Abstract
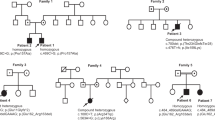
Myofibrillar myopathy (MFM) is a group of chronic muscular disorders that show the focal dissolution of myofibrils and accumulation of degradation products. The major genetic basis of MFMs is unknown. In 1993, our group reported a Japanese family with dominantly inherited cytoplasmic body myopathy, which is now included in MFM, characterized by late-onset chronic progressive distal muscle weakness and early respiratory failure. In this study, we performed linkage analysis and exome sequencing on these patients and identified a novel c.90263G>T mutation in the TTN gene (NM_001256850). During the course of our study, another groups reported three mutations in TTN in patients with hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure (HMERF, MIM #603689), which is characterized by overlapping pathologic findings with MFMs. Our patients were clinically compatible with HMERF. The mutation identified in this study and the three mutations in patients with HMERF were located on the A-band domain of titin, suggesting a strong relationship between mutations in the A-band domain of titin and HMERF. Mutation screening of TTN has been rarely carried out because of its huge size, consisting of 363 exons. It is possible that focused analysis of TTN may detect more mutations in patients with MFMs, especially in those with early respiratory failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Nakano, S., Engel, A. G., Waclawik, A. J., Emslie-Smith, A. M. & Busis, N. A. Myofibrillar myopathy with abnormal foci of desmin positivity. I. Light and electron microscopy analysis of 10 cases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55, 549–562 (1996).
Olive, M., Odgerel, Z., Martinez, A., Poza, J. J., Bragado, F. G., Zabalza, R. J. et al. Clinical and myopathological evaluation of early- and late-onset subtypes of myofibrillar myopathy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 21, 533–542 (2011).
Olive, M., Goldfarb, L. G., Shatunov, A., Fischer, D. & Ferrer, I. Myotilinopathy: refining the clinical and myopathological phenotype. Brain 128, 2315–2326 (2005).
Selcen, D. & Engel, A. G. Myofibrillar myopathy caused by novel dominant negative alpha B-crystallin mutations. Ann. Neurol. 54, 804–810 (2003).
Abe, K., Kobayashi, K., Chida, K., Kimura, N. & Kogure, K. Dominantly inherited cytoplasmic body myopathy in a Japanese kindred. Tohoku. J. Exp. Med. 170, 261–272 (1993).
Abecasis, G. R., Cherny, S. S., Cookson, W. O. & Cardon, L. R. Merlin–rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat. Genet. 30, 97–101 (2002).
Li, H. & Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25, 1754–1760 (2009).
McKenna, A., Hanna, M., Banks, E., Sivachenko, A., Cibulskis, K., Kernytsky, A. et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome. Res. 20, 1297–1303 (2010).
Wang, K., Li, M. & Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data.. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, e164 (2010).
Adzhubei, I. A., Schmidt, S., Peshkin, L., Ramensky, V. E., Gerasimova, A., Bork, P. et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 7, 248–249 (2010).
Nicolao, P., Xiang, F., Gunnarsson, L. G., Giometto, B., Edstrom, L., Anvret, M. et al. Autosomal dominant myopathy with proximal weakness and early respiratory muscle involvement maps to chromosome 2q. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64, 788–792 (1999).
Edstrom, L., Thornell, L. E., Albo, J., Landin, S. & Samuelsson, M. Myopathy with respiratory failure and typical myofibrillar lesions. J. Neurol. Sci. 96, 211–228 (1990).
Lange, S., Xiang, F., Yakovenko, A., Vihola, A., Hackman, P., Rostkova, E. et al. The kinase domain of titin controls muscle gene expression and protein turnover. Science 308, 1599–1603 (2005).
Ohlsson, M., Hedberg, C., Bradvik, B., Lindberg, C., Tajsharghi, H., Danielsson, O. et al. Hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure associated with a mutation in A-band titin. Brain 135, 1682–1694 (2012).
Pfeffer, G., Elliott, H. R., Griffin, H., Barresi, R., Miller, J., Marsh, J. et al. Titin mutation segregates with hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure. Brain 135, 1695–1713 (2012).
Vasli, N., Bohm, J., Le Gras, S., Muller, J., Pizot, C., Jost, B. et al. Next generation sequencing for molecular diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases. Acta. Neuropathol. 124, 273–283 (2012).
Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos, A., Ackermann, M. A., Bowman, A. L., Yap, S. V. & Bloch, R. J. Muscle giants: molecular scaffolds in sarcomerogenesis. Physiol. Rev. 89, 1217–1267 (2009).
Ottenheijm, C. A. & Granzier, H. Role of titin in skeletal muscle function and disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 682, 105–122 (2010).
Hackman, P., Vihola, A., Haravuori, H., Marchand, S., Sarparanta, J., De Seze, J. et al. Tibial muscular dystrophy is a titinopathy caused by mutations in TTN, the gene encoding the giant skeletal-muscle protein titin. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 492–500 (2002).
