Abstract
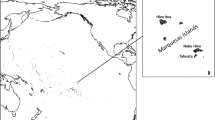
We examined nine Y chromosome short tandem repeats (Y-STRs) and the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) hypervariable segment 1 region in the Fijian island populations of Viti Levu, Vanua Levu, Kadavu, the Lau islands and Rotuma. We found significant genetic structure among these populations for the Y-STRs, both with and without the Rotumans, but not for the mtDNA. We also found that all five populations exhibited the sex-biased admixture associated with areas settled by Austronesian-speaking people, with paternal lineages more strongly associated with Melanesian populations and maternal lineages more strongly associated with Polynesian populations. We also found that the Rotumans in the north and the Lau Islanders in the east were genetically more similar to Polynesian populations than were the other Fijians, but only for the mtDNA. For the Y-STRs, the Rotumans and the Lau Islanders were genetically as similar to Melanesian populations as were the other three populations. Of the five populations, the Rotumans were the most different in almost every regard. Although past genetic studies treated the Fijians as being genetically homogenous despite known geographic, phenotypic, cultural and linguistic variation, our findings show significant genetic variation and a need for a closer examination of individual island populations within Fiji, particularly the Rotumans, in order to better understand the process of the peopling of Fiji and of the surrounding regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Kirch, P. On the Road of the Winds: An Archaeological History of the Pacific Islands before European Contact, (University of California Press, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2000).
Wilmshurst, J. M., Hunt, T. L., Lipo, C. P. & Anderson, A. J. High-precision radiocarbon dating shows recent and rapid initial colonization of East Polynesia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 1815–1820 (2011).
Diamond, J. M. Express train to Polynesia. Nature 336, 307–308 (1988).
Terrell, J. Prehistory in the Pacific Islands, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1986).
Kayser, M., Brauer, S., Weiss, G., Underhill, P. A., Roewer, L., Schiefenhovel, W. et al. Melanesian origin of Polynesian Y Chromosomes. Curr. Biol. 10, 1237–1246 (2000).
Kayser, M., Brauer, S., Cordaux, R., Casto, A., Lao, O. & Zhivotovsky, L. A. et al. Melanesian and Asian origins of Polynesians: mtDNA and Y chromosome gradients across the Pacific. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23, 2234–2244 (2006).
Kayser, M., Choi, Y., Van Oven, M., Mona, S., Brauer, S. & Trent, R. J. et al. The impact of the Austronesian expansion: evidence from mtDNA and Y chromosome diversity in the Admiralty Islands of Melanesia. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 1362–1374 (2008).
Mirabal, S., Herrera, K. J., Gayden, T., Regueiro, M., Underhill, P. A. & Garcia-Bertrand, R. L. et al. Increased Y-chromosome resolution of haplogroup O suggests genetic ties between the Ami aborigines of Taiwan and the Polynesian Islands of Samoa and Tonga. Gene 492, 339–348 (2012).
Soares, P., Rito, T., Trejaut, J., Mormina, M., Hill, C. & Tinkler-Hundal, E. et al. Ancient voyaging and Polynesian origins. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 88, 239–247 (2011).
Rutherford, J. S., Almond, M. J. & Nunn, P. D. Analysis of pottery samples from Bourewa, the earliest known Lapita site in Fiji. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 85, 155–159 (2012).
Wollstein, A., Lao, O., Becker, C., Brauer, S., Trent., R. J. & Nurnberg, P. et al. Demographic history of Oceania inferred from genome-wide data. Curr. Biol. 20, 1983–1992 (2010).
Spriggs, M. The Island Melanesians, (Blackwell, Oxford, UK, 1997).
Geraghty, P. The history of the Fijian languages. Ocean. Linguist. Spec. Publ. 19, 1–483 (1983).
Howells, W. W. & Moss, W. L. Anthropometry and Blood Types in Fiji and the Solomon Islands, (American Museum of Natural History, New York, NY, USA, 1933).
Geraghty, P. A. In FOCAL II: Papers from the Fourth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics (eds Geraghty P., Carrington L., Wurm S. A.) 289–312 (The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, 1986).
Burley, D. V. Fijian polygenesis and the Melanesian/Polynesian divide. Curr. Anthropol. 54, 436–462 (2013).
Hage, P. & Marck, J. Matrilineality and the Melanesian origin of Polynesian Y chromosomes. Curr. Anthropol. 44 (Suppl), S121–S127 (2003).
Sambrook, J. & Russell, D. W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001).
Delfin, F., Myles, S., Choi, Y., Hughes, D., Illek, R. & Van Oven, M. et al. Bridging near and remote Oceania: MtDNA and NRY variation in the Solomon Islands. Mol. Biol. Evol. 29, 545–564 (2012).
Slatkin, M. A measure of population subdivision based on microsatellite allele frequencies. Genetics 139, 457–462 (1995).
Excoffier, L. & Schneider, S. Arlequin Ver. 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. Online 1, 47–50 (2005).
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M. & Kumar, S. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599 (2007).
Friedlaender, J., Friedlaender, F., Hodgson, J., Stoltz, M., Koki, G. & Horvat, G. et al. Melanesian mtDNA complexity. PLoS One 2, e248 (2007).
Van Oven, M. & Kayser, M. Updated comprehensive phylogenetic tree of global human mitochondrial DNA variation. Hum. Mutat. 30, E386–E394 (2009).
Redd, A., Takezaki, N., Sherry, S., McGarvey, S., Sofro, A. & Stoneking, M. Evolutionary history of the COII/tRNALys intergenic 9 base pair deletion in human mitochondrial DNAs from the Pacific. Mol. Biol. Evol. 12, 604–615 (1995).
Duggan, A. T. & Stoneking, M. A highly unstable recent mutation in human mtDNA. Am J. Hum. Genet. 92, 279–284 (2013).
Duggan, A. T., Evans, B., Friedlaender, F. R., Friedlaender, J. S., Koik, G. & Merriweather, D. A. et al. Maternal history of Oceania from complete mtDNA genomes: contrasting ancient diversity with recent homogenization due to the Austronesian expansion. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 94, 721–733 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We thank Julio J Mulero of Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. for his assistance. We are also grateful for receiving two Carroll D Clark research awards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shipley, G., Taylor, D., Tyagi, A. et al. Genetic structure among Fijian island populations. J Hum Genet 60, 69–75 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2014.105
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2014.105
This article is cited by
-
Factors associated with macrosomia, hypoglycaemia and low Apgar score among Fijian women with gestational diabetes mellitus
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2020)