Abstract
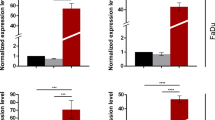
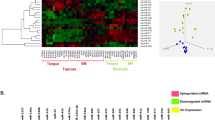
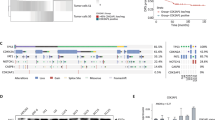
Our studies of microRNA (miRNA) expression signatures have shown that microRNA-1 (miR-1) and microRNA-206 (miR-206) were downregulated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) clinical specimens. The seed sequences of these miRNAs are identical, suggesting that the identification of the molecular targets regulated by miR-1 and miR-206 will provide new insights into novel mechanisms of HNSCC pathogenesis. Our present data showed that restoration of miR-1 and miR-206 significantly inhibited HNSCC cells’ aggressiveness. A combination of gene expression data and in silico analysis revealed that several pathways (‘pathway in cancer’, ‘focal adhesion pathway’, ‘MAPK signaling pathway’, ‘regulation of actin cytoskeleton pathway’ and ‘ECM–receptor interaction pathway’) were regulated by miR-1 and miR-206. Among them, we found that two growth factor receptors, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-MET), were directly regulated by both miR-1 and miR-206 in HNSCC cells. Also, downstream oncogenic signaling of these receptors was reduced by restoration of miR-1 or miR-206 expression. Moreover, overexpression of EGFR and c-MET was observed in HNSCC clinical specimens. The identification of targets modulated by tumor-suppressive miR-1 and miR-206 may lead to a better understanding of molecular pathogenesis of HNSCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Leemans, C. R., Braakhuis, B. J. & Brakenhoff, R. H. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11, 9–22 (2011).
Carthew, R. W. & Sontheimer, E. J. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136, 642–655 (2009).
Filipowicz, W., Bhattacharyya, S. N. & Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 102–114 (2008).
Esquela-Kerscher, A. & Slack, F. J. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 259–269 (2006).
Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 (2004).
Wiemer, E. A. The role of microRNAs in cancer: no small matter. Eur. J. Cancer 43, 1529–1544 (2007).
Iorio, M. V. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNAs in cancer: small molecules with a huge impact. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 5848–5856 (2009).
Fukumoto, I., Hanazawa, T., Kinoshita, T., Kikkawa, N., Koshizuka, K., Goto, Y. et al. MicroRNA expression signature of oral squamous cell carcinoma: functional role of microRNA-26a/b in the modulation of novel cancer pathways. Br. J. Cancer 112, 891–900 (2015).
Fukumoto, I., Kinoshita, T., Hanazawa, T., Kikkawa, N., Chiyomaru, T., Enokida, H. et al. Identification of tumour suppressive microRNA-451a in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma based on microRNA expression signature. Br. J. Cancer 111, 386–394 (2014).
Kikkawa, N., Hanazawa, T., Fujimura, L., Nohata, N., Suzuki, H., Chazono, H. et al. miR-489 is a tumour-suppressive miRNA target PTPN11 in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC). Br. J. Cancer 103, 877–884 (2010).
Nohata, N., Hanazawa, T., Kikkawa, N., Sakurai, D., Fujimura, L., Chiyomaru, T. et al. Tumour suppressive microRNA-874 regulates novel cancer networks in maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 105, 833–841 (2011).
Fukumoto, I., Kikkawa, N., Matsushita, R., Kato, M., Kurozumi, A., Nishikawa, R. et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNAs (miR-26a/b, miR-29a/b/c and miR-218) concertedly suppressed metastasis-promoting LOXL2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 61, 109–118 (2016).
Kinoshita, T., Hanazawa, T., Nohata, N., Kikkawa, N., Enokida, H., Yoshino, H. et al. Tumor suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion through targeting laminin-332 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 3, 1386–1400 (2012).
Kinoshita, T., Nohata, N., Hanazawa, T., Kikkawa, N., Yamamoto, N., Yoshino, H. et al. Tumour-suppressive microRNA-29s inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting laminin-integrin signalling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 109, 2636–2645 (2013).
Gilcrease, M. Z. Integrin signaling in epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 247, 1–25 (2007).
Kim, S. H., Turnbull, J. & Guimond, S. Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: the dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. J. Endocrinol. 209, 139–151 (2011).
Kurozumi, A., Goto, Y., Matsushita, R., Fukumoto, I., Kato, M., Nishikawa, R. et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-223 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting ITGA3/ITGB1 signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 107, 84–94 (2015).
Nohata, N., Hanazawa, T., Enokida, H. & Seki, N. microRNA-1/133a and microRNA-206/133b clusters: dysregulation and functional roles in human cancers. Oncotarget 3, 9–21 (2012).
Nohata, N., Hanazawa, T., Kikkawa, N., Mutallip, M., Sakurai, D., Fujimura, L. et al. Tumor suppressive microRNA-375 regulates oncogene AEG-1/MTDH in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). J. Hum. Genet. 56, 595–601 (2011).
Nohata, N., Sone, Y., Hanazawa, T., Fuse, M., Kikkawa, N., Yoshino, H. et al. miR-1 as a tumor suppressive microRNA targeting TAGLN2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2, 29–42 (2011).
Mataki, H., Seki, N., Chiyomaru, T., Enokida, H., Goto, Y., Kumamoto, T. et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-206 as a dual inhibitor of MET and EGFR oncogenic signaling in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 46, 1039–1050 (2015).
Koeppen, H., Yu, W., Zha, J., Pandita, A., Penuel, E., Rangell, L. et al. Biomarker analyses from a placebo-controlled phase II study evaluating erlotinib+/-onartuzumab in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: MET expression levels are predictive of patient benefit. Clin. Cancer Res. 20, 4488–4498 (2014).
