Abstract
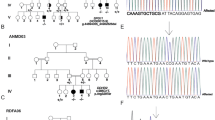
Hypertension and brachydactyly syndrome (HTNB) with short stature is an autosomal-dominant disorder. Mutations in the PDE3A gene located at 12p12.2-p11.2 were recently identified in HTNB families. We found a novel heterozygous missense mutation c.1336T>C in exon 4 of the PDE3A gene in a Japanese family with multiple HTNB patients. This mutation was found to be completely linked to the family members who inherited this condition. The mutation, resulting in p.Ser446Pro, was located within the cluster region of reported mutations. This mutation may also affect the phosphodiesterase activity of PDE3A to reduce the cyclic AMP level in the cell and thereby influencing the development of limbs and the function of the cardiovascular system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Pereda, A., Garin, I., Garcia-Barcina, M., Gener, B., Beristain, E., Ibañez, A. E. et al. Brachydactyly E: isolated or as a feature of a syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 8, 141 (2013).
Bilginturan, N., Zileli, S., Karacadag, S. & Pirnar, T. Hereditary brachydactyly associated with hypertension. J. Med. Genet. 10, 253–259 (1973).
Schuster, H., Wienker, T. F., Bähring, S., Bilginturan, N., Toka, H. R., Neitzel, H. et al. Severe autosomal dominant hypertension and brachydactyly in a unique Turkish kindred maps to human chromosome 12. Nat. Genet. 13, 98–100 (1996).
Gong, M., Zhang, H., Schulz, H., Lee, Y. A., Sun, K., Bähring, S. et al. Genome-wide linkage reveals a locus for human essential (primary) hypertension on chromosome 12p. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, 1273–1277 (2003).
Bähring, S., Nagai, T., Toka, H. R., Nitz, I., Toka, O., Aydin, A. et al. Deletion at 12p in a Japanese child with brachydactyly overlaps the assigned locus of brachydactyly with hypertension in a Turkish family. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 60, 732–735 (1997).
Bähring, S., Rauch, A., Toka, O., Schroeder, C., Hesse, C., Siedler, H. et al. Autosomal-dominant hypertension with type E brachydactyly is caused by rearrangement on the short arm of chromosome 12. Hypertension 43, 471–476 (2004).
Maass, P. G., Aydin, A., Luft, F. C., Schächterle, C., Weise, A., Stricker, S. et al. PDE3A mutations cause autosomal dominant hypertension with brachydactyly. Nat. Genet. 47, 647–653 (2015).
MacDonald, J. R., Ziman, R., Yuen, R. K., Feuk, L. & Scherer, S. W. The database of genomic variants: a curated collection of structural variation in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, D986–D992 (2013).
Li, H. & Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25, 1754–1760 (2009).
Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., Fennell, T., Ruan, J., Homer, N. et al. The sequence alignment/map (SAM) format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079 (2009).
McKenna, A., Hanna, M., Banks, E., Sivachenko, A., Cibulskis, K., Kernytsky, A. et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 20, 1297–1303 (2010).
Adzhubei, I. A., Schmidt, S., Peshkin, L., Ramensky, V. E., Gerasimova, A., Bork, P. et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 7, 248–249 (2010).
Ng, P. C. & Henikoff, S. Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions. Genome Res. 11, 863–874 (2001).
Choi, Y., Sims, G. E., Murphy, S., Miller, J. R. & Chan, A. P. Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLoS ONE 7, e46688 (2012).
Lu, H. Y., Cui, Y. X., Shi, Y. C., Xia, X. Y., Liang, Q., Yao, B. et al. A girl with distinctive features of borderline high blood pressure, short stature, characteristic brachydactyly, and 11.47Mb deletion in 12p11.21-12p12.2 by oligonucleotide array CGH. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 149A, 2321–2323 (2009).
Narahara, M., Higasa, K., Nakamura, S., Tabara, Y., Kawaguchi, T., Ishii, M. et al. Large-scale East-Asian eQTL mapping reveals novel candidate genes for LD mapping and the genomic landscape of transcriptional effects of sequence variants. PLoS ONE 9, e100924 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families for participating in this study. We also thank to E Hosoba for technical assistance and T Ohye, M Tsutsumi and T Kato for helpful discussions. This work was support by the MEXT-Supported Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boda, H., Uchida, H., Takaiso, N. et al. A PDE3A mutation in familial hypertension and brachydactyly syndrome. J Hum Genet 61, 701–703 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.32
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.32
This article is cited by
-
An aggressive systemic mastocytosis preceded by ovarian dysgerminoma
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
Whole-exome sequencing identifies a de novo PDE3A variant causing autosomal dominant hypertension with brachydactyly type E syndrome: a case report
BMC Medical Genetics (2020)
-
A genome-wide association study for harness racing success in the Norwegian-Swedish coldblooded trotter reveals genes for learning and energy metabolism
BMC Genetics (2018)
-
RNA Sequencing Reveals Novel Transcripts from Sympathetic Stellate Ganglia During Cardiac Sympathetic Hyperactivity
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Diagnosis and management of pseudohypoparathyroidism and related disorders: first international Consensus Statement
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2018)