Abstract
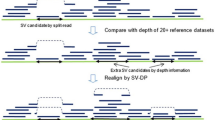
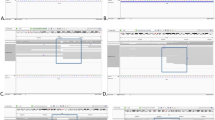
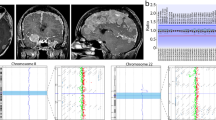
Structural variations (SVs), including translocations, inversions, deletions and duplications, are potentially associated with Mendelian diseases and contiguous gene syndromes. Determination of SV-related breakpoints at the nucleotide level is important to reveal the genetic causes for diseases. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) by next-generation sequencers is expected to determine structural abnormalities more directly and efficiently than conventional methods. In this study, 14 SVs (9 balanced translocations, 1 inversion and 4 microdeletions) in 9 patients were analyzed by WGS with a shallow (5 × ) to moderate read coverage (20 × ). Among 28 breakpoints (as each SV has two breakpoints), 19 SV breakpoints had been determined previously at the nucleotide level by any other methods and 9 were uncharacterized. BreakDancer and Integrative Genomics Viewer determined 20 breakpoints (16 translocation, 2 inversion and 2 deletion breakpoints), but did not detect 8 breakpoints (2 translocation and 6 deletion breakpoints). These data indicate the efficacy of WGS for the precise determination of translocation and inversion breakpoints.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Feuk L, Carson AR, Scherer SW Structural variation in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 7, 85–97 (2006).
Utami KH, Hillmer AM, Aksoy I, Chew EG, Teo AS, Zhang Z et al. Detection of chromosomal breakpoints in patients with developmental delay and speech disorders. PLoS One 9, e90852 (2014).
Vandeweyer G, Kooy RF Balanced translocations in mental retardation. Hum. Genet. 126, 133–147 (2009).
Fantes JA, Boland E, Ramsay J, Donnai D, Splitt M, Goodship JA et al. FISH mapping of de novo apparently balanced chromosome rearrangements identifies characteristics associated with phenotypic abnormality. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 916–926 (2008).
Rizzolio F, Bione S, Sala C, Goegan M, Gentile M, Gregato G et al. Chromosomal rearrangements in Xq and premature ovarian failure: mapping of 25 new cases and review of the literature. Hum. Reprod. 21, 1477–1483 (2006).
Imaizumi K, Kimura J, Matsuo M, Kurosawa K, Masuno M, Niikawa N et al. Sotos syndrome associated with a de novo balanced reciprocal translocation t(5;8)(q35;q24.1). Am. J. Med. Genet. 107, 58–60 (2002).
Dong Z, Jiang L, Yang C, Hu H, Wang X, Chen H et al. A robust approach for blind detection of balanced chromosomal rearrangements with whole-genome low-coverage sequencing. Hum. Mutat. 35, 625–636 (2014).
Schluth-Bolard C, Labalme A, Cordier MP, Till M, Nadeau G, Tevissen H et al. Breakpoint mapping by next generation sequencing reveals causative gene disruption in patients carrying apparently balanced chromosome rearrangements with intellectual deficiency and/or congenital malformations. J. Med. Genet. 50, 144–150 (2013).
Abel HJ, Duncavage EJ Detection of structural DNA variation from next generation sequencing data: a review of informatic approaches. Cancer Genet. 206, 432–440 (2013).
Saitsu H, Osaka H, Sugiyama S, Kurosawa K, Mizuguchi T, Nishiyama K et al. Early infantile epileptic encephalopathy associated with the disrupted gene encoding Slit-Robo Rho GTPase activating protein 2 (SRGAP2). Am. J. Med. Genet. A 158A, 199–205 (2012).
Saitsu H, Igarashi N, Kato M, Okada I, Kosho T, Shimokawa O et al. De novo 5q14.3 translocation 121.5-kb upstream of MEF2C in a patient with severe intellectual disability and early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 155A, 2879–2884 (2011).
Nishimura-Tadaki A, Wada T, Bano G, Gough K, Warner J, Kosho T et al. Breakpoint determination of X;autosome balanced translocations in four patients with premature ovarian failure. J. Hum. Genet. 56, 156–160 (2011).
Kurotaki N, Imaizumi K, Harada N, Masuno M, Kondoh T, Nagai T et al. Haploinsufficiency of NSD1 causes Sotos syndrome. Nat. Genet. 30, 365–366 (2002).
Saitsu H, Kurosawa K, Kawara H, Eguchi M, Mizuguchi T, Harada N et al. Characterization of the complex 7q21.3 rearrangement in a patient with bilateral split-foot malformation and hearing loss. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 149A, 1224–1230 (2009).
Li H, Durbin R Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25, 1754–1760 (2009).
Chen K, Wallis JW, McLellan MD, Larson DE, Kalicki JM, Pohl CS et al. BreakDancer: an algorithm for high-resolution mapping of genomic structural variation. Nat. Methods 6, 677–681 (2009).
Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 14, 178–192 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients and their families for their participation in this study. We also thank Nobuko Watanabe for her technical assistance. This work was supported by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan; the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B), and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A)); the Takeda Science Foundation; the fund for Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas Program in the Project for Developing Innovation Systems; the Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences; and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (Transcription Cycle) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, T., Tsurusaki, Y., Nakashima, M. et al. Precise detection of chromosomal translocation or inversion breakpoints by whole-genome sequencing. J Hum Genet 59, 649–654 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2014.88
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2014.88
This article is cited by
-
Gene sequencing and result analysis of balanced translocation carriers by third-generation gene sequencing technology
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The clinical utility and costs of whole-genome sequencing to detect cancer susceptibility variants—a multi-site prospective cohort study
Genome Medicine (2023)
-
Kagami–Ogata syndrome in a patient with 46,XX,t(2;14)(q11.2;q32.2)mat disrupting MEG3
Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
Long-term spatial tracking of cells affected by environmental insults
Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (2020)
-
A rare cardiac phenotype of dextrocardia observed in a fetus with 1p36 deletion syndrome and a balanced translocation: a prenatal case report
Molecular Cytogenetics (2020)