J. W. Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 51, 1229–1239 (1992).
Carrel, L. & Willard, H. F. An assay for X inactivation based on differential methylation at the fragile X locus, FMR1. Am. J. Med. Genet. 64, 27–30 (1996).
Nishimura-Tadaki, A., Wada, T., Bano, G., Gough, K., Warner, J., Kosho, T. et al. Breakpoint determination of X; autosome balanced translocations in four patients with premature ovarian failure. J. Hum. Genet. 56, 156–160 (2011).
Kubota, T., Nonoyama, S., Tonoki, H., Masuno, M., Imaizumi, K., Kojima, M. et al. A new assay for the analysis of X-chromosome inactivation based on methylation-specific PCR. Hum. Genet. 104, 49–55 (1999).
Amos-Landgraf, J. M., Cottle, A., Plenge, R. M., Friez, M., Schwartz, C. E., Longshore, J. et al. X chromosome-inactivation patterns of 1,005 phenotypically unaffected females. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 79, 493–499 (2006).
Srinivasan, R. S., de Erkenez, A. C. & Hemenway, C. S. The mixed lineage leukemia fusion partner AF9 binds specific isoforms of the BCL-6 corepressor. Oncogene 22, 3395–3406 (2003).
Gearhart, M. D., Corcoran, C. M., Wamstad, J. A. & Bardwell, V. J. Polycomb group and SCF ubiquitin ligases are found in a novel BCOR complex that is recruited to BCL6 targets. Mol. Cell Biol. 26, 6880–6889 (2006).
Ghetu, A. F., Corcoran, C. M., Cerchietti, L., Bardwell, V. J., Melnick, A. & Prive, G. G. Structure of a BCOR corepressor peptide in complex with the BCL6 BTB domain dimer. Mol. Cell. 29, 384–391 (2008).
Ye, B. H., Cattoretti, G., Shen, Q., Zhang, J., Hawe, N., de Waard, R. et al. The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2-type inflammation. Nat. Genet. 16, 161–170 (1997).
Dent, A. L., Shaffer, A. L., Yu, X., Allman, D. & Staudt, L. M. Control of inflammation, cytokine expression, and germinal center formation by BCL-6. Science 276, 589–592 (1997).
Honda, S., Hayashi, S., Imoto, I., Toyama, J., Okazawa, H., Nakagawa, E. et al. Copy-number variations on the X chromosome in Japanese patients with mental retardation detected by array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 55, 590–599 (2010).
Carrie, A., Jun, L., Bienvenu, T., Vinet, M. C., McDonell, N., Couvert, P. et al. A new member of the IL-1 receptor family highly expressed in hippocampus and involved in X-linked mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 23, 25–31 (1999).
Nawara, M., Klapecki, J., Borg, K., Jurek, M., Moreno, S., Tryfon, J. et al. Novel mutation of IL1RAPL1 gene in a nonspecific X-linked mental retardation (MRX) family. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 146A, 3167–3172 (2008).
Hedera, P. & Gorski, J. L. Oculo-facio-cardio-dental syndrome: skewed X chromosome inactivation in mother and daughter suggest X-linked dominant Inheritance. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 123A, 261–266 (2003).
Bartnik, M., Derwinska, K., Gos, M., Obersztyn, E., Kolodziejska, K. E., Erez, A. et al. Early-onset seizures due to mosaic exonic deletions of CDKL5 in a male and two females. Genet. Med. 13, 447–452 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We thank the family members for their participation in this study. This work was supported by Research Grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (HS, N Miyake and N Matsumoto) and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (N Matsumoto) and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (N Matsumoto).
Web Resources
The URLs for data presented herein are as follows: UCSC Genome Browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, Y., Saitsu, H., Miyamoto, T. et al. A family of oculofaciocardiodental syndrome (OFCD) with a novel BCOR mutation and genomic rearrangements involving NHS. J Hum Genet 57, 197–201 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expanding the phenotype of the X-linked BCOR microphthalmia syndromes
Human Genetics (2019)
-
Ocular findings in a patient with oculofaciocardiodental (OFCD) syndrome and a novel BCOR pathogenic variant
International Ophthalmology (2018)
-
De novo mutations in the autophagy gene WDR45 cause static encephalopathy of childhood with neurodegeneration in adulthood
Nature Genetics (2013)