Udd, B., Partanen, J., Halonen, P., Falck, B., Hakamies, L., Heikkila, H. et al. Tibial muscular dystrophy. Late adult-onset distal myopathy in 66 Finnish patients. Arch. Neurol. 50, 604–608 (1993).
de Seze, J., Udd, B., Haravuori, H., Sablonniere, B., Maurage, C. A., Hurtevent, J. F. et al. The first European family with tibial muscular dystrophy outside the Finnish population. Neurology 51, 1746–1748 (1998).
Van den Bergh, P. Y., Bouquiaux, O., Verellen, C., Marchand, S., Richard, I., Hackman, P. et al. Tibial muscular dystrophy in a Belgian family. Ann. Neurol. 54, 248–251 (2003).
Hackman, P., Marchand, S., Sarparanta, J., Vihola, A., Penisson-Besnier, I., Eymard, B. et al. Truncating mutations in C-terminal titin may cause more severe tibial muscular dystrophy (TMD). Neuromuscul. Disord. 18, 922–928 (2008).
Pollazzon, M., Suominen, T., Penttila, S., Malandrini, A., Carluccio, M. A., Mondelli, M. et al. The first Italian family with tibial muscular dystrophy caused by a novel titin mutation. J. Neurol. 257, 575–579 (2010).
Udd, B., Rapola, J., Nokelainen, P., Arikawa, E. & Somer, H. Nonvacuolar myopathy in a large family with both late adult onset distal myopathy and severe proximal muscular dystrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 113, 214–221 (1992).
Carmignac, V., Salih, M. A., Quijano-Roy, S., Marchand, S., Al Rayess, M. M., Mukhtar, M. M. et al. C-terminal titin deletions cause a novel early-onset myopathy with fatal cardiomyopathy. Ann. Neurol. 61, 340–351 (2007).
Labeit, S., Barlow, D. P., Gautel, M., Gibson, T., Holt, J., Hsieh, C. L. et al. A regular pattern of two types of 100-residue motif in the sequence of titin. Nature 345, 273–276 (1990).
Labeit, S. & Kolmerer, B. Titins: giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticity. Science 270, 293–296 (1995).
Tskhovrebova, L., Walker, M. L., Grossmann, J. G., Khan, G. N., Baron, A. & Trinick, J. Shape and flexibility in the titin 11-domain super-repeat. J. Mol. Biol. 397, 1092–1105 (2010).
Bucher, R. M., Svergun, D. I., Muhle-Goll, C. & Mayans, O. The structure of the FnIII Tandem A77-A78 points to a periodically conserved architecture in the myosin-binding region of titin. J. Mol. Biol. 401, 843–853 (2010).
Muhle-Goll, C., Habeck, M., Cazorla, O., Nilges, M., Labeit, S. & Granzier, H. Structural and functional studies of titin's fn3 modules reveal conserved surface patterns and binding to myosin S1–a possible role in the Frank-Starling mechanism of the heart. J. Mol. Biol. 313, 431–447 (2001).
Bang, M. L., Centner, T., Fornoff, F., Geach, A. J., Gotthardt, M., McNabb, M. et al. The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ. Res. 89, 1065–1072 (2001).
Maruyama, K., Yoshioka, T., Higuchi, H., Ohashi, K., Kimura, S. & Natori, R. Connectin filaments link thick filaments and Z lines in frog skeletal muscle as revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. J. Cell. Biol. 101, 2167–2172 (1985).
Guo, W., Bharmal, S. J., Esbona, K. & Greaser, M. L. Titin diversity–alternative splicing gone wild. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 753675 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their family. We are grateful to Yoko Tateda, Kumi Kato, Naoko Shimakura, Risa Ando, Riyo Takahashi, Miyuki Tsuda, Nozomi Koshita, Mami Kikuchi and Kiyotaka Kuroda for their technical assistance. We also acknowledge the support of the Biomedical Research Core of Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine. This work was supported by a grant of Research on Applying Health Technology provided by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare to YM, an Intramural Research Grant (23-5) for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders of NCNP and JSPS KAKENHI Grant number 24659421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Izumi, R., Niihori, T., Aoki, Y. et al. Exome sequencing identifies a novel TTN mutation in a family with hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure. J Hum Genet 58, 259–266 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2013.9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2013.9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel deletion in the C-terminal region of HSPB8 in a family with rimmed vacuolar myopathy
Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
Expanding the importance of HMERF titinopathy: new mutations and clinical aspects
Journal of Neurology (2019)
-
Myofibrillar myopathy in the genomic context
Journal of Applied Genetics (2018)
-
Performance comparison of two commercial human whole-exome capture systems on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded lung adenocarcinoma samples
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
Diagnosis of muscle diseases presenting with early respiratory failure
Journal of Neurology (2015)