Abstract
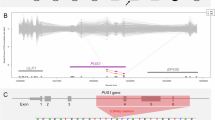
Mitochondrial diseases are associated with defects of adenosine triphosphate production and energy supply to organs as a result of dysfunctions of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biallelic mutations in the YARS2 gene encoding mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase cause myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia 2 (MLASA2), a type of mitochondrial disease. Here, we report a consanguineous Turkish family with two siblings showing severe metabolic decompensation including recurrent hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, and transfusion-dependent anemia. Using whole-exome sequencing of the proband and his parents, we identified a novel YARS2 mutation (c.1303A>G, p.Ser435Gly) that was homozygous in the patient and heterozygous in his parents. This mutation is located at the ribosomal protein S4-like domain of the gene, while other reported YARS2 mutations are all within the catalytic domain. Interestingly, the proband showed more severe symptoms and an earlier onset than previously reported patients, suggesting the functional importance of the S4-like domain in tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Antonellis, A. & Green, E. D. The role of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in genetic diseases. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 9, 87–107 (2008).
Stenson, P. D., Mort, M., Ball, E. V., Shaw, K., Phillips, A. D. & Cooper, D. N. The Human Gene Mutation Database: building a comprehensive mutation repository for clinical and molecular genetics, diagnostic testing and personalized genomic medicine. Hum. Genet. (e-pub ahead of print 28 Sep 2013; doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1358-4).
Scheper, G. C., van der Klok, T., van Andel, R. J., van Berkel, C. G., Sissler, M., Smet, J. et al. Mitochondrial aspartyl-tRNA synthetase deficiency causes leukoencephalopathy with brain stem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation. Nat. Genet. 39, 534–539 (2007).
Edvardson, S., Shaag, A., Kolesnikova, O., Gomori, J. M., Tarassov, I., Einbinder, T. et al. Deleterious mutation in the mitochondrial arginyl-transfer RNA synthetase gene is associated with pontocerebellar hypoplasia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 857–862 (2007).
Gotz, A., Tyynismaa, H., Euro, L., Ellonen, P., Hyotylainen, T., Ojala, T. et al. Exome sequencing identifies mitochondrial alanyl-tRNA synthetase mutations in infantile mitochondrial cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 88, 635–642 (2011).
Elo, J. M., Yadavalli, S. S., Euro, L., Isohanni, P., Gotz, A., Carroll, C. J. et al. Mitochondrial phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase mutations underlie fatal infantile Alpers encephalopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 4521–4529 (2012).
DiMauro, S. & Schon, E. A. Mitochondrial respiratory-chain diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 2656–2668 (2003).
Sasarman, F., Nishimura, T., Thiffault, I. & Shoubridge, E. A. A novel mutation in YARS2 causes myopathy with lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia. Hum. Mutat. 33, 1201–1206 (2012).
Riley, L. G., Cooper, S., Hickey, P., Rudinger-Thirion, J., McKenzie, M., Compton, A. et al. Mutation of the mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase gene, YARS2, causes myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia—MLASA syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 87, 52–59 (2010).
Shahni, R., Wedatilake, Y., Cleary, M. A., Lindley, K. J., Sibson, K. R. & Rahman, S. A distinct mitochondrial myopathy, lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia (MLASA) phenotype associates with YARS2 mutations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 161, 2334–2338 (2013).
Adzhubei, I. A., Schmidt, S., Peshkin, L., Ramensky, V. E., Gerasimova, A., Bork, P. et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 7, 248–249 (2010).
Schwarz, J. M., Rodelsperger, C., Schuelke, M. & Seelow, D. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat. Methods 7, 575–576 (2010).
Seelow, D., Schuelke, M., Hildebrandt, F. & Nurnberg, P. HomozygosityMapper—an interactive approach to homozygosity mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W593–599 (2009).
Inbal, A., Avissar, N., Shaklai, M., Kuritzky, A., Schejter, A., Ben-David, E. et al. Myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia: a new syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 55, 372–378 (1995).
Bonnefond, L., Fender, A., Rudinger-Thirion, J., Giege, R., Florentz, C. & Sissler, M. Toward the full set of human mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: characterization of AspRS and TyrRS. Biochemistry 44, 4805–4816 (2005).
Yaremchuk, A., Kriklivyi, I., Tukalo, M. & Cusack, S. Class I tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase has a class II mode of cognate tRNA recognition. EMBO J. 21, 3829–3840 (2002).
Guijarro, J. I., Pintar, A., Prochnicka-Chalufour, A., Guez, V., Gilquin, B., Bedouelle, H. et al. Structure and dynamics of the anticodon arm binding domain of Bacillus stearothermophilus Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase. Structure 10, 311–317 (2002).
Grantham, R. Amino acid difference formula to help explain protein evolution. Science 185, 862–864 (1974).
Tucker, E. J., Compton, A. G. & Thorburn, D. R. Recent advances in the genetics of mitochondrial encephalopathies. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 10, 277–285 (2010).
Bernier, F. P., Boneh, A., Dennett, X., Chow, C. W., Cleary, M. A. & Thorburn, D. R. Diagnostic criteria for respiratory chain disorders in adults and children. Neurology 59, 1406–1411 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient and his family for participating in this work. We also thank Ms S Sugimoto and K Takabe for technical assistance. This work was supported by research grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (N. Matsumoto, N. Miyake), the fund for Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas Program in the Project for Developing Innovation Systems from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (N. Matsumoto), the Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences (N. Matsumoto), a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas-(Transcription cycle)-from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (N. Matsumoto), a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (H. Saitsu, N. Matsumoto, N. Miyake), the Takeda Science Foundation (N. Matsumoto, N. Miyake), and the Hayashi Memorial Foundation for Female Natural Scientists (N. Miyake).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, J., Eminoglu, T., Vatansever, G. et al. A novel homozygous YARS2 mutation causes severe myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia 2. J Hum Genet 59, 229–232 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2013.143
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2013.143
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Iron metabolism in erythroid cells and patients with congenital sideroblastic anemia
International Journal of Hematology (2018)
-
Mutations in methionyl-tRNA synthetase gene in a Chinese family with interstitial lung and liver disease, postnatal growth failure and anemia
Journal of Human Genetics (2017)
-
Clinical and molecular study in a long-surviving patient with MLASA syndrome due to novel PUS1 mutations
neurogenetics (2016)
-
A peep into mitochondrial disorder: multifaceted from mitochondrial DNA mutations to nuclear gene modulation
Protein & Cell (2015)
-
Familial schwannomatosis with a germline mutation of SMARCB1 in Japan
Brain Tumor Pathology (2015)