Kalyankrishna, S. & Grandis, J. R. Epidermal growth factor receptor biology in head and neck cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 2666–2672 (2006).
Chung, C. H., Ely, K., McGavran, L., Varella-Garcia, M., Parker, J., Parker, N. et al. Increased epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 4170–4176 (2006).
Seiwert, T. Y., Jagadeeswaran, R., Faoro, L., Janamanchi, V., Nallasura, V., El Dinali, M. et al. The MET receptor tyrosine kinase is a potential novel therapeutic target for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 69, 3021–3031 (2009).
Datta, J., Kutay, H., Nasser, M. W., Nuovo, G. J., Wang, B., Majumder, S. et al. Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 68, 5049–5058 (2008).
Nasser, M. W., Datta, J., Nuovo, G., Kutay, H., Motiwala, T., Majumder, S. et al. Down-regulation of micro-RNA-1 (miR-1) in lung cancer. Suppression of tumorigenic property of lung cancer cells and their sensitization to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by miR-1. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 33394–33405 (2008).
Song, G. & Wang, L. Nuclear receptor SHP activates miR-206 expression via a cascade dual inhibitory mechanism. PLoS ONE 4, e6880 (2009).
Mataki, H., Enokida, H., Chiyomaru, T., Mizuno, K., Matsushita, R., Goto, Y. et al. Downregulation of the microRNA-1/133a cluster enhances cancer cell migration and invasion in lung-squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of Coronin1C. J. Hum. Genet. 60, 53–61 (2015).
Migliore, C., Martin, V., Leoni, V. P., Restivo, A., Atzori, L., Petrelli, A. et al. MiR-1 downregulation cooperates with MACC1 in promoting MET overexpression in human colon cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 737–747 (2012).
Yan, D., Dong Xda, E., Chen, X., Wang, L., Lu, C., Wang, J. et al. MicroRNA-1/206 targets c-Met and inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma development. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 29596–29604 (2009).
Yoshino, H., Chiyomaru, T., Enokida, H., Kawakami, K., Tatarano, S., Nishiyama, K. et al. The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting TAGLN2 in bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 104, 808–818 (2011).
Lin, F., Yao, L., Xiao, J., Liu, D. & Ni, Z. MiR-206 functions as a tumor suppressor and directly targets K-Ras in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 7, 1583–1591 (2014).
Zhang, L., Liu, X., Jin, H., Guo, X., Xia, L., Chen, Z. et al. miR-206 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation in part by repressing cyclinD2. Cancer Lett. 332, 94–101 (2013).
Yang, Q., Zhang, C., Huang, B., Li, H., Zhang, R., Huang, Y. et al. Downregulation of microRNA-206 is a potent prognostic marker for patients with gastric cancer. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 25, 953–957 (2013).
Rajalingam, K., Schreck, R., Rapp, U. R. & Albert, S. Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1773, 1177–1195 (2007).
Caulin, C., Nguyen, T., Longley, M. A., Zhou, Z., Wang, X. J. & Roop, D. R. Inducible activation of oncogenic K-ras results in tumor formation in the oral cavity. Cancer Res. 64, 5054–5058 (2004).
Han, C., Zhou, Y., An, Q., Li, F., Li, D., Zhang, X. et al. MicroRNA-1 (miR-1) inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting MET. Tumour Biol. 36, 6715–6723 (2015).
Liu, L., Shao, X., Gao, W., Zhang, Z., Liu, P., Wang, R. et al. MicroRNA-133b inhibits the growth of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. FEBS J. 279, 3800–3812 (2012).
Cui, W., Zhang, S., Shan, C., Zhou, L. & Zhou, Z. microRNA-133a regulates the cell cycle and proliferation of breast cancer cells by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor through the EGFR/Akt signaling pathway. FEBS J. 280, 3962–3974 (2013).
Bonner, J. A., Harari, P. M., Giralt, J., Azarnia, N., Shin, D. M., Cohen, R. B. et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 354, 567–578 (2006).
Vermorken, J. B., Mesia, R., Rivera, F., Remenar, E., Kawecki, A., Rottey, S. et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 1116–1127 (2008).
Bertotti, A. & Sassi, F. Molecular pathways: sensitivity and resistance to anti-EGFR antibodies. Clin. Cancer Res. 21, 3377–3383 (2015).
Rabinowits, G. & Haddad, R. I. Overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibitor in head and neck cancer: a review of the literature. Oral Oncol. 48, 1085–1089 (2012).
Madoz-Gurpide, J., Zazo, S., Chamizo, C., Casado, V., Carames, C., Gavin, E. et al. Activation of MET pathway predicts poor outcome to cetuximab in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. J. Transl. Med. 13, 282 (2015).
Ma, P. C., Tretiakova, M. S., MacKinnon, A. C., Ramnath, N., Johnson, C., Dietrich, S. et al. Expression and mutational analysis of MET in human solid cancers. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 47, 1025–1037 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the KAKENHI (C), 15K10800, 15K10801, 25462676 and 26462596.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koshizuka, K., Hanazawa, T., Fukumoto, I. et al. Dual-receptor (EGFR and c-MET) inhibition by tumor-suppressive miR-1 and miR-206 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Hum Genet 62, 113–121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.47
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.47
This article is cited by
-
LINC01518 functions as an oncogene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) by modulating miR-1-3p/Slug and miR-216b-5p/GRP78 axis
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets for receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in solid tumors: current status and future directions
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
Study of MicroRNA (miR-221-3p, miR-133a-3p, and miR-9-5p) Expressions in Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry (2023)
-
Emerging roles and mechanisms of miR-206 in human disorders: a comprehensive review
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
The effect of 2D and 3D cell cultures on treatment response, EMT profile and stem cell features in head and neck cancer
Cancer Cell International (2019)