Abstract
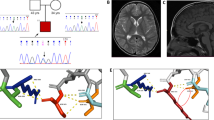
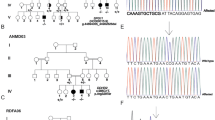
Recently, de novo KIF1A mutations were identified in patients with intellectual disability, spasticity and cerebellar atrophy and/or optic nerve atrophy. In this study, we analyzed a total of 62 families, including 68 patients with genetically unsolved childhood cerebellar atrophy, by whole-exome sequencing (WES). We identified five de novo missense KIF1A mutations, including only one previously reported mutation (p.Arg316Trp). All the mutations are located in the motor domain of KIF1A. In all patients, initial symptom onset was during the infantile period, and included developmental delay in three patients and gait disturbance in two. Thereafter, they showed gait disturbances, exaggerated deep tendon reflexes, cerebellar symptoms and cerebellar atrophy on brain magnetic resonance imaging. Four patients showed lower limb spasticity, upper limb clumsiness and visual disturbances. Nerve conduction study revealed peripheral neuropathy in three patients. This study further delineates clinical features of de novo KIF1A mutations. Genetic testing of KIF1A should be considered in children with developmental delay, cerebellar atrophy and pyramidal features.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hirokawa, N., Niwa, S. & Tanaka, Y. Molecular motors in neurons: transport mechanisms and roles in brain function, development, and disease. Neuron 68, 610–638 (2010).
Hirokawa, N., Noda, Y., Tanaka, Y. & Niwa, S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 682–696 (2009).
Klebe, S., Azzedine, H., Durr, A., Bastien, P., Bouslam, N., Elleuch, N. et al. Autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia (SPG30) with mild ataxia and sensory neuropathy maps to chromosome 2q37.3. Brain 129, 1456–1462 (2006).
Klebe, S., Lossos, A., Azzedine, H., Mundwiller, E., Sheffer, R., Gaussen, M. et al. KIF1A missense mutations in SPG30, an autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia: distinct phenotypes according to the nature of the mutations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 20, 645–649 (2012).
Riviere, J. B., Ramalingam, S., Lavastre, V., Shekarabi, M., Holbert, S., Lafontaine, J. et al. KIF1A, an axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles, is mutated in hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 89, 219–230 (2011).
Hamdan, F. F., Gauthier, J., Araki, Y., Lin, D. T., Yoshizawa, Y., Higashi, K. et al. Excess of de novo deleterious mutations in genes associated with glutamatergic systems in nonsyndromic intellectual disability. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 88, 306–316 (2011).
Lee, J. R., Srour, M., Kim, D., Hamdan, F. F., Lim, S. H., Brunel-Guitton, C. et al. De novo mutations in the motor domain of KIF1A cause cognitive impairment, spastic paraparesis, axonal neuropathy and cerebellar atrophy. Hum. Mutat. 36, 69–78 (2015).
Okamoto, N., Miya, F., Tsunoda, T., Yanagihara, K., Kato, M., Saitoh, S. et al. KIF1A mutation in a patient with progressive neurodegeneration. J. Hum. Genet. 59, 639–641 (2014).
Ohba, C., Osaka, H., Iai, M., Yamashita, S., Suzuki, Y., Aida, N. et al. Diagnostic utility of whole exome sequencing in patients showing cerebellar and/or vermis atrophy in childhood. Neurogenetics 14, 225–232 (2013).
Saitsu, H., Nishimura, T., Muramatsu, K., Kodera, H., Kumada, S., Sugai, K. et al. De novo mutations in the autophagy gene WDR45 cause static encephalopathy of childhood with neurodegeneration in adulthood. Nat. Genet. 45, 445–449, 449e1 (2013).
Saitsu, H., Kato, M., Mizuguchi, T., Hamada, K., Osaka, H., Tohyama, J. et al. De novo mutations in the gene encoding STXBP1 (MUNC18-1) cause early infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Nat. Genet. 40, 782–788 (2008).
Kikkawa, M., Sablin, E. P., Okada, Y., Yajima, H., Fletterick, R. J. & Hirokawa, N. Switch-based mechanism of kinesin motors. Nature 411, 439–445 (2001).
Nitta, R., Kikkawa, M., Okada, Y. & Hirokawa, N. KIF1A alternately uses two loops to bind microtubules. Science 305, 678–683 (2004).
Nitta, R., Okada, Y. & Hirokawa, N. Structural model for strain-dependent microtubule activation of Mg-ADP release from kinesin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 1067–1075 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patients and their families for their participation in this study. We thank Nobuko Watanabe, Kiyomi Masuko, Sayaka Sasamoto and Mai Satoh for their excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan; the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (25293085, 25293235), Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (26670505), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) (13313587) and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (26461549, 24591500, 26330331)); the Takeda Science Foundation; the Fund for Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas Program in the Project for Developing Innovation Systems from the Japan Science and Technology Agency; the Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences (11105137); and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (Transcription Cycle) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (12024421).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohba, C., Haginoya, K., Osaka, H. et al. De novo KIF1A mutations cause intellectual deficit, cerebellar atrophy, lower limb spasticity and visual disturbance. J Hum Genet 60, 739–742 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.108
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.108
This article is cited by
-
Monoallelic KIF1A-related disorders: a multicenter cross sectional study and systematic literature review
Journal of Neurology (2022)
-
Challenges and Controversies in the Genetic Diagnosis of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2021)
-
KIF1A-related autosomal dominant spastic paraplegias (SPG30) in Russian families
BMC Neurology (2020)
-
KIF1A variants are a frequent cause of autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia
European Journal of Human Genetics (2020)
-
Mutations in the KIF21B kinesin gene cause neurodevelopmental disorders through imbalanced canonical motor activity
Nature Communications (2